(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements ofAmbush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
题目
(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements of
Ambush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
相似考题
更多“(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements ofAmbush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
正确答案:
4 (i) Proposed dividend
The dividend was proposed after the balance sheet date and the company, therefore, did not have a liability at the balance
sheet date. No provision for the dividend should be recognised. The approval by the directors and the shareholders are
enough to create a valid expectation that the payment will be made and give rise to an obligation. However, this occurred
after the current year end and, therefore, will be charged against the profits for the year ending 31 October 2006.
The existence of a good record of dividend payments and an established dividend policy does not create a valid expectation
or an obligation. However, the proposed dividend will be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements as the directors
approved it prior to the authorisation of the financial statements.
(ii) Disposal of subsidiary
It would appear that the loss on the sale of the subsidiary provides evidence that the value of the consolidated net assets of
the subsidiary was impaired at the year end as there has been no significant event since 31 October 2005 which would have
caused the reduction in the value of the subsidiary. The disposal loss provides evidence of the impairment and, therefore,
the value of the net assets and goodwill should be reduced by the loss of $9 million plus the loss ($2 million) to the date of
the disposal, i.e. $11 million. The sale provides evidence of a condition that must have existed at the balance sheet date
(IAS10). This amount will be charged to the income statement and written off goodwill of $12 million, leaving a balance of
$1 million on that account. The subsidiary’s assets are impaired because the carrying values are not recoverable. The net
assets and goodwill of Krup would form. a separate income generating unit as the subsidiary is being disposed of before the
financial statements are authorised. The recoverable amount will be the sale proceeds at the date of sale and represents the
value-in-use to the group. The impairment loss is effectively taking account of the ultimate loss on sale at an earlier point in
time. IFRS5, ‘Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations’, will not apply as the company had no intention
of selling the subsidiary at the year end. IAS10 would require disclosure of the disposal of the subsidiary as a non-adjusting
event after the balance sheet date.
(iii) Issue of ordinary shares
IAS33 ‘Earnings per share’ states that if there is a bonus issue after the year end but before the date of the approval of the
financial statements, then the earnings per share figure should be based on the new number of shares issued. Additionally
a company should disclose details of all material ordinary share transactions or potential transactions entered into after the
balance sheet date other than the bonus issue or similar events (IAS10/IAS33). The principle is that if there has been a
change in the number of shares in issue without a change in the resources of the company, then the earnings per share
calculation should be based on the new number of shares even though the number of shares used in the earnings per share
calculation will be inconsistent with the number shown in the balance sheet. The conditions relating to the share issue
(contingent) have been met by the end of the period. Although the shares were issued after the balance sheet date, the issue
of the shares was no longer contingent at 31 October 2005, and therefore the relevant shares will be included in the
computation of both basic and diluted EPS. Thus, in this case both the bonus issue and the contingent consideration issue
should be taken into account in the earnings per share calculation and disclosure made to that effect. Any subsequent change
in the estimate of the contingent consideration will be adjusted in the period when the revision is made in accordance with
IAS8.
Additionally IFRS3 ‘Business Combinations’ requires the fair value of all types of consideration to be reflected in the cost of
the acquisition. The contingent consideration should be included in the cost of the business combination at the acquisition
date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. In the case of Metalic, the contingent consideration has
been paid in the post-balance sheet period and the value of such consideration can be determined ($11 per share). Thus
an accurate calculation of the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Metalic can be made in the period to 31 October 2005.
Prior to the issue of the shares on 12 November 2005, a value of $10 per share would have been used to value the
contingent consideration. The payment of the contingent consideration was probable because the average profits of Metalic
averaged over $7 million for several years. At 31 October 2005 the value of the contingent shares would be included in a
separate category of equity until they were issued on 12 November 2005 when they would be transferred to the share capital
and share premium account. Goodwill will increase by 300,000 x ($11 – $10) i.e. $300,000.
(iv) Property
IFRS5 (paragraph 7) states that for a non-current asset to be classified as held for sale, the asset must be available for
immediate sale in its present condition subject to the usual selling terms, and its sale must be highly probable. The delay in
this case in the selling of the property would indicate that at 31 October 2005 the property was not available for sale. The
property was not to be made available for sale until the repairs were completed and thus could not have been available for
sale at the year end. If the criteria are met after the year end (in this case on 30 November 2005), then the non-current
asset should not be classified as held for sale in the previous financial statements. However, disclosure of the event should
be made if it meets the criteria before the financial statements are authorised (IFRS5 paragraph 12). Thus in this case,
disclosure should be made.
