(c) Identify and evaluate other strategic options ONA could consider to address the airline’s current financial andoperational weaknesses.Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks (10 marks)
题目
(c) Identify and evaluate other strategic options ONA could consider to address the airline’s current financial and
operational weaknesses.
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks (10 marks)
相似考题
更多“(c) Identify and evaluate other strategic options ONA could consider to address the airline’s current financial andoperational weaknesses.Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks (10 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Both divisions have recognised the need for a strategic alliance to help them achieve a successful entry into
European markets.
Critically evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of the divisions using strategic alliances to develop their
respective businesses in Europe. (15 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Johnson, Scholes and Whittington define a strategic alliance as ‘where two or more organisations share resources and
activities to pursue a strategy’. There are a number of types of alliance ranging from a formal joint venture through to networks
where there is collaboration but no formal agreement. The type of strategic alliance will be affected by how quickly market
conditions are changing – swift rates of change may require flexible less formal types of alliance and determine whether
specific dedicated resources are required or whether the partners can use existing resources. Johnson, Scholes and
Whittington argue that for an alliance to be successful there needs to be a clear strategic purpose and senior management
support; compatibility between the partners at all levels – this may be complicated if it is a cross-border alliance; time spent
defining and meeting performance expectations including clear goals, governance and organisational arrangements; and
finally trust both in terms of respective competences and trustworthiness.
6D–ENGAA
Paper 3.5
6D–ENGAA
Paper 3.5
The advantages that may be gained by a successful strategic alliance include creating a joint operation that has a ‘critical
mass’ that may lead to lower costs or an improved offer to the customer. It may also allow each partner to specialise in areas
where they have a particular advantage or competence. Interestingly, alliances are often entered into where a company is
seeking to enter new geographical markets, as is the case with both divisions. The partner brings local knowledge and
expertise in distribution, marketing and customer support. A good strategic alliance will also enable the partners to learn from
one another and develop competences that may be used in other markets. Often firms looking to develop an e-business will
use an alliance with a partner with experience in website development. Once its e-business is up and running a firm may
eventually decide to bring the website design skills in-house and acquire the partner.
Disadvantages of alliances range from over-dependence on the partner, not developing own core competences and a tendency
for them not to have a defined end date. Clearly there is a real danger of the partner eventually becoming a competitor.
In assessing the suitability for each division in using a strategic alliance to enter European markets one clearly has to analyse
the very different positions of the divisions in terms of what they can offer a potential partner. The earlier analysis suggests
that the Shirtmaster division may have the greater difficulty in attracting a partner. One may seriously question the feasibility
of using the Shirtmaster brand in Europe and the competences the division has in terms of manufacturing and selling to large
numbers of small independent UK clothing retailers would seem inappropriate to potential European partners. Ironically, if
the management consultant recommends that the Shirtmaster division sources some or all of its shirts from low cost
manufacturers in Europe this may provide a reason for setting up an alliance with such a manufacturer.
The prospects of developing a strategic alliance in the Corporate Clothing division are much more favourable. The division
has developed a value added service for its corporate customers, indeed its relationship with its customers can be seen as a
relatively informal network or alliance and there seems every chance this could be replicated with large corporate customers
in Europe. Equally, there may be European workwear companies looking to grow and develop who would welcome sharingthe Corporate Clothing division’s expertise. -
第2题:
(b) Assess the likely strategic impact of the new customer delivery system on Supaserve’s activities and its ability
to differentiate itself from its competitors. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Supaserve, through its electronic point of sale system (EPOS), is already likely to have useful information on the overall
patterns of buying behaviour in terms of products bought frequently, peak periods, etc. It is less likely to have detailed
information on individual customer purchase patterns, though it may be monitoring where its customers are living, travel
patterns, etc. The introduction of the new online system has the potential to have a major strategic impact on the company
and its relationship with its customers. Impact can be measured by assessing the significance of the change on the company’s
operations and the likelihood of its occurrence. In Michael Porter’s words, ‘the basic tool for understanding the influence of
information technology on companies is the value chain . . . and how it affects both a company’s cost and the value delivered
to buyers’.
Clearly the investment in Internet based technology will affect both the cost and revenue sides of the business. In terms of
operations the company will need to decide the way in which to integrate the new method of customer buying with its
traditional methods. Does it create a separate ‘dedicated’ warehouse operation solely involved with the online business or does
it integrate it within its existing operations? The customer will have immediate access to information on whether goods are in
stock or not, and this may have a significant impact on the procurement systems Supaserve has with its suppliers and the
inbound logistics which get the products to where they are needed for dispatch to the customers.
Online shopping will have a major impact on outbound logistics in that a totally new distribution process will have to be
created. The extent to which this new service is provided in-house by setting up a new activity within Supaserve, or
alternatively is outsourced to specialist distributors is a key decision affecting costs and efficiency. Supaserve’s delivery
performance will be both measurable and potentially available to competitors and a real source of competitive advantage or
disadvantage.
The new online system will have an immediate impact on marketing and sales. Can customers pay over the Internet?
Opportunities for direct marketing to individual customers are opened up and customisation becomes a real possibility.
Customers can link into after-sales services and provide insights into customer satisfaction. On the support side of the value
chain the impact on human resources may be profound and technology lies at the heart of the change. Above all there is a
key need to link the new strategy to the operational systems needed to deliver it.
