(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposedrestructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)
题目
(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposed
restructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.
(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(b) The tax implications of the proposed restructuring of the Rapier Ltd group
(i) Immediate implications
Corporation tax
Rapier Ltd and its subsidiaries are in a capital gains group as Rapier Ltd owns at least 75% of the ordinary share capital
of each of the subsidiary companies. Any non-exempt items of plant and machinery owned by the subsidiaries will
therefore be transferred to Rapier Ltd at no gain, no loss.
No taxable credit or allowable debit will arise on the transfer of the subsidiaries’ goodwill to Rapier Ltd because the
companies are in a capital gains group.
The trading losses brought forward in Dirk Ltd will be transferred with the trade to Rapier Ltd as the effective ownership
of the three trades will not change (Rapier Ltd owns the subsidiaries which own the trades and, following the
restructuring, will own the three trades directly). The losses will be restricted to being offset against the future trading
profits of the Dirk trade only.
There will be no balancing adjustments in respect of the plant and machinery transferred to Rapier Ltd. Writing down
allowances will be claimed by the subsidiaries in respect of the year ending 30 June 2007 and by Rapier Ltd in respect
of future periods.
Value added tax (VAT)
No VAT should be charged on the sales of the businesses to Rapier Ltd as they are outside the scope of VAT. This is
because the trades are to be transferred as going concerns to a VAT registered person with no significant break in trading.
Switch Ltd must notify HM Revenue and Customs by 30 July 2007 that it has ceased to make taxable supplies.
更多“(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposedrestructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(c) Assuming that Joanne registers for value added tax (VAT) with effect from 1 April 2006:
(i) Calculate her income tax (IT) and capital gains tax (CGT) payable for the year of assessment 2005/06.
You are not required to calculate any national insurance liabilities in this sub-part. (6 marks)
正确答案:
-
第2题:
(c) (i) Explain the capital gains tax (CGT) implications of a takeover where the consideration is in the form. of
shares (a ‘paper for paper’ transaction) stating any conditions that need to be satisfied. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) Paper for paper rules
The proposed transaction broadly falls under the ‘paper for paper’ rules. Where this is the case, chargeable gains do not
arise. Instead, the new holding stands in the shoes (and inherits the base cost) of the original holding.
The company issuing the new shares must:
(i) end up with more than 25% of the ordinary share capital (or a majority of the voting power) of the old company,
OR
(ii) make a general offer to shareholders in the other company with a condition that, if satisfied, would give the
acquiring company control of the other company.
The exchange must be for bona fide commercial reasons and must not have as its main purpose (or one of its main
purposes) the avoidance of CGT or corporation tax. The acquiring company can obtain advance clearance from the
Inland Revenue that the conditions will be met.
If part of the offer consideration is in the form. of cash, a gain must be calculated using the part disposal rules. If the
cash received is not more than the higher of £3,000 or 5% of the total value on takeover, then the amount received in
cash can be deducted from the base cost of the securities under the small distribution rules. -
第3题:
(ii) Explain the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and capital gains tax (CGT) implications arising on
the grant to and exercise by an employee of an option to buy shares in an unapproved share option
scheme and on the subsequent sale of these shares. State clearly how these would apply in Henry’s
case. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Exercising of share options
The share option is not part of an approved scheme, and will not therefore enjoy the benefits of such a scheme. There
are three events with tax consequences – grant, exercise and sale.
Grant. If shares or options over shares are sold or granted at less than market value, an income tax charge can arise on
the difference between the price paid and the market value. [Weight v Salmon]. In addition, if options can be exercised
more than 10 years after the date of the grant, an employment income charge can arise. This is based on the market
value at the date of grant less the grant and exercise priced.
In Henry’s case, the options were issued with an exercise price equal to the then market value, and cannot be exercised
more than 10 years from the grant. No income tax charge therefore arises on grant.
Exercise. On exercise, the individual pays the agreed amount in return for a number of shares in the company. The price
paid is compared with the open market value at that time, and if less, the difference is charged to income tax. National
insurance also applies, and the company has to pay Class 1 NIC. If the company and shareholder agree, the national
insurance can be passed onto the individual, and the liability becomes a deductible expense in calculating the income
tax charge.