The property on the application of IFRS5 should have been carried at the lower of its carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell. However, the company has simply used fair value less costs to sell as the basis of valuation and shown the
property at $27 million in the financial statements.
The carrying amount of the property would have been $20 million less depreciation $1 million, i.e. $19 million. Because
the property is not held for sale under IFRS5, then its classification in the balance sheet will change and the property will be
valued at $19 million. Thus the gain of $7 million on the wrong application of IFRS5 will be deducted from reserves, and
the property included in property, plant and equipment. Total equity will therefore be reduced by $8 million.
(v) Share appreciation rights
IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ (paragraph 30) requires a company to re-measure the fair value of a liability to pay cash-settled
share based payment transactions at each reporting date and the settlement date, until the liability is settled. An example of
such a transaction is share appreciation rights. Thus the company should recognise a liability of ($8 x 10 million shares),
i.e. $80 million at 31 October 2005, the vesting date. The liability recognised at 31 October 2005 was in fact based on the
share price at the previous year end and would have been shown at ($6 x 1/2) x 10 million shares, i.e. $30 million. This
liability at 31 October 2005 had not been changed since the previous year end by the company. The SARs vest over a twoyear
period and thus at 31 October 2004 there would be a weighting of the eventual cost by 1 year/2 years. Therefore, an
additional liability and expense of $50 million should be accounted for in the financial statements at 31 October 2005. The
SARs would be settled on 1 December 2005 at $9 x 10 million shares, i.e. $90 million. The increase in the value of the
SARs since the year end would not be accrued in the financial statements but charged to profit or loss in the year ended31 October 2006. -
第2题:
(b) Misson has purchased goods from a foreign supplier for 8 million euros on 31 July 2006. At 31 October 2006,
the trade payable was still outstanding and the goods were still held by Misson. Similarly Misson has sold goods
to a foreign customer for 4 million euros on 31 July 2006 and it received payment for the goods in euros on
31 October 2006. Additionally Misson had purchased an investment property on 1 November 2005 for
28 million euros. At 31 October 2006, the investment property had a fair value of 24 million euros. The company
uses the fair value model in accounting for investment properties.
Misson would like advice on how to treat these transactions in the financial statements for the year ended 31
October 2006. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in accordance with the advice required by the
directors.
(Candidates should show detailed workings as well as a discussion of the accounting treatment used.)
正确答案:
(b) Inventory, Goods sold and Investment property
The inventory and trade payable initially would be recorded at 8 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $5 million. At the year end, the
amount payable is still outstanding and is retranslated at 1 dollar = 1·3 euros, i.e. $6·2 million. An exchange loss of
$(6·2 – 5) million, i.e. $1·2 million would be reported in profit or loss. The inventory would be recorded at $5 million at the
year end unless it is impaired in value.
The sale of goods would be recorded at 4 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $2·5 million as a sale and as a trade receivable. Payment
is received on 31 October 2006 in euros and the actual value of euros received will be 4 million euros ÷ 1·3,
i.e. $3·1 million.
Thus a gain on exchange of $0·6 million will be reported in profit or loss.
The investment property should be recognised on 1 November 2005 at 28 million euros ÷ 1·4, i.e. $20 million. At
31 October 2006, the property should be recognised at 24 million euros ÷ 1·3, i.e. $18·5 million. The decrease in fair value
should be recognised in profit and loss as a loss on investment property. The property is a non-monetary asset and any foreign
currency element is not recognised separately. When a gain or loss on a non-monetary item is recognised in profit or loss,
any exchange component of that gain or loss is also recognised in profit or loss. If any gain or loss is recognised in equity ona non-monetary asset, any exchange gain is also recognised in equity. -
第3题:
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
正确答案: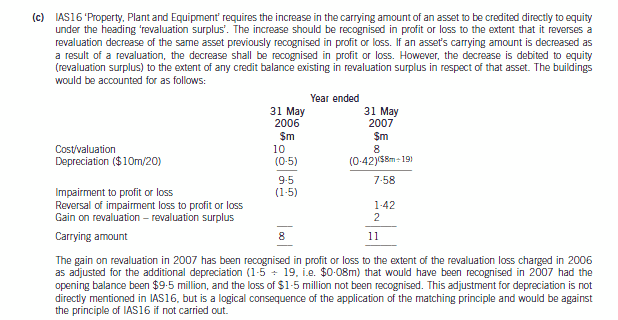
-
第4题:
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(c) Acquisition of Marne
All business combinations within the scope of IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ must be accounted for using the purchase
method. (IFRS 3.14) The pooling of interests method is prohibited. Under IFRS 3, an acquirer must be identified for all
business combinations. (IFRS 3.17) Sirus will be identified as the acquirer of Marne and must measure the cost of a business
combination at the sum of the fair values, at the date of exchange, of assets given, liabilities incurred or assumed, in exchange
for control of Marne; plus any costs directly attributable to the combination. (IFRS 3.24) If the cost is subject to adjustment
contingent on future events, the acquirer includes the amount of that adjustment in the cost of the combination at the
acquisition date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. (IFRS 3.32) However, if the contingent payment
either is not probable or cannot be measured reliably, it is not measured as part of the initial cost of the business combination.