Clearly, the introduction of the online shopping system offers an opportunity for Supaserve to differentiate itself from its
aggressive competitors. The online service, as suggested above, is likely to appeal to a limited but growing segment of its
customers. In strategic terms it is a focus differentiation strategy enabling Supaserve to provide an improved level of service
to its customers. For this customers are willing to pay a small premium. Perhaps the more significant impact on its profit
margins will be derived from improved levels of customer retention and the attraction of customers who formerly shopped
with its competitors. The ability to sustain its competitive advantage will be measured by the impact on its competitors and
their ability to introduce a similar service.
There are a number of useful models for assessing the impact of an IT related change. These could include the five forces
model and the frameworks developed by Michael Earl assessing the strategic impact of IT. Michael Earl argues persuasively
for the correct alignment between business strategy and IT strategy. Indeed he sees a need for a ‘binary approach’ with the
alignment of IT investment activities in existing ways of doing business as having to be accommodated with the IT investments
associated with more radical change to the ways business is conducted.
-
第3题:
(c) Discuss how the manipulation of financial statements by company accountants is inconsistent with their
responsibilities as members of the accounting profession setting out the distinguishing features of a
profession and the privileges that society gives to a profession. (Your answer should include reference to the
above scenario.) (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 marks for the quality of the discussion.
正确答案:
(c) Accounting and ethical implications of sale of inventory
Manipulation of financial statements often does not involve breaking laws but the purpose of financial statements is to present
a fair representation of the company’s position, and if the financial statements are misrepresented on purpose then this could
be deemed unethical. The financial statements in this case are being manipulated to show a certain outcome so that Hall
may be shown to be in a better financial position if the company is sold. The retained earnings of Hall will be increased by
$4 million, and the cash received would improve liquidity. Additionally this type of transaction was going to be carried out
again in the interim accounts if Hall was not sold. Accountants have the responsibility to issue financial statements that do
not mislead the public as the public assumes that such professionals are acting in an ethical capacity, thus giving the financial
statements credibility.
A profession is distinguished by having a:
(i) specialised body of knowledge
(ii) commitment to the social good
(iii) ability to regulate itself
(iv) high social status
Accountants should seek to promote or preserve the public interest. If the idea of a profession is to have any significance,
then it must make a bargain with society in which they promise conscientiously to serve the public interest. In return, society
allocates certain privileges. These might include one or more of the following:
– the right to engage in self-regulation
– the exclusive right to perform. particular functions
– special status
There is more to being an accountant than is captured by the definition of the professional. It can be argued that accountants
should have the presentation of truth, in a fair and accurate manner, as a goal. -
第4题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第5题:
(c) Critically evaluate Vincent Viola’s view that corporate governance provisions should vary by country.
(8 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Corporate governance provisions varying by country
There is a debate about the extent to which corporate governance provisions (in the form. of either written codes, laws or
general acceptances) should be global or whether they should vary to account for local differences. In this answer, Vincent
Viola’s view is critically evaluated.
In general terms, corporate governance provisions vary depending on such factors as local business culture, businesses’
capital structures, the extent of development of capital funding of businesses and the openness of stock markets. In Germany,
for example, companies have traditionally drawn much of their funding from banks thereby reducing their dependence on
shareholders’ equity. Stock markets in the Soviet Union are less open and less liquid than those in the West. In many
developing countries, business activity is concentrated among family-owned enterprises.
Against Vincent’s view
Although business cultures vary around the world, all business financed by private capital have private shareholders. Any
dilution of the robustness of provisions may ignore the needs of local investors to have their interests adequately represented.
This dilution, in turn, may allow bad practice, when present, to exist and proliferate.
Some countries suffer from a poor reputation in terms of endemic corruption and fraud and any reduction in the rigour with
which corporate governance provisions are implemented fail to address these shortcomings, notwithstanding the fact that they
might be culturally unexpected or difficult to implement.
In terms of the effects of macroeconomic systems, Vincent’s views ignore the need for sound governance systems to underpin
confidence in economic systems. This is especially important when inward investment needs are considered as the economic
wealth of affected countries are partly underpinned by the robustness, or not, of their corporate governance systems.
Supporting Vincent’s view
In favour of Vincent’s view are a number of arguments. Where local economies are driven more by small family businesses
and less by public companies, accountability relationships are quite different (perhaps the ‘family reasons’ referred to in the
case) and require a different type of accounting and governance.
There is a high compliance and monitoring cost to highly structured governance regimes that some developing countries may
deem unnecessary to incur.
There is, to some extent, a link between the stage of economic development and the adoption of formal governance codes.
It is generally accepted that developing countries need not necessarily observe the same levels of formality in governance as
more mature, developed economies.
Some countries’ governments may feel that they can use the laxity of their corporate governance regimes as a source of
international comparative advantage. In a ‘race to the bottom’, some international companies seeking to minimise the effects
of structured governance regimes on some parts of their operations may seek countries with less tight structures for some
operations.
-
第6题:
(c) Comment on four reasons why the Managing Director of Quicklink Ltd might consider the acquisition of the
Celer Transport business to be a ‘good strategic move’ insofar as may be determined from the information
provided. (5 marks)
正确答案: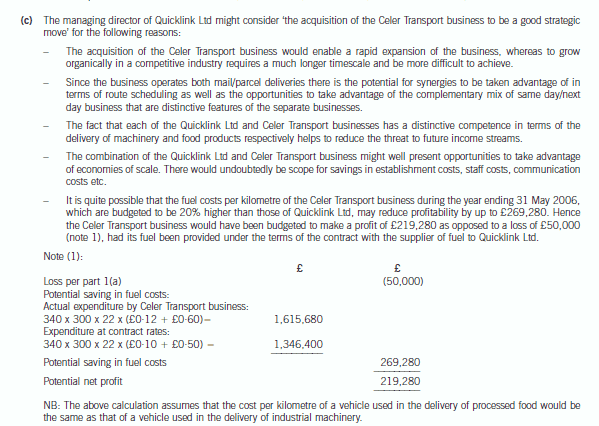
-
第7题:
Note: requirement (a) includes 4 professional marks.