In Henry’s case on exercise, the difference between market value (£14) and the price paid (£1) per share will be taxed
as income. Therefore, £130,000 (10,000 x (£14 – £1)) will be taxed as income. In addition, national insurance will
be chargeable on the company at 12·8% (£16,640) and on Henry at the rate of 1% (£1,300).
Sale. The base cost of the shares is taken to be the market value at the time of exercise. On the sale of the shares, any
gain or loss arising falls under the capital gains tax rules, and CGT will be payable on any gain. Business asset taper
relief will be available as the company is an unquoted trading company, but the relief will only run from the time that
the share options are exercised – i.e. from the time when the shares were acquired.
In Henry’s case, the sale of the shares will immediately follow the exercise of the option (6 days later). The sale proceeds
and the market value at the time of exercise are likely to be similar; thus little to no gain is likely to arise. -
第4题:
(d) Explain whether or not Dovedale Ltd, Hira Ltd and Atapo Inc can register as a group for the purposes of value
added tax. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Dovedale Ltd and Hira Ltd can register as a group for the purposes of value added tax (VAT) because Dovedale Ltd controls
Hira Ltd and both companies are established in the UK in that their head offices are in the UK.
Dovedale Ltd will also control Atapo Inc. However, Atapo Inc cannot be part of a group registration unless it is established
in the UK or has a fixed establishment in the UK. It will be regarded as established in the UK if it is centrally managed and
controlled in the UK or if its head office is in the UK. A fixed establishment is a place where the company has staff and
equipment and where its business is carried on. -
第5题:
(b) (i) Compute the corporation tax liability of Speak Write Ltd for its first trading period on the assumption
that the IR 35 legislation applies to all of its income. (2 marks)
正确答案: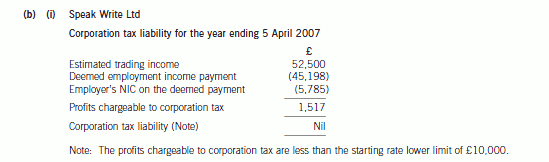
-
第6题:
(iii) State the value added tax (VAT) and stamp duty (SD) issues arising as a result of inserting Bold plc as
a holding company and identify any planning actions that can be taken to defer or minimise these tax
costs. (4 marks)
You should assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates
and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(iii) Bold plc will be making a taxable supply of services, likely to exceed the VAT threshold. It should therefore consider
registering for VAT – either immediately on a voluntary basis, or when its cumulative taxable supplies in the previous
twelve months exceed £60,000.
As an alternative, the new group can apply for a group VAT registration. This will simplify its VAT administration as intragroup
transactions are broadly disregarded for VAT purposes, and only one VAT return is required for the group as a
whole.
Stamp duty normally applies at 0·5% on the consideration payable in respect of transactions in shares. However, an
exemption is available in the case of a takeover, reconstruction or amalgamation where there is no real change in
ownership, i.e. the new shareholdings mirror the old shareholdings, and the transaction is for commercial purposes. The
insertion of a new holding company over an existing company, as proposed here, would qualify for this exemption.
There is no VAT on transactions in shares. -
第7题:
(d) Advise Trent Limited of the consequences arising from the submission of the incorrect value added tax (VAT)
return, assuming that the company has previously had a good compliance record with regard to accounting
for VAT. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Default surcharge
Although the VAT return was submitted on time (i.e. within one month of the end of the tax period), part of the quarterly VAT
liability has not yet been paid. As a result this payment will be made late and a surcharge liability notice will be issued on
the company. The surcharge period will run from the date of the notice until the anniversary of the end of the period for which
the VAT was paid late (i.e. until 31 March 2007). During this period any further default will extend the surcharge period and
any further late payments of VAT will attract a surcharge penalty of 2% on the first occasion, rising to 15% for successive late
payments.