If that adjustment subsequently becomes probable and can be measured reliably, the additional consideration is treated as
an adjustment to the cost of the combination. (IAS 3.34) The issue with the increased profit share payable to the directors
of Marne is whether the payment constitutes remuneration or consideration for the business acquired. Because the directors
of Marne fall back to normal remuneration levels after the two year period, it appears that this additional payment will
constitute part of the purchase consideration with the resultant increase in goodwill. It seems as though these payments can
be measured reliably and therefore the cost of the acquisition should be increased by the net present value of $11 million at
1 May 2007 being $5 million discounted for 1 year and $6 million for 2 years. -
第5题:
Required:
Discuss the principles and practices which should be used in the financial year to 30 November 2008 to account
for:(b) the costs incurred in extending the network; (7 marks)
正确答案:
Costs incurred in extending network
The cost of an item of property, plant and equipment should be recognised when
(i) it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the entity, and
(ii) the cost of the item can be measured reliably (IAS16, ‘Property, plant and equipment’ (PPE))
It is necessary to assess the degree of certainty attaching to the flow of economic benefits and the basis of the evidence available
at the time of initial recognition. The cost incurred during the initial feasibility study ($250,000) should be expensed as incurred,
as the flow of economic benefits to Johan as a result of the study would have been uncertain.
IAS16 states that the cost of an item of PPE comprises amongst other costs, directly attributable costs of bringing the asset to the
location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in a manner intended by management (IAS16, para 16).
Examples of costs given in IAS16 are site preparation costs, and installation and assembly costs. The selection of the base station
site is critical for the optimal operation of the network and is part of the process of bringing the network assets to a working
condition. Thus the costs incurred by engaging a consultant ($50,000) to find an optimal site can be capitalised as it is part of
the cost of constructing the network and depreciated accordingly as planning permission has been obtained.
Under IAS17, ‘Leases’, a lease is defined as an agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee, in return for a payment or
series of payments, the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time. A finance lease is a lease that transfers substantially all
the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of the leased asset to the lessee. An operating lease is a lease other than a finance
lease. In the case of the contract regarding the land, there is no ownership transfer and the term is not for the major part of the
asset’s life as it is land which has an indefinite economic life. Thus substantially all of the risks and rewards incidental to ownership
have not been transferred. The contract should be treated, therefore, as an operating lease. The payment of $300,000 should be
treated as a prepayment in the statement of financial position and charged to the income statement over the life of the contract on
the straight line basis. The monthly payments will be expensed and no value placed on the lease contract in the statement of
financial position -
第6题:
5 The directors of Quapaw, a limited liability company, are reviewing the company’s draft financial statements for the
year ended 31 December 2004.
The following material matters are under discussion:
(a) During the year the company has begun selling a product with a one-year warranty under which manufacturing
defects are remedied without charge. Some claims have already arisen under the warranty. (2 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors on the correct treatment of these matters, stating the relevant accounting standard which
justifies your answer in each case.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three matters
正确答案:
(a) The correct treatment is to provide for the best estimate of the costs likely to be incurred under the warranty, as required by
IAS37 Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets. -
第7题:
(b) Historically, all owned premises have been measured at cost depreciated over 10 to 50 years. The management
board has decided to revalue these premises for the year ended 30 September 2005. At the balance sheet date
two properties had been revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another 15 properties have since been revalued by
$5·4 million and there remain a further three properties which are expected to be revalued during 2006. A
revaluation surplus of $7·1 million has been credited to equity. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Revaluation of owned premises
(i) Matters
■ The revaluations are clearly material as $1·7 million, $5·4 million and $7·1 million represent 5·5% , 17·6% and
23·1% of total assets, respectively.
■ The change in accounting policy, from a cost model to a revaluation model, should be accounted for in accordance
with IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’ does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
■ The basis on which the valuations have been carried out, for example, market-based fair value (IAS 16).