A central feature of the performance measurement system at TSC is the widespread use of league tables that display
each depot’s performance relative to one another.
Required:
(b) Evaluate the potential benefits and problems associated with the use of ‘league tables’ as a means of
measuring performance. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) A central feature of many performance measurement systems is the widespread use of league tables that display each
business unit’s performance relative to one another. In the case of service organisations such as TSC the use of league tables
emphasises the company’s critical success factors of profitability and quality of service by reporting results on a weekly basis
at the depot level. The fact that such league tables are used by management will actively encourage competition, in terms of
performance, among depots. The individual position of a business unit in the league table is keenly observed both by the
manager of that unit and his/her peers.
In theory, performance is transparent. In practice although each depot performs essentially the same function and is subject
to the same modes of measurement, circumstances pertaining to different business units may vary significantly. Some depots
may be situated near to the hub (main distribution centre), some may be located far away and some may be in urban zones
with well developed road networks whilst others may be in remote rural areas. Measuring performance via a league table
makes no allowance whatsoever for these relative differences, hence, inequality is built into the performance measurement
system.
Moreover, depot managers might be held responsible for areas over which they have no formal control. The network nature
of the business suggests that there will be a high degree of interdependence of depots; the depot responsible for collection
will very often not be the depot responsible for delivery. Therefore, it is frequently the case that business may be gained for
which the collecting depot receives the revenue, but for which the delivering depot bears the cost. Obviously this impacts
upon the profit statements of both depots. The formal system might not recognise such difficulties, the corporate view being
that ‘the business needs to be managed’; the depots should therefore see any such anomalies as mild constraints to work
around rather than barriers to break down. In such circumstances delivering depots and collecting depots should discuss such
problems on an informal basis. Such informal discussions are aided by close communications between depots recognising
the interdependencies of the business. -
第8题:
(c) Your firm has provided financial advice to the Pholey family for many years and this has sometimes involved your
firm in carrying out transactions on their behalf. The eldest son, Esau, is to take up a position as a senior
government official to a foreign country next month. (4 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of these matters and state what
action, if any, Dedza should now take.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three situations
正确答案:
(c) Financial advisor
■ Customer due diligence (CDD) and record-keeping measures apply to designated non-financial businesses and
professions (such as Dedza) who prepare for or carry out certain transactions on behalf of their clients.
■ Esau is a ‘politically exposed person’ (‘PEP’) (i.e. an individual who is to be entrusted with prominent public functions
in a foreign country).
■ Dedza’s business relationships with Pholey therefore involve reputational risks similar to those with Esau. In addition
to performing normal due diligence measures Dedza should:
? have risk management systems to have determined that Esau is a PEP;
? obtain senior partner approval for maintaining business relationships with such customers;
? take reasonable measures to establish the source of wealth and source of funds;
? conduct enhanced ongoing monitoring of the business relationship.
■ Dedza can choose to decline to act for Pholey and/or Esau (if asked).
■ If the business relationship is to be continued senior partner approval should be obtained for any transactions carried
out on Pholey’s behalf in future.
Tutorial note: The Pholey family is not described as an audit client therefore no familiarity threat arises in relation to an
audit (the family may not have any involvement in entities requiring an audit). -
第9题:
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements is to
establish standards and provide guidance on the auditor’s responsibility to consider laws and regulations in an
audit of financial statements.
Explain the auditor’s responsibilities for reporting non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention
during the conduct of an audit. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 CLEEVES CO
(a) Reporting non-compliance
Non-compliance refers to acts of omission or commission by the entity being audited, either intentional or unintentional, that
are contrary to the prevailing laws or regulations.
To management
Regarding non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention the auditor should, as soon as practicable, either:
■ communicate with those charged with governance; or
■ obtain audit evidence that they are appropriately informed.
However, the auditor need not do so for matters that are clearly inconsequential or trivial and may reach agreement1 in
advance on the nature of such matters to be communicated.
If in the auditor’s judgment the non-compliance is believed to be intentional and material, the auditor should communicate
the finding without delay.
If the auditor suspects that members of senior management are involved in non-compliance, the auditor should report the
matter to the next higher level of authority at the entity, if it exists (e.g. an audit committee or a supervisory board). Where
no higher authority exists, or if the auditor believes that the report may not be acted upon or is unsure as to the person to
whom to report, the auditor would consider seeking legal advice.
To the users of the auditor’s report on the financial statements
If the auditor concludes that the non-compliance has a material effect on the financial statements, and has not been properly
reflected in the financial statements, the auditor expresses a qualified (i.e. ‘except for disagreement’) or an adverse opinion.
If the auditor is precluded by the entity from obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence to evaluate whether or not noncompliance
that may be material to the financial statements has (or is likely to have) occurred, the auditor should express a
qualified opinion or a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements on the basis of a limitation on the scope of the audit.
Tutorial note: For example, if management denies the auditor access to information from which he would be able to assess
whether or not illegal dumping had taken place (and, if so, the extent of it).
If the auditor is unable to determine whether non-compliance has occurred because of limitations imposed by circumstances
rather than by the entity, the auditor should consider the effect on the auditor’s report.
Tutorial note: For example, if new legal requirements have been announced as effective but the detailed regulations are not
yet published.
To regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor’s duty of confidentiality ordinarily precludes reporting non-compliance to a third party. However, in certain
circumstances, that duty of confidentiality is overridden by statute, law or by courts of law (e.g. in some countries the auditor
is required to report non-compliance by financial institutions to the supervisory authorities). The auditor may need to seek
legal advice in such circumstances, giving due consideration to the auditor’s responsibility to the public interest. -
第10题:
(b) With reference to CF Co, explain the ethical and other professional issues raised. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several issues that must be addressed as a matter of urgency:
Extra work must be planned to discover the extent of the breakdown in internal controls that occurred during the year. It is
important to decide whether the errors were isolated, or continued through the accounting period and whether similar errors
have occurred in other areas e.g. cash receipts from existing customers or cash payments. A review of the working papers of
the internal audit team should be carried out as soon as possible. The materiality of the errors should be documented.
Errors discovered in the accounting systems will have serious implications for the planned audit approach of new customer
deposits. Nate & Co must plan to expand audit testing on this area as control risk is high. Cash deposits will represent a
significant class of transaction in CF Co. A more detailed substantive approach than used in prior year audits may be needed
in this material area if limited reliance can be placed on internal controls.
A combination of the time spent investigating the reasons for the errors, their materiality, and a detailed substantive audit on
this area means that the audit is likely to take longer than previously anticipated. This may have cost and recoverability
implications. Extra staff may need to be assigned to the audit team, and the deadline for completion of audit procedures may
need to be extended. This will need to be discussed with CF Co.
Due to the increased audit risk, Nate & Co should consider increasing review procedures throughout the audit. In addition CF
Co is likely to be a highly regulated company as it operates in financial services, increasing possible attention focused on the
audit opinion. These two factors indicate that a second partner review would be recommended.
A separate issue is that of Jin Sayed offering advice to the internal audit team. The first problem raised is that of quality control.
A new and junior member of the audit team should be subject to close direction and supervision which does not appear to
have been the case during this assignment.
Secondly, Jin Sayed should not have offered advice to the internal audit team. On being made aware of the errors, he should
have alerted a senior member of the audit team, who then would have decided the action to be taken. This implies that he
does not understand the limited extent of his responsibilities as a junior member of the audit team. Nate & Co may wish to
review the training provided to new members of staff, as it should be made clear when matters should be reported to a senior,
and when matters can be dealt with by the individual.
Thirdly, Jin Sayed must be questioned to discover what exactly he advised the internal audit team to do. Despite his academic
qualification, he has little practical experience in the financial information systems of CF Co. He may have given inappropriate
advice, and it will be crucial to confirm that no action has been taken by the internal audit team.
The audit partner should consider if Nate & Co are at risk because of the advice that has been provided by Jin Sayed. As he
is a member of the audit team, his advice would be considered by the client as advice offered by Nate & Co, and the partner
should ascertain by discussion with the client whether this advice has been acted upon.
Finally Nate & Co should consider whether as a firm they could provide the review of the financial information technology
system, as requested by CF Co. IFAC’s Code of Ethics, and ACCA’s Code of Ethics and Conduct places restrictions on the
provision of non-audit services. Nate & Co must be clear in what exactly the ‘review’ will involve.
Providing a summary of weaknesses in the system, with appropriate recommendations is considered part of normal audit
procedures. However, given the errors that have arisen in the year, CF Co may require Nate & Co to design and implement
changes to the system. This would constitute a self-review threat and should only be considered if significant safeguards are
put in place, for example, using a separate team to provide the non-audit service and/or having a second partner review of
the work. -
第11题:
A new internal auditor, Daisy Rosepetal, has recently joined Bluebell Co. She has been asked by management to
establish and to monitor a variety of social and environmental Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Daisy has no
experience in this area, and has asked you for some advice. It has been agreed with Bluebell Co’s audit committee
that you are to provide guidance to Daisy to help her in this part of her role, and that this does not impair the
objectivity of the audit.
(c) Recommend EIGHT KPIs which could be used to monitor Bluebell Co’s social and environmental
performance, and outline the nature of evidence that should be available to provide assurance on the
accuracy of the KPIs recommended. Your answer should be in the form. of briefing notes to be used at a
meeting with Daisy Rosepetal. (10 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks.
正确答案:

-
第12题:
(c) Prepare briefing notes, to be used by an audit partner in your firm, assessing the professional, ethical and
other issues to be considered in deciding whether to proceed with the appointment as auditor of Medix Co.
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Briefing notes
To: Audit partner
From: Audit manager
Subject: Issues to consider regarding appointment as auditor of Medix Co
Introduction
Medix Co has recently invited our firm to become appointed as auditor. These briefing notes summarise the main issues we
should consider in deciding whether to take the appointment a stage further. My comments are based on a discussion held
with Ricardo Feller, finance director of Medix Co, a discussion with the current audit partner, and information provided in the
local newspaper.
Legal actions and investigations
There are several indications that Medix Co has a history of non compliance with law and regulations. The former finance
director is claiming unfair dismissal, and in the past the local authority has successfully taken legal action against the
company and has a current case pending. In addition, there have been two tax investigations in recent years hinting at noncompliance
with relevant tax regulations.
There are two problems for us in taking on a client with a propensity for legal actions and investigations. Firstly, the reputation
of the company must be considered. If we become associated with the company through being appointed as auditor, we could
be ‘tarred with the same brush’ and our own reputation also tarnished.