Mis-declaration penalty
As the return understates the VAT payable, a potential mis-declaration penalty arises. The amount understated exceeds 30%
of the sum of the true input tax and output tax, known as the gross amount of tax (GAT) ((30% of (87,500 + 55,000) +
40,000) = 54,750). There has, thus, been a significant understatement of the true VAT return liability, resulting in a penalty
rate of 15% of the VAT which would have been lost had the error not been discovered. However, where an under declaration
arises out of a true error i.e. there is no intention to evade tax involved, and it is voluntarily disclosed, then a mis-declaration
penalty is not normally imposed. Although the company is still within the ‘period of grace’ allowed by HMRC for the correction
of errors in the next following VAT return, it would be advisable for Trent Limited to notify HMRC of the error immediately, in
writing, unless it has a ‘reasonable excuse’ for the error having occurred.
Default interest
Default interest is chargeable when an assessment to VAT arises for an amount that has been under declared in a previous
period, whether as a result of voluntary disclosure or as identified by HMRC. Interest is charged on a daily basis from the
date the under declaration should have been declared (i.e. 1 May 2006) to the date shown on the notice of assessment or
notice of voluntary disclosure. As given the size of the error the de minimis relief for voluntarily declared errors of less than
£2,000 is not applicable, the only way for Trent Limited to minimise the interest charge is by means of early disclosure and
payment of the additional VAT due. -
第8题:
(c) (i) Explain the inheritance tax (IHT) implications and benefits of Alvaro Pelorus varying the terms of his
father’s will such that part of Ray Pelorus’s estate is left to Vito and Sophie. State the date by which a
deed of variation would need to be made in order for it to be valid; (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) Variation of Ray’s will
The variation by Alvaro of Ray’s will, such that assets are left to Vito and Sophie, will not be regarded as a gift by Alvaro.
Instead, provided the deed states that it is intended to be effective for IHT purposes, it will be as if Ray had left the assets
to the children in his will.
This strategy, known as skipping a generation, will have no effect on the IHT due on Ray’s death but will reduce the
assets owned by Alvaro and thus his potential UK IHT liability. A deed of variation is more tax efficient than Alvaro
making gifts to the children as such gifts would be PETs and IHT may be due if Alvaro were to die within seven years.
The deed of variation must be entered into by 31 January 2009, i.e. within two years of the date of Ray’s death. -
第9题:
(ii) Advise Mr Fencer of the income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements
Mr Fencer has borrowed money from a UK bank in order to make a loan to Rapier Ltd, a close company. The interest
paid by Mr Fencer to the bank will be an allowable charge on income as long as he continues to hold more than 5% of
Rapier Ltd. Charges on income are deductible in arriving at an individual’s statutory total income.
Mr Fencer will receive interest from Rapier Ltd net of 20% income tax. The gross amount of interest will be subject to
income tax at either 10%, 20% or 40% depending on whether the income falls into Mr Fencer’s starting rate, basic rate
or higher rate tax band. Mr Fencer will obtain a tax credit for the 20% income tax suffered at source. -
第10题:
(b) Explain why making sales of Sabals in North America will have no effect on Nikau Ltd’s ability to recover its
input tax. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year to 31 March 2007
will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
– you should ignore indexation allowance.
正确答案:
(b) Recoverability of input tax
Sales by Nikau Ltd of its existing products are subject to UK VAT at 17·5% because it is selling to domestic customers who
will not be registered for VAT. Accordingly, at present, Nikau Ltd can recover all of its input tax.
Sales to customers in North America will be zero rated because the goods are being exported from the EU. Zero rated supplies
are classified as taxable for the purposes of VAT and therefore Nikau Ltd will continue to be able to recover all of its input tax. -
第11题:
(b) Advise Maureen on deregistration for the purposes of value added tax (VAT) and any possible alternative
strategy. (8 marks)
An additional mark will be awarded for the effectiveness with which the information is communicated.
(1 mark)
正确答案:
(b) Advice on Maureen’s VAT position
Deregistration
In order to voluntarily deregister for VAT you must satisfy HMRC that the value of your taxable supplies in the next twelve
months will not exceed £62,000. You will then be deregistered with effect from the date of your request or a later date as
agreed with HMRC.
On deregistering you are regarded as making a supply of all stocks and equipment in respect of which input tax has been
claimed. However, the VAT on this deemed supply need only be paid to HMRC if it exceeds £1,000.