■ Independence, qualifications and expertise of valuer(s).
■ IAS 16 does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class of premises should have been
revalued.
■ The valuations of properties after the year end are adjusting events (i.e. providing additional evidence of conditions
existing at the year end) per IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be
expected to reflect year-end values.
■ If $5·4 million is a net amount of surpluses and deficits it should be grossed up so that the credit to equity reflects
the sum of the surpluses with any deficits being expensed through profit and loss (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ The revaluation exercise is incomplete. If the revaluations on the remaining three properties are expected to be
material and cannot be reasonably estimated for inclusion in the financial statements for the year ended
30 September 2005 perhaps the change in policy should be deferred for a year.
■ Depreciation for the year should have been calculated on cost as usual to establish carrying amount before
revaluation.
■ Any premises held under finance leases should be similarly revalued.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of owned premises extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Calculation of difference between valuation and depreciated cost by property. Separate summation of surpluses
and deficits.
■ Copy of valuation certificate for each property.
■ Physical inspection of properties with largest surpluses (including the two valued before the year end) to confirm
condition.
■ Extracts from local property guides/magazines indicating a range of values of similarly styled/sized properties.
■ Separate presentation of the revaluation surpluses (gross) in:
– the statement of changes in equity; and
– reconciliation of carrying amount at the beginning and end of the period.
■ IAS 16 disclosures in the notes to the financial statements including:
– the effective date of revaluation;
– whether an independent valuer was involved;
– the methods and significant assumptions applied in estimating fair values; and
– the carrying amount that would have been recognised under the cost model. -
第8题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第9题:
(b) Seymour offers health-related information services through a wholly-owned subsidiary, Aragon Co. Goodwill of
$1·8 million recognised on the purchase of Aragon in October 2004 is not amortised but included at cost in the
consolidated balance sheet. At 30 September 2006 Seymour’s investment in Aragon is shown at cost,
$4·5 million, in its separate financial statements.
Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show a loss before taxation of
$0·6 million (2005 – $0·5 million loss) and total assets of $4·9 million (2005 – $5·7 million). The notes to
Aragon’s financial statements disclose that they have been prepared on a going concern basis that assumes that
Seymour will continue to provide financial support. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Goodwill
(i) Matters
■ Cost of goodwill, $1·8 million, represents 3·4% consolidated total assets and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: Any assessments of materiality of goodwill against amounts in Aragon’s financial statements are
meaningless since goodwill only exists in the consolidated financial statements of Seymour.
■ It is correct that the goodwill is not being amortised (IFRS 3 Business Combinations). However, it should be tested
at least annually for impairment, by management.
■ Aragon has incurred losses amounting to $1·1 million since it was acquired (two years ago). The write-off of this
amount against goodwill in the consolidated financial statements would be material (being 61% cost of goodwill,
8·3% PBT and 2·1% total assets).
■ The cost of the investment ($4·5 million) in Seymour’s separate financial statements will also be material and
should be tested for impairment.
■ The fair value of net assets acquired was only $2·7 million ($4·5 million less $1·8 million). Therefore the fair
value less costs to sell of Aragon on other than a going concern basis will be less than the carrying amount of the
investment (i.e. the investment is impaired by at least the amount of goodwill recognised on acquisition).
■ In assessing recoverable amount, value in use (rather than fair value less costs to sell) is only relevant if the going
concern assumption is appropriate for Aragon.
■ Supporting Aragon financially may result in Seymour being exposed to actual and/or contingent liabilities that
should be provided for/disclosed in Seymour’s financial statements in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions,
Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying values of cost of investment and goodwill arising on acquisition to prior year audit working papers and
financial statements.
■ A copy of Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 showing loss for year.
■ Management’s impairment test of Seymour’s investment in Aragon and of the goodwill arising on consolidation at
30 September 2006. That is a comparison of the present value of the future cash flows expected to be generated
by Aragon (a cash-generating unit) compared with the cost of the investment (in Seymour’s separate financial
statements).
■ Results of any impairment tests on Aragon’s assets extracted from Aragon’s working paper files.
■ Analytical procedures on future cash flows to confirm their reasonableness (e.g. by comparison with cash flows for
the last two years).
■ Bank report for audit purposes for any guarantees supporting Aragon’s loan facilities.