Secondly, we could become quickly exposed to an advocacy independence threat, which clearly should be avoided. Our
ethical status should not be compromised for the sake of gaining a new audit client. Mick Evans only ‘believes’ that the tax
matter has been resolved by the directors, and we should avoid taking on a new client which is involved in an on-going
investigation.
Public interest
The problems noted above are compounded by the bad publicity which the company is currently receiving. The local press
contained a recent article discussing Medix Co’s past and current breach of planning regulations. Given the current level of
public interest in environmental issues, and emphasis on corporate responsibility, it would seem that Medix Co has a poor
public perception, which we would not want to be associated with.
Potential liability to lender
The company is currently negotiating a significant bank loan, and the lender will be using the audited financial statements to
make a decision on whether to advance a loan, and the terms of any finance that might be advanced to Medix Co. This means
that our audit opinion for the forthcoming year end will be scrutinised by the lender, and our firm is exposed to a relatively
high risk of liability to a third party. Given that this will be our first audit, and the limited time we have available (discussed
below) our firm may feel that the risk of this audit engagement is too high. Should the appointment be accepted, disclaimers
should be put in place to ensure that we could not be sued in the event of the bank suffering a financial loss as a result of
their lending decision.
Timeframe. and resources
It is currently the last month of the financial year. If we are appointed as auditor we need to work quickly to develop a thorough
understanding of the business, and to begin to plan the assignment. We need to consider whether our firm has sufficient
resources to put together an audit team so quickly without detracting from other client work currently being conducted.
To make this matter worse, Mick Evans states that Medix Co likes ‘a quick audit’, and we need to consider how to manage
this expectation, as first year audit procedures such as systems documentation, and developing business understanding tend
to take a long time. We must be careful that the client does not pressure us into a ‘quick audit’, which could compromise
quality.
Medix Co operates in a reasonably specialist and highly regulated industry, so our firm should take care to ensure we have
expertise in this industry.
Potentially aggressive management style
There are several indicators that the management may take a confrontational approach, such as the unfair dismissal claim
brought against the company by the ex-finance director. In addition, the auditors prior to Mick Evans resigned following a
disagreement with management. This history shows that we may find it difficult to establish a good working relationship with
the management. As the company is owner managed the presence of a dominant managing director exacerbates this problem.
Management bias
There is incentive for the financial statements to be manipulated in order to secure bank finance. There is considerable risk
of material misstatement which our firm may consider to be unacceptably high.
Internal systems and controls
The current auditors have found systems and controls to be poor, and management has not acted upon recommendations
made by the auditors. Of course this does not mean that we should not take on the assignment – many companies have
weak controls. However, if we did take on the appointment, we would not be able to rely on controls or use a controls based
approach for the audit. We would need to take a substantive approach to the audit. One practical issue here is availability of
staff to conduct the audit testing, as substantive procedures tend to be more time consuming than if we could have taken a
systems based approach.
Opening balances
In all new audit assignments, work must be conducted to verify the opening balances. Given the possible fraud and poor
controls described above, we would need to perform. detailed testing on the opening balances as there is a high risk of fraud
and/or error in previous accounting periods. We may also wish to consider the competence of the previous auditors, who
appeared to disregard potential fraud indicator (two cash books) and had only one audit client.
Fees
Mick Evans has made it clear that Medix Co’s management likes to keep a tight control on costs, and it may put pressure on
us to charge a low audit fee. We need to bear in mind the risks associated with this engagement, as discussed above, and
only take on this high risk audit if the audit fee is high enough to compensate.
We should also consider the cash flow problems being experienced by the company. As a business we need to ensure that
we only take on clients with a good credit rating, and it seems that Medix Co, operating with an overdraft, may not be able
to pay our invoices.
Indication of fraud or money laundering
Surely the most serious issue to consider is that Jon Tate, the managing director, has kept two cash books. We need further
detail on this, but it clearly could indicate a fraud being perpetrated at the highest level of management. The fact that he has
maintained two cash books could indicate money laundering activites taking place, especially when considered in the context
of an owner-managed business with overseas operations. If this were the ONLY problem discovered it could be deemed
serious enough to bring to an end our appointment process. It would be reckless for our firm to take on a client where the
managing director is a fraudster.
Conclusion
Further information is needed in many areas before a final decision is made. However, from the information we have gathered
so far, it appears that Medix Co would represent a high risk client, and our firm must therefore be very careful to assess each
problem noted above before deciding whether to proceed with the appointment. -
第13题:
(c) What changes to Churchill’s existing marketing mix will be needed to achieve the three strategic goals?
(15 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Each of the strategic goals will have a profound impact on the marketing mix as it currently exists. As each goal affects the
market position of Churchill developing an appropriate marketing mix will be the key to successful implementation of the
overall growth strategy. The product, the brand and the reputation it creates are at the heart of the company’s marketing
strategy. Their focus on the premium segment of the market seems a sensible one and one which allows a small family-owned
business to survive and grow slowly. Evidence suggests this is a luxury indulgence market reflecting changing consumer tastes
and lifestyles. Managing the product range will be a major marketing activity. While the core products may develop an almost
timeless quality there will be a need to respond to the product innovations introduced by its much larger competitors. The
company’s emphasis on the quality of its products resulting from the quality of its ingredients is at the heart of its competitive
advantage. Growing the product range will also bring the danger of under performing products and a consequent need to
divest such products. Packaging is likely to be a key part of the products’ appeal and will be an area where constant innovation
is important.