Once you have deregistered, you must no longer charge VAT on your sales. You will also be unable to recover the input tax
on the costs incurred by your business. Instead, the VAT you pay on your costs will be allowable when computing your taxable
profits.
You should monitor your sales on a monthly basis; if your sales in a twelve-month period exceed £64,000 you must notify
HMRC within the 30 days following the end of the twelve-month period. You will be registered from the end of the month
following the end of the twelve-month period.
Flat rate scheme
Rather than deregistering you may wish to consider operating the flat rate scheme. This would reduce the amount of
administration as you would no longer need to record and claim input tax in respect of the costs incurred by your business.
Under the flat rate scheme you would continue to charge your customers VAT in the way that you do at the moment. You
would then pay HMRC a fixed percentage of your VAT inclusive turnover each quarter rather than calculating output tax less
input tax. This may be financially advantageous as compared with deregistering; I would be happy to prepare calculations for
you if you wish. -
第12题:
What does VAT stand for?
A. Value-Assist Tag
B. Value-Added Tax
C. Value-Added Tag
D. Value-Assist Tax
正确答案:B
-
第13题:
(b) (i) Advise Alasdair of the tax implications and relative financial risks attached to the following property
investments:
(1) buy to let residential property;
(2) commercial property; and
(3) shares in a property investment company/unit trust. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Income tax:
Direct investment in residential or commercial property
The income will be taxed under Schedule A for both residential and commercial property investment. Expenses can be
offset against income under the normal trading rules. These will include interest charges incurred in borrowing funds to
acquire the properties. Schedule A losses are restricted to use against future Schedule A profits, with the earliest profits
being relieved first.
When acquiring commercial properties, it may be possible to claim capital allowances on the fixtures and plant held in
the building. In addition, industrial buildings allowances (IBA) may also be available if the property qualifies as an
industrial building.
Capital allowances are not normally available for fixtures and fittings included in a residential property. Instead, a wear
and tear allowance can be claimed if the property is furnished. This is equal to 10% of the rental income after any
tenants cost (for example, council tax) paid by the landlord.
Income tax is levied at the normal tax rates (10/22/40%) as appropriate.
Collective investment (shares in a property investment company/unit trust)
With collective investments, the investor either buys shares (in an investment company) or units (in an equity unit trust).
The income tax treatment of both is the same in that the investor receives dividends. These are taxed at 10% and 32·5%
respectively (for basic and higher rate taxpayers).
Investors are not able to claim income tax relief on either interest costs (of borrowing) or any other expenses.
Capital gains tax (CGT):
The normal rules apply for CGT purposes in all situations. Property investments do not normally qualify for business
rates of taper relief unless they are furnished holiday lets or in certain circumstances, commercial property. Investments
in unit trusts or property investment companies will never qualify for business taper rates.
It is possible to use an individual savings account (ISA) to make collective investments. If this is done, income and
capital gains will be exempt from tax.
Other taxes:
New commercial property is subject to value added tax (VAT) at the standard rate, but new residential property is subject
to VAT at the zero rate. If a commercial building is acquired second hand as an investment, VAT may be payable if a
previous owner has opted to tax the property. If this is the case, VAT at the standard rate will be payable on the purchase
price, and rental charges to tenants will also be subject to VAT, again at the standard rate.
The acquisition of shares is not subject ot VAT.
Stamp duty land tax (SDLT) will be payable broadly on the direct acquisition of any property. The rates vary from 0 to
4% depending on the value of the land and building and its nature (whether residential or non-residential). Stamp duty
is payable at a rate of 0·5% on the acquisition of shares.
Investment risks/benefits
Direct investment
Investing directly in property represents a long term investment, and unless this is the case, investment risks are high.
Substantial initial costs (such as SDLT, VAT and transactions costs) are incurred, and ongoing running costs (such as
letting agents’ fees and vacant periods) can be significant. The investments are illiquid, particularly commercial
properties which can take months to sell.
All types of properties are dependent on a cyclical market, and the values of property investments can vary significantly
as a result. However, residential property has (on a long term basis) proven to be a good hedge against inflation.