■ A copy of Seymour’s ‘comfort letter’ confirming continuing financial support of Aragon for the foreseeable future. -
第10题:
(ii) Briefly explain the implications of Parr & Co’s audit opinion for your audit opinion on the consolidated
financial statements of Cleeves Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Implications for audit opinion on consolidated financial statements of Cleeves
■ If the potential adjustments to non-current asset carrying amounts and loss are not material to the consolidated
financial statements there will be no implication. However, as Howard is material to Cleeves and the modification
appears to be ‘so material’ (giving rise to adverse opinion) this seems unlikely.
Tutorial note: The question clearly states that Howard is material to Cleeves, thus there is no call for speculation
on this.
■ As Howard is wholly-owned the management of Cleeves must be able to request that Howard’s financial statements
are adjusted to reflect the impairment of the assets. The auditor’s report on Cleeves will then be unmodified
(assuming that any impairment of the investment in Howard is properly accounted for in the separate financial
statements of Cleeves).
■ If the impairment losses are not recognised in Howard’s financial statements they can nevertheless be adjusted on
consolidation of Cleeves and its subsidiaries (by writing down assets to recoverable amounts). The audit opinion
on Cleeves should then be unmodified in this respect.
■ If there is no adjustment of Howard’s asset values (either in Howard’s financial statements or on consolidation) it
is most likely that the audit opinion on Cleeves’s consolidated financial statements would be ‘except for’. (It should
not be adverse as it is doubtful whether even the opinion on Howard’s financial statements should be adverse.)
Tutorial note: There is currently no requirement in ISA 600 to disclose that components have been audited by another
auditor unless the principal auditor is permitted to base their opinion solely upon the report of another auditor. -
第11题:
(ii) Describe the procedures to verify the number of serious accidents in the year ended 30 November 2007.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Procedures to verify the number of serious accidents during 2007 could include the following:
Tutorial note: procedures should focus on the completeness of the disclosure as it is in the interest of Sci-Tech Co to
understate the number of serious accidents.
– Review the accident log book and count the total number of accidents during the year
– Discuss the definition of ‘serious accident’ with the directors and clarify exactly what criteria need to be met to
satisfy the definition
– For serious accidents identified:
? review HR records to determine the amount of time taken off work
? review payroll records to determine the financial amount of sick pay awarded to the employee
? review correspondence with the employee regarding the accident.
Tutorial note: the above will help to clarify that the accident was indeed serious.
– Review board minutes where the increase in the number of serious accidents has been discussed
– Review correspondence with Sci-Tech Co’s legal advisors to ascertain any legal claims made against the company
due to accidents at work
– Enquire as to whether any health and safety visits have been conducted during the year by regulatory bodies, and
review any documentation or correspondence issued to Sci-Tech Co after such visits.
Tutorial note: it is highly likely that in a regulated industry such as pharmaceutical research, any serious accident
would trigger a health and safety inspection from the appropriate regulatory body.
– Discuss the level of accidents with representatives of Sci-Tech Co’s employees to reach an understanding as to
whether accidents sometimes go unreported in the accident log book. -
第12题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第13题:
(b) Ambush loaned $200,000 to Bromwich on 1 December 2003. The effective and stated interest rate for this
loan was 8 per cent. Interest is payable by Bromwich at the end of each year and the loan is repayable on
30 November 2007. At 30 November 2005, the directors of Ambush have heard that Bromwich is in financial
difficulties and is undergoing a financial reorganisation. The directors feel that it is likely that they will only
receive $100,000 on 30 November 2007 and no future interest payment. Interest for the year ended
30 November 2005 had been received. The financial year end of Ambush is 30 November 2005.
Required:
(i) Outline the requirements of IAS 39 as regards the impairment of financial assets. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) IAS 39 requires an entity to assess at each balance sheet date whether there is any objective evidence that financial
assets are impaired and whether the impairment impacts on future cash flows. Objective evidence that financial assets
are impaired includes the significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor and whether it becomes probable that the
borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganisation.
For investments in equity instruments that are classified as available for sale, a significant and prolonged decline in the
fair value below its cost is also objective evidence of impairment.
If any objective evidence of impairment exists, the entity recognises any associated impairment loss in profit or loss.
Only losses that have been incurred from past events can be reported as impairment losses. Therefore, losses expected
from future events, no matter how likely, are not recognised. A loss is incurred only if both of the following two
conditions are met:
(i) there is objective evidence of impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition
of the asset (a ‘loss event’), and
(ii) the loss event has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset or group of financial assets
that can be reliably estimated
The impairment requirements apply to all types of financial assets. The only category of financial asset that is not subject
to testing for impairment is a financial asset held at fair value through profit or loss, since any decline in value for such
assets are recognised immediately in profit or loss.