Pricing raises a number of issues. Why is Churchill’s core product priced at £1 less than its immediate competition? What is
the basis on which Churchill prices this product? Each of the methods of pricing has its advantages and disadvantages. Using
cost plus may create an illusion of security in that all costs are covered, but at the same time raises issues as to whether
relevant costs have been included and allocated. Should the company price in anticipation of cost reductions as volume
increases? Should the basis for pricing be what your competitors are charging? As a luxury product one would assume that
its demand is relatively price inelastic: a significant increase in price e.g. £1 would lead to only a small reduction in quantity
demanded. Certainly, profit margins would be enhanced to help provide the financial resources the company needs if it is to
grow. One interesting issue on pricing is the extent to which it is pursuing a price skimming or price penetration policy –
evidence from the scenario suggests more of a price skimming policy in line with the luxury nature of the product.
Place is an equally important issue – the vertical integration strategy of the company has led to company-owned shops being
the main way customers can buy the product. At the same time, this distribution strategy has led to Churchill’s sales being
largely confined to one region in the UK – although it is the most populous. If Churchill has a desire to grow, does it do this
through expanding the number of company owned and franchised outlets or look for other channels of distribution in
particular the increasingly dominant supermarket chains? Each distribution strategy will have significant implications for other
elements in the marketing mix and for the resources and capabilities required in the company.
Finally, promotion is an interesting issue for the company. The relatively recent appointment of a sales and marketing director
perhaps reflects a need to balance the previous dominance of the manufacturing side of the business. Certainly there is
evidence to suggest that John Churchill is not convinced of the need to advertise. There are some real concerns about how
the brand is developed and promoted. Certainly sponsorship is now seen as a key part of the firm’s promotional strategy. The
company has a good reputation but customer access to the product is fairly limited. Overall there is scope for the company
to critically review its marketing mix and implement a very different mix if it wants to grow.
The four Ps above are very much the ‘hard’ elements in the marketing mix and Churchill in its desire to grow will need toensure that the ‘softer’ elements of people, physical evidence and processes are aligned to its ambitious strategy. -
第14题:
(c) Discuss the ethical and social responsibilities of the Beth Group and whether a change in the ethical and
social attitudes of the management could improve business performance. (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks for development of the discussion of the ethical and social
responsibilities of the Beth Group.
正确答案:
(c) Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is concerned with business ethics and the company’s accountability to its stakeholders,
and about the way it meets its wider obligations. CSR emphasises the need for companies to adopt a coherent approach to
a range of stakeholders including investors, employees, suppliers, and customers. Beth has paid little regard to the promotion
of socially and ethically responsible policies. For example, the decision to not pay the SME creditors on the grounds that they
could not afford to sue the company is ethically unacceptable. Additionally, Beth pays little regard to local customs and
cultures in its business dealings.
The stagnation being suffered by Beth could perhaps be reversed if it adopted more environmentally friendly policies. The
corporate image is suffering because of its attitude to the environment. Environmentally friendly policies could be cost effective
if they help to increase market share and reduce the amount of litigation costs it has to suffer. The communication of these
policies would be through the environmental report, and it is critical that stakeholders feel that the company is being
transparent in its disclosures.
Evidence of corporate misbehaviour (Enron, World.com) has stimulated interest in the behaviour of companies. There has
been pressure for companies to show more awareness and concern, not only for the environment but for the rights and
interests of the people they do business with. Governments have made it clear that directors must consider the short-term
and long-term consequences of their actions, and take into account their relationships with employees and the impact of the
business on the community and the environment. The behaviour of Beth will have had an adverse effect on their corporate
image.
CSR requires the directors to address strategic issues about the aims, purposes, and operational methods of the organisation,
and some redefinition of the business model that assumes that profit motive and shareholder interests define the core purpose
of the company. The profits of Beth will suffer if employees are not valued and there is poor customer support.
Arrangements should be put in place to ensure that the business is conducted in a responsible manner. The board should
look at broad social and environmental issues affecting the company and set policy and targets, monitoring performance and
improvements.
-
第15题:
(b) Discuss how management’s judgement and the financial reporting infrastructure of a country can have a
significant impact on financial statements prepared under IFRS. (6 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Management judgement may have a greater impact under IFRS than generally was the case under national GAAP. IFRS
utilises fair values extensively. Management have to use their judgement in selecting valuation methods and formulating
assumptions when dealing with such areas as onerous contracts, share-based payments, pensions, intangible assets acquired
in business combinations and impairment of assets. Differences in methods or assumptions can have a major impact on
amounts recognised in financial statements. IAS1 expects companies to disclose the sensitivity of carrying amounts to the
methods, assumptions and estimates underpinning their calculation where there is a significant risk of material adjustment
to their carrying amounts within the next financial year. Often management’s judgement is that there is no ‘significant risk’
and they often fail to disclose the degree of estimation or uncertainty and thus comparability is affected.
In addition to the IFRSs themselves, a sound financial reporting infrastructure is required. This implies effective corporate
governance practices, high quality auditing standards and practices, and an effective enforcement or oversight mechanism.
Therefore, consistency and comparability of IFRS financial statements will also depend on the robust nature of the other
elements of the financial reporting infrastructure.
Many preparers of financial statements will have been trained in national GAAP and may not have been trained in the
principles underlying IFRS and this can lead to unintended inconsistencies when implementing IFRS especially where the
accounting profession does not have a CPD requirement. Additionally where the regulatory system of a country is not well
developed, there may not be sufficient market information to utilise fair value measurements and thus this could lead to
hypothetical markets being created or the use of mathematical modelling which again can lead to inconsistencies because of
lack of experience in those countries of utilising these techniques. This problem applies to other assessments or estimates
relating to such things as actuarial valuations, investment property valuations, impairment testing, etc.