Collective investments
The nature of collective investments is that the investor’s risk is reduced by the investment being spread over a large
portfolio as opposed to one or a few properties. In addition, investors can take advantage of the higher levels of liquidity
afforded by such vehicles. -
第14题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:
-
第15题:
(ii) Briefly outline the tax consequences for Henry if the types of protection identified in (i) were to be
provided for him by Happy Home Ltd compared to providing them for himself. You are not required to
discuss the corporation tax (CT) consequences for Happy Home Ltd. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Provision of protection: company or individual
If any of the policies are taken out and paid for by Henry personally, then there will be no tax relief on the premiums,
but neither will there normally be any tax payable on the proceeds or benefits received.
If Happy Home Ltd were to pay the premiums on a policy taken out by Henry, and of which he was the direct beneficiary,
then this will constitute a benefit, on the grounds that the company will have satisfied a personal liability of Henry’s.
Accordingly, income tax and Class 1A national insurance contributions will be payable on the benefit.
If, however, Happy Home Ltd were to decide to offer protection benefits to their employees on a group basis (and not
just to Henry), then it would be possible to avoid a charge under the benefits rules and/or obtain a lower rate of premium
under a collective policy. For example:
– A death in service benefit of up to four times remuneration can be provided as part of an approved pension scheme.
No benefit charge arises on Henry and any lump sum will be paid tax free. This could be considered a substitute
for a term assurance policy.
– If a group permanent health insurance policy were taken out, no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but any
benefits payable under the policy would be paid to Happy Home Ltd in the first instance. When subsequently paid
on to Henry, such payments would be treated as arising from his employment and subject to PAYE and national
insurance as for normal salary payments.
– If a group critical illness policy were taken out, again no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but in this case also,
any benefits received by Henry directly from Happy Home Ltd as a result of the payments under the policy would
be considered as derived from his employment and subject to income tax and national insurance. Such a charge
to tax and national insurance would however be avoided if these payments were made in terms of a trust. -
第16题:
(d) Explain how Gloria would be taxed in the UK on the dividends paid by Bubble Inc and the capital gains tax
and inheritance tax implications of a future disposal of the shares. Clearly state, giving reasons, whether or
not the payment made to Eric is allowable for capital gains tax purposes. (9 marks)
You should assume that the rates and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(d) UK tax implications of shares in Bubble Inc
Income tax
Gloria is UK resident and is therefore subject to income tax on her worldwide income. However, because she is non-UK
domiciled, she will only be taxed on the foreign dividends she brings into the UK.
Dividends brought into the UK will be grossed up for any tax paid in Oceania. The gross amount is taxed at 10% if it falls
into the starting or basic rate band and at 321/2% if it falls into the higher rate band. The tax suffered in Oceania is available
for offset against the UK tax liability. The offset is restricted to a maximum of the UK tax on the dividend income.
Capital gains tax
Individuals are subject to capital gains tax on worldwide assets if they are resident or ordinarily resident in the UK. However,
because Gloria is non-UK domiciled and the shares are situated abroad, the gain is only taxable to the extent that the sales
proceeds are brought into the UK. Any tax suffered in Oceania in respect of the gain is available for offset against the UK
capital gains tax liability arising on the shares.
Any loss arising on the disposal of the shares would not be available for relief in the UK.
In computing a capital gain or allowable loss, a deduction is available for the incidental costs of acquisition. However, to be
allowable, such costs must be incurred wholly and exclusively for the purposes of acquiring the asset. The fee paid to Eric
related to general investment advice and not to the acquisition of the shares and therefore, would not be deductible in
computing the gain.
Taper relief will be at non-business asset rates as Bubble Inc is an investment company.
Inheritance tax
Assets situated abroad owned by non-UK domiciled individuals are excluded property for the purposes of inheritance tax.
However, Gloria will be deemed to be UK domiciled (for the purposes of inheritance tax only) if she has been resident in the
UK for 17 out of the 20 tax years ending with the year in which the disposal occurs.
Gloria has been running a business in the UK since June 1992 and would therefore, appear to have been resident for at least
15 tax years (1992/93 to 2006/07 inclusive).