For loans and receivables and held-to-maturity investments, impaired assets are measured at the present value of the
estimated future cash flows discounted using the original effective interest rate of the financial assets. Any difference
between the carrying amount and the new value of the impaired asset is an impairment loss.
For investments in unquoted equity instruments that cannot be reliably measured at fair value, impaired assets are
measured at the present value of the estimated future cash flows discounted using the current market rate of return for
a similar financial asset. Any difference between the previous carrying amount and the new measurement of theimpaired asset is recognised as an impairment loss in profit or loss. -
第14题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: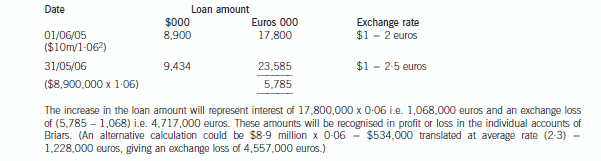
-
第15题:
(b) (i) Discusses the principles involved in accounting for claims made under the above warranty provision.
(6 marks)
(ii) Shows the accounting treatment for the above warranty provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ for the year ended 31 October 2007. (3 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and communication of advice. (2 marks)
正确答案:(b) Provisions – IAS37
An entity must recognise a provision under IAS37 if, and only if:
(a) a present obligation (legal or constructive) has arisen as a result of a past event (the obligating event)
(b) it is probable (‘more likely than not’), that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle
the obligation
(c) the amount can be estimated reliably
An obligating event is an event that creates a legal or constructive obligation and, therefore, results in an enterprise having
no realistic alternative but to settle the obligation. A constructive obligation arises if past practice creates a valid expectation
on the part of a third party. If it is more likely than not that no present obligation exists, the enterprise should disclose a
contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of resources is remote.
The amount recognised as a provision should be the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation
at the balance sheet date, that is, the amount that an enterprise would rationally pay to settle the obligation at the balance
sheet date or to transfer it to a third party. This means provisions for large populations of events such as warranties, are
measured at a probability weighted expected value. In reaching its best estimate, the entity should take into account the risks
and uncertainties that surround the underlying events.
Expected cash outflows should be discounted to their present values, where the effect of the time value of money is material
using a risk adjusted rate (it should not reflect risks for which future cash flows have been adjusted). If some or all of the
expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement should be
recognised as a separate asset when, and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the entity
settles the obligation. The amount recognised should not exceed the amount of the provision. In measuring a provision future
events should be considered. The provision for the warranty claim will be determined by using the expected value method.
The past event which causes the obligation is the initial sale of the product with the warranty given at that time. It would be
appropriate for the company to make a provision for the Year 1 warranty of $280,000 and Year 2 warranty of $350,000,
which represents the best estimate of the obligation (see Appendix 2). Only if the insurance company have validated the
counter claim will Macaljoy be able to recognise the asset and income. Recovery has to be virtually certain. If it is virtually
certain, then Macaljoy may be able to recognise the asset. Generally contingent assets are never recognised, but disclosed
where an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
The company could discount the provision if it was considered that the time value of money was material. The majority of
provisions will reverse in the short term (within two years) and, therefore, the effects of discounting are likely to be immaterial.
In this case, using the risk adjusted rate (IAS37), the provision would be reduced to $269,000 in Year 1 and $323,000 in
Year 2. The company will have to determine whether this is material.
Appendix 1
The accounting for the defined benefit plan is as follows:


-
第16题:
(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is to
be paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirus
to redeem the loan after seven years by paying the full amount of the interest to be charged over the ten year
period, plus a penalty of $200,000 and the principal of $2 million. The effective interest rate of the repayment
option is 9·1%. The directors of Sirus are currently restructuring the funding of the company and are in initial
discussions with the bank about the possibility of repaying the loan within the next financial year. Sirus is
uncertain about the accounting treatment for the current loan agreement and whether the loan can be shown as
a current liability because of the discussions with the bank. (6 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(d) Repayment of the loan
If at the beginning of the loan agreement, it was expected that the repayment option would not be exercised, then the effective
interest rate would be 8% and at 30 April 2008, the loan would be stated at $2 million in the statement of financial position
with interest of $160,000 having been paid and accounted for. If, however, at 1 May 2007, the option was expected to be
exercised, then the effective interest rate would be 9·1% and at 30 April 2008, the cash interest paid would have been
$160,000 and the interest charged to the income statement would have been (9·1% x $2 million) $182,000, giving a
statement of financial position figure of $2,022,000 for the amount of the financial liability. However, IAS39 requires the
carrying amount of the financial instrument to be adjusted to reflect actual and revised estimated cash flows. Thus, even if
the option was not expected to be exercised at the outset but at a later date exercise became likely, then the carrying amount
would be revised so that it represented the expected future cash flows using the effective interest rate. As regards the
discussions with the bank over repayment in the next financial year, if the loan was shown as current, then the requirements
of IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ would not be met. Sirus has an unconditional right to defer settlement for longer
than twelve months and the liability is not due to be legally settled in 12 months. Sirus’s discussions should not be considered
when determining the loan’s classification.