The transition to IFRS can bring significant improvement to the quality of financial performance and improve comparability
worldwide. However, there are issues still remaining which can lead to inconsistency and lack of comparability with those
financial statements. -
第16题:
(d) Draft a letter for Tim Blake to send to WM’s investors to include the following:
(i) why you believe robust internal controls to be important; and
(ii) proposals on how internal systems might be improved in the light of the overestimation of mallerite at
WM.
Note: four professional marks are available within the marks allocated to requirement (d) for the structure,
content, style. and layout of the letter.
(16 marks)
正确答案:
You will be aware of the importance of accurate resource valuation to Worldwide Minerals (WM). Unfortunately, I have to
inform. you that the reserve of mallerite, one of our key minerals in a new area of exploration, was found to have been
overestimated after the purchase of a mine. It has been suggested that this information may have an effect on shareholder
value and so I thought it appropriate to write to inform. you of how the board intends to respond to the situation.
In particular, I would like to address two issues. It has been suggested that the overestimation arose because of issues with
the internal control systems at WM. I would firstly like to reassure you of the importance that your board places on sound
internal control systems and then I would like to highlight improvements to internal controls that we shall be implementing
to ensure that the problem should not recur.
(i) Importance of internal control
Internal control systems are essential in all public companies and Worldwide Minerals (WM) is no exception. If anything,
WM’s strategic position makes internal control even more important, operating as it does in many international situations
and dealing with minerals that must be guaranteed in terms of volume, grade and quality. Accordingly, your board
recognises that internal control underpins investor confidence. Investors have traditionally trusted WM’s management
because they have assumed it capable of managing its internal operations. This has, specifically, meant becoming aware
of and controlling known risks. Risks would not be known about and managed without adequate internal control
systems. Internal control, furthermore, helps to manage quality throughout the organisation and it provides
management with information on internal operations and compliance. These features are important in ensuring quality
at all stages in the WM value chain from the extraction of minerals to the delivery of product to our customers. Linked
to this is the importance of internal control in helping to expose and improve underperforming internal operations.
Finally, internal control systems are essential in providing information for internal and external reporting upon which, in
turn, investor confidence rests.
(ii) Proposals to improve internal systems at WM
As you may be aware, mineral estimation and measurement can be problematic, particularly in some regions. Indeed,
there are several factors that can lead to under or overestimation of reserves valuations as a result of geological survey
techniques and regional cultural/social factors. In the case of mallerite, however, the issues that have been brought to
the board’s attention are matters of internal control and it is to these that I would now like to turn.
In first instance, it is clear from the fact that the overestimate was made that we will need to audit geological reports at
an appropriate (and probably lower) level in the organisation in future.
Once a claim has been made about a given mineral resource level, especially one upon which investor returns might
depend, appropriate systems will be instituted to ask for and obtain evidence that such reserves have been correctly and
accurately quantified.
We will recognise that single and verbal source reports of reserve quantities may not necessarily be accurate. This was
one of the apparent causes of the overestimation of mallerite. A system of auditing actual reserves rather than relying
on verbal evidence will rectify this.
The purchase of any going concern business, such as the mallerite mine, is subject to due diligence. WM will be
examining its procedures in this area to ensure that they are fit for purpose in the way that they may not have been in
respect of the purchase of the mallerite mine. I will be taking all appropriate steps to ensure that all of these internal
control issues can be addressed in future.
Thank you for your continued support of Worldwide Minerals and I hope the foregoing goes some way to reassure you
that the company places the highest value on its investors and their loyalty.
Yours faithfully,
Tim Blake
Chairman -
第17题:
(b) Distinguish between strategic and operational risks, and explain why the secrecy option would be a source
of strategic risk. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Strategic and operational risks
Strategic risks
These arise from the overall strategic positioning of the company in its environment. Some strategic positions give rise to
greater risk exposures than others. Because strategic issues typically affect the whole of an organisation and not just one or
more of its parts, strategic risks can potentially concern very high stakes – they can have very high hazards and high returns.
Because of this, they are managed at board level in an organisation and form. a key part of strategic management.
Operational risks
Operational risks refer to potential losses arising from the normal business operations. Accordingly, they affect the day-to-day
running of operations and business systems in contrast to strategic risks that arise from the organisation’s strategic positioning.
Operational risks are managed at risk management level (not necessarily board level) and can be managed and mitigated by
internal control systems.
The secrecy option would be a strategic risk for the following reasons.
It would radically change the environment that SHC is in by reducing competition. This would radically change SHC’s strategic
fit with its competitive environment. In particular, it would change its ‘five forces’ positioning which would change its risk
profile.
It would involve the largest investment programme in the company’s history with new debt substantially changing the
company’s financial structure and making it more vulnerable to short term liquidity problems and monetary pressure (interest
rates).
It would change the way that stakeholders view SHC, for better or worse. It is a ‘crisis issue’, certain to polarise opinion either
way.
It will change the economics of the industry thereby radically affecting future cost, revenue and profit forecasts.
There may be retaliatory behaviour by SHC’s close competitor on 25% of the market.
[Tutorial note: similar reasons if relevant and well argued will attract marks] -
第18题:
(c) Excluding the number of complaints by patients, identify and briefly explain THREE quantitative
non-financial performance measures that could be used to assess the ‘quality of service’ provided by the
Dental Health Partnership. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) In order to assess the quality of patient care provided by the Dental Health Partnership the following performance measures
might be used:
– The percentage of ‘on time’ treatment of those patients who arrived prior to their appointment time would provide an
indication regarding the effectiveness of the scheduling of appointments by the Dental Health Partnership.