If Gloria is deemed to be UK domiciled such that the shares in Bubble Inc are not excluded property, business property relief
will not be available because Bubble Inc is an investment company. -
第17题:
(b) (i) State the condition that would need to be satisfied for the exercise of Paul’s share options in Memphis
plc to be exempt from income tax and the tax implications if this condition is not satisfied.
(2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Paul has options in an HMRC approved share scheme. Under such schemes, no tax liabilities arise either on the grant
or exercise of the option. The excess of the proceeds over the price paid for the shares (the exercise price) is charged to
capital gains tax on their disposal.
However, in order to secure this treatment, one of the conditions to be satisfied is that the options cannot be exercised
within three years of the date of grant. If Paul were to exercise his options now (i.e. before the third anniversary of the
grant), the exercise would instead be treated as an unapproved exercise. At that date, income tax would be charged on
the difference between the market value of the shares on exercise and the price paid to exercise the option. -
第18题:
(iii) Explain the potential corporation tax (CT) implications of Tay Limited transferring work to Trent Limited,
and suggest how these can be minimised or eliminated. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Trading losses may not be carried forward where, within a period of three years there is both a change in the ownership
of a company and a major change in the nature or conduct of its trade. The transfer of work from Tay Limited to Trent
Limited is likely to constitute a major change in the nature or conduct of the latter’s trade. As a consequence, any tax
losses at the date of acquisition will be forfeited. Assuming losses were incurred uniformly in 2005, the tax losses at the
date of acquisition were £380,000 (300,000 + 2/3 x 120,000)). This is worth £114,000 assuming a corporation tax
rate of 30%.
Thus, Tay Limited should not consider transferring any trade to Trent Limited until after the third anniversary of the date
of the change of ownership i.e. not before 1 September 2008. As the trades are similar, there should be little problem
in transferring work from that date onwards. -
第19题:
(ii) Advise Andrew of the tax implications arising from the disposal of the 7% Government Stock, clearly
identifying the tax year in which any liability will arise and how it will be paid. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Government stock is an exempt asset for the purposes of capital gains tax, however, as Andrew’s holding has a nominal
value in excess of £5,000, a charge to income tax will arise under the accrued income scheme. This charge to income
tax will arise in 2005/06, being the tax year in which the next interest payment following disposal falls due (20 April
2005) and it will relate to the income accrued for the period 21 October 2004 to 14 March 2005 of £279 (145/182
x £350). As interest on Government Stock is paid gross (unless the holder applies to receive it net), the tax due of £112
(£279 x 40%) will be collected via the self-assessment system and as the interest was an ongoing source of income
will be included within Andrew’s half yearly payments on account payable on 31 January and 31 July 2006. -
第20题:
(ii) The UK value added tax (VAT) implications for Razor Ltd of selling tools to and purchasing tools from
Cutlass Inc; (2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Value added tax (VAT)
Goods exported are zero-rated. Razor Ltd must retain appropriate documentary evidence that the export has taken place.
Razor Ltd must account for VAT on the value of the goods purchased from Cutlass Inc at the time the goods are brought
into the UK. The VAT payable should be included as deductible input tax on the company’s VAT return. -
第21题:
(c) Explanatory notes, together with relevant supporting calculations, in connection with the loan. (8 marks)
Additional marks will be awarded for the appropriateness of the format and presentation of the schedules, the
effectiveness with which the information is communicated and the extent to which the schedules are structured in
a logical manner. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and for the financial year
to 31 March 2007 apply throughout the question.
– you should ignore value added tax (VAT).
正确答案:
(c) Tax implications of there being a loan from Flores Ltd to Banda
Flores Ltd should have paid tax to HMRC equal to 25% of the loan, i.e. £5,250. The tax should have been paid on the
company’s normal due date for corporation tax in respect of the accounting period in which the loan was made, i.e. 1 April
following the end of the accounting period.
The tax is due because Flores Ltd is a close company that has made a loan to a participator and that loan is not in the ordinary
course of the company’s business.
HMRC will repay the tax when the loan is either repaid or written off.
Flores Ltd should have included the loan on Banda’s Form. P11D in order to report it to HMRC.
Banda should have paid income tax on an annual benefit equal to 5% of the amount of loan outstanding during each tax
year. Accordingly, for each full year for which the loan was outstanding, Banda should have paid income tax of £231
(£21,000 x 5% x 22%).