It is hoped that the above report clarifies matters. -
第17题:
Discuss the principles and practices which should be used in the financial year to 30 November 2008 to account
for:(c) the purchase of handsets and the recognition of revenue from customers and dealers. (8 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
正确答案:Handsets and revenue recognition
The inventory of handsets should be measured at the lower of cost and net realisable value (IAS2, ‘Inventories’, para 9). Johan
should recognise a provision at the point of purchase for the handsets to be sold at a loss. The inventory should be written down
to its net realisable value (NRV) of $149 per handset as they are sold both to prepaid customers and dealers. The NRV is $51
less than cost. Net realisable value is the estimated selling price in the normal course of business less the estimated selling costs.
IAS18, ‘Revenue’, requires the recognition of revenue by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the reporting
date. Revenue associated with the provision of services should be recognised as service as rendered. Johan should record the
receipt of $21 per call card as deferred revenue at the point of sale. Revenue of $18 should be recognised over the six month
period from the date of sale. The unused call credit of $3 would be recognised when the card expires as that is the point at which
the obligation of Johan ceases. Revenue is earned from the provision of services and not from the physical sale of the card.
IAS18 does not deal in detail with agency arrangements but says the gross inflows of economic benefits include amounts collected
on behalf of the principal and which do not result in increases in equity for the entity. The amounts collected on behalf of the
principal are not revenue. Revenue is the amount of the ‘commission’. Additionally where there are two or more transactions, they
should be taken together if the commercial effect cannot be understood without reference to the series of transactions as a whole.
As a result of the above, Johan should not recognise revenue when the handset is sold to the dealer, as the dealer is acting as an
agent for the sale of the handset and the service contract. Johan has retained the risk of the loss in value of the handset as they
can be returned by the dealer and the price set for the handset is under the control of Johan. The handset sale and the provision
of the service would have to be assessed as to their separability. However, the handset cannot be sold separately and is
commercially linked to the provision of the service. Johan would, therefore, recognise the net payment of $130 as a customer
acquisition cost which may qualify as an intangible asset under IAS38, and the revenue from the service contract will be recognised
as the service is rendered. The intangible asset would be amortised over the 12 month contract. The cost of the handset from the
manufacturer will be charged as cost of goods sold ($200). -
第18题:
(ii) Illustrate the benefit of revising the corporate structure by calculating the corporation tax (CT) payable
for the year ended 31 March 2006, on the assumptions that:
(1) no action is taken; and
(2) an amended structure as recommended in (i) above is implemented from 1 June 2005. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第19题:
4 (a) Explain the auditor’s responsibilities in respect of subsequent events. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
4 JINACK CO
(a) Auditor’s responsibilities for subsequent events
■ Auditors must consider the effect of subsequent events on:
– the financial statements;
– the auditor’s report.
■ Subsequent events are all events occurring after a period end (i.e. reporting date) i.e.:
– events after the balance sheet date (as defined in IAS 10); and
– events after the financial statements have been authorised for issue.
Events occurring up to date of auditor’s report
■ The auditor is responsible for carrying out procedures designed to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that all
events up to the date of the auditor’s report that may require adjustment of, or disclosure in, the financial statements
have been identified.
■ These procedures are in addition to those applied to specific transactions occurring after the period end that provide
audit evidence of period-end account balances (e.g. inventory cut-off and receipts from trade receivables). Such
procedures should ordinarily include:
– reviewing minutes of board/audit committee meetings;
– scrutinising latest interim financial statements/budgets/cash flows, etc;
– making/extending inquiries to legal advisors on litigation matters;
– inquiring of management whether any subsequent events have occurred that might affect the financial statements
(e.g. commitments entered into).
■ When the auditor becomes aware of events that materially affect the financial statements, the auditor must consider
whether they have been properly accounted for and adequately disclosed in the financial statements.
Facts discovered after the date of the auditor’s report but before financial statements are issued
Tutorial note: After the date of the auditor’s report it is management’s responsibility to inform. the auditor of facts which
may affect the financial statements.