Interest and penalties may be charged in respect of the tax underpaid by both Flores Ltd and Banda and in respect of the
incorrect returns made to HMRC
Willingness to act for Banda
We would not wish to be associated with a client who has engaged in deliberate tax evasion as this poses a threat to the
fundamental principles of integrity and professional behaviour. Accordingly, we should refuse to act for Banda unless she is
willing to disclose the details regarding the loan to HMRC and pay the ensuing tax liabilities. Even if full disclosure is made,
we should consider whether the loan was deliberately hidden from HMRC or Banda’s previous tax adviser.
In addition, companies are prohibited from making loans to directors under the Companies Act. We should advise Banda to
seek legal advice on her own position and that of Flores Ltd. -
第22题:
(b) State the immediate tax implications of the proposed gift of the share portfolio to Avril and identify an
alternative strategy that would achieve Crusoe’s objectives whilst avoiding a possible tax liability in the
future. State any deadline(s) in connection with your proposed strategy. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Gift of the share portfolio to Avril
Inheritance tax
The gift would be a potentially exempt transfer at market value. No inheritance tax would be due at the time of the gift.
Capital gains tax
The gift would be a disposal by Crusoe deemed to be made at market value for the purposes of capital gains tax. No gain
would arise as the deemed proceeds will equal Crusoe’s base cost of probate value.
Stamp duty
There is no stamp duty on a gift of shares for no consideration.
Strategy to avoid a possible tax liability in the future
Crusoe should enter into a deed of variation directing the administrators to transfer the shares to Avril rather than to him. This
will not be regarded as a gift by Crusoe. Instead, provided the deed states that it is intended to be effective for inheritance tax
purposes, it will be as if Noland had left the shares to Avril in a will.
This strategy is more tax efficient than Crusoe gifting the shares to Avril as such a gift would be a potentially exempt transfer
and inheritance tax may be due if Crusoe were to die within seven years.
The deed of variation must be entered into by 1 October 2009, i.e. within two years of the date of Noland’s death. -
第23题:
(b) Provide the directors of Acrux Ltd with a detailed explanation of the maximum rate of tax that will be suffered
on both the distributed and non-distributed profits of the non-UK resident investee companies where:
(1) there is a double tax treaty between the UK and the country in which the individual companies are
resident; and
(2) there is no such double tax treaty.
Note: you are not required to explain the position of the overseas resident branches. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Rate of tax on profits of non-UK resident investee companies
Undistributed profits
The companies will be subject to tax in the countries in which they are resident; this is because of their residency status or
because they have a permanent establishment in that country. Undistributed profits will not be taxed in the UK.
The rate of tax on undistributed profits will therefore be the rate of tax in the country of residency of the respective companies.
Distributed profits with double tax treaty
The dividends received by Acrux Ltd from each of the overseas companies will be grossed up in respect of underlying tax (the
overseas corporation tax paid on the distributed profits) because Acrux Ltd will own at least 10% of the overseas companies.
The gross amount will then be included in Acrux Ltd’s profits chargeable to corporation tax.
The treaty will provide double tax relief in the UK for the overseas tax suffered in respect of each dividend up to a maximum
of the UK tax on the grossed up overseas dividend. As a result of the double tax relief, the overall rate of tax suffered will be
the higher of the UK rate paid by Acrux Ltd and the overseas tax rate borne by the overseas company.
Where the rate of overseas tax in respect of a particular dividend exceeds the rate of corporation tax in the UK, excess foreign
tax will arise. This can be relieved, via onshore pooling, against the UK tax due on those dividends where the rate of tax in
the UK exceeds the rate overseas. This will reduce the overall rate of tax suffered on the total overseas profits of the overseas
companies as a whole.
Distributed profits with no double tax treaty
Where there is no double tax treaty, unilateral double tax relief will be available in the UK. This relief will operate in the same
way as double tax relief under a double tax treaty such that the overall rate of tax on each dividend will be the higher of the
UK rate paid by Acrux Ltd and the overseas rate borne by the overseas company. Relief via onshore pooling will also be
available.