■ If the auditor becomes aware of such facts which may materially affect the financial statements, the auditor:
– considers whether the financial statements need amendment;
– discusses the matter with management; and
– takes appropriate action (e.g. audit any amendments to the financial statements and issue a new auditor’s report).
■ If management does not amend the financial statements (where the auditor believes they need to be amended) and the
auditor’s report has not been released to the entity, the auditor should express a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion
(as appropriate).
■ If the auditor’s report has been released to the entity, the auditor must notify those charged with governance not to issue
the financial statements (and the auditor’s report thereon) to third parties.
Tutorial note: The auditor would seek legal advice if the financial statements and auditor’s report were subsequently issued.
Facts discovered after the financial statements have been issued
■ The auditor has no obligation to make any inquiry regarding financial statements that have been issued.
■ However, if the auditor becomes aware of a fact which existed at the date of the auditor’s report and which, if known
at that date, may have caused the auditor’s report to be modified, the auditor should:
– consider whether the financial statements need revision;
– discuss the matter with management; and
– take appropriate action (e.g. issuing a new report on revised financial statements). -
第20题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第21题:
(c) In November 2006 Seymour announced the recall and discontinuation of a range of petcare products. The
product recall was prompted by the high level of customer returns due to claims of poor quality. For the year to
30 September 2006, the product range represented $8·9 million of consolidated revenue (2005 – $9·6 million)
and $1·3 million loss before tax (2005 – $0·4 million profit before tax). The results of the ‘petcare’ operations
are disclosed separately on the face of the income statement. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
■ The discontinuation of the product line after the balance sheet date provides additional evidence that, as at the
balance sheet date, it was of poor quality. Therefore, as at the balance sheet date:
– an allowance (‘provision’) may be required for credit notes for returns of products after the year end that were
sold before the year end;
– goods returned to inventory should be written down to net realisable value (may be nil);
– any plant and equipment used exclusively in the production of the petcare range of products should be tested
for impairment;
– any material contingent liabilities arising from legal claims should be disclosed.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A copy of Seymour’s announcement (external ‘press release’ and any internal memorandum).
■ Credit notes raised/refunds paid after the year end for faulty products returned.
■ Condition of products returned as inspected during physical attendance of inventory count.
■ Correspondence from customers claiming reimbursement/compensation for poor quality.
■ Direct confirmation from legal adviser (solicitor) regarding any claims for customers including estimates of possible
payouts. -
第22题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it. -
第23题:
(ii) Identify and explain the potential financial statement risks caused by the breach of planning regulations
discussed in the press cutting. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Several significant financial statement risks are indicated by the press cutting.
Overstatement of property, plant and equipment
Medix Co has constructed a research laboratory which is likely to be impaired at the year end. The local authority has
the power to shut down the facility, and it is clear from the press cutting that this is likely to happen before the year end.
Following IAS 36 Impairment of Assets, the premises should be written down to recoverable amount, and the
impairment loss recognised as an expense. The directors should carry out an impairment review before the year end. If
the premises cannot be used as intended then the recoverable amount (measured using the higher of value in use and
fair value less selling cost) is likely to be less than current carrying value. In this case, assuming the local authority is
successful in shutting down the research laboratory, the recoverable amount is likely to be nil, as the premises have no
value in use, as it will never be used commercially, and has no market value as it is likely to be demolished.
In addition, any tangible assets such as laboratory equipment located at the premises should be tested for impairment
as if the company cannot use the premises then the assets contained within it are likely to have a lower recoverable
amount than carrying value.
Contingency – fines or penalties imposed by local authority
The press cutting indicates that Medix Co has been sued before, and that the local authority may again take legal action
against the company. IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets states that a provision should be
recognised if the company has a probable obligation at the year end which can be measured reliably. If payment is
deemed only possible at the year end, then disclosure of the contingent liability should be made in a note to the financial
statements.
If the local authority commences legal proceedings against Medix Co before the year end of 30 June 2008, then
management should assess the probability of payment. The financial statement risk is not recognising a provision (and
associated expense within the income statement), or not disclosing a contingency.
Demolition costs
The local authority may require Medix Co to demolish the premises. If this demand is made before the year end, Medix
Co should recognise a provision for demolition costs as an unavoidable legal obligation would have been created. The
financial statement risk is that in this situation, Medix Co fails to recognise a provision and associated expense within
the income statement.
Going concern
The above issues could indicate that the company may not continue in operational existence. The potential lack of
disclosure of these issues represents a financial statement risk.