– the percentage of patient appointments which were re-arranged at the request of the Dental Health Partnership.
Rearranged appointments represent the provision of a lower level of service provision to clients who may, as a result,
switch to an alternative dental practice.
– the percentage of patients who return for treatment after their first appointment would provide an indication that they
were satisfied with the service they received.
– the percentage of patients who were able to gain an appointment at their preferred date and time is an indication of the
availability of the service to clients.
Note: Candidates were only required to discuss three measures. -
第19题:
(ii) Compute the annual income tax saving from your recommendation in (i) above as compared with the
situation where Cindy retains both the property and the shares. Identify any other tax implications
arising from your recommendation. Your answer should consider all relevant taxes. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第20题:
(b) Identify and explain the financial statement risks to be taken into account in planning the final audit.
(12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Tutorial note: Note the timeframe. Financial statements for the year to 30 June 2006 are draft. Certain misstatements
may therefore exist due to year-end procedures not yet having taken place.
Revenue/(Receivables)
■ Revenue has increased by 11·8% ((161·5 – 144·4)/144·4 × 100). Overstatement could arise if rebates due to customers
have not yet been accounted for in full (as they are calculated in arrears). If rebates have still to be accounted for trade
receivables will be similarly overstated.
Materials expense
■ Materials expense has increased by 17·8% ((88.0 – 74·7)/74·7 × 100). This is more than the increase in revenue. This
could be legitimate (e.g. if fuel costs have increased significantly). However, the increase could indicate misclassification
of:
– revenue expenditure (see fall in other expenses below);
– capital expenditure (e.g. on overhauls or major refurbishment) as revenue;
– finance lease payments as operating lease.
Depreciation/amortisation
■ This has fallen by 10·5% ((8·5 – 9·5)/9·5 × 100). This could be valid (e.g. if Yates has significant assets already fully
depreciated or the asset base is lower since last year’s restructuring). However, there is a risk of understatement if, for
example:
– not all assets have been depreciated (or depreciated at the wrong rates, or only for 11 months of the year);
– cost of non-current assets is understated (e.g. due to failure to recognise capital expenditure)1;
– impairment losses have not been recognised (as compared with the prior year).
Tutorial note: Depreciation on vehicles and transport equipment represents only 7% of cost. If all items were being
depreciated on a straight-line basis over eight years this should be 12·5%. The depreciation on other equipment looks more
reasonable as it amounts to 14% which would be consistent with an average age of vehicles of seven years (i.e. in the middle
of the range 3 – 13 years).
Other expenses
■ These have fallen by 15·5% ((19·6 – 23·2)/23·2 × 100). They may have fallen (e.g. following the restructuring) or may be
understated due to:
– expenses being misclassified as materials expense;
– underestimation of accrued expenses (especially as the financial reporting period has not yet expired).
Intangibles
■ Intangible assets have increased by $1m (16% on the prior year). Although this may only just be material to the
financial statements as a whole (see (a)) this is the net movement, therefore additions could be material.
■ Internally-generated intangibles will be overstated if:
– any of the IAS 38 recognition criteria cannot be demonstrated;
– any impairment in the year has not yet been written off in accordance with IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’.
Tangible assets
■ The net book value of property (at cost) has fallen by 5%, vehicles are virtually unchanged (increased by just 2·5%)
and other equipment (though the least material category) has fallen by 20·4%.
■ Vehicles and equipment may be overstated if:
– disposals have not been recorded;
– depreciation has been undercharged (e.g. not for a whole year);
– impairments have not yet been accounted for.
■ Understatement will arise if finance leases are treated as operating leases.
Receivables
■ Trade receivables have increased by just 2·2% (although sales increased by 11·8%) and may be understated due to a
cutoff error resulting in overstatement of cash receipts.
■ There is a risk of overstatement if sufficient allowances have not been made for the impairment of individually significant
balances and for the remainder assessed on a portfolio or group basis.
Restructuring provision
■ The restructuring provision that was made last year has fallen/been utilised by 10·2%. There is a risk of overstatement
if the provision is underutilised/not needed for the purpose for which it was established.
Finance lease liabilities
■ Although finance lease liabilities have increased (by $1m) there is a greater risk of understatement than overstatement
if leased assets are not recognised on the balance sheet (i.e. capitalised).
■ Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 17 ‘Leases’ (e.g. in respect of minimum lease payments) are not met.
Trade payables
■ These have increased by only 5·3% compared with the 17·8% increase in materials expense. There is a risk of
understatement as notifications (e.g. suppliers’ invoices) of liabilities outstanding at 30 June 2006 may have still to be
received (the month of June being an unexpired period).
Other (employee) liabilities
■ These may be understated as they have increased by only 7·5% although staff costs have increased by 14%. For
example, balances owing in respect of outstanding holiday entitlements at the year end may not yet be accurately
estimated.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given to other financial statements risks specific to the scenario. For example, ‘time-sensitive
delivery schedules’ might give rise to penalties or claims, that could result in understated provisions or undisclosed
contingent liabilities. Also, given that this is a new audit and the result has changed significantly (from loss to profit) might
suggest a risk of misstatement in the opening balances (and hence comparative information).
1 Tutorial note: This may be unlikely as other expenses have fallen also. -
第21题:
(d) Discuss the professional accountant’s liability for reporting on prospective financial information and the
measures that the professional accountant might take to reduce that liability. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Professional accountant’s liability
Liability for reporting on PFI
Independent accountants may be required to report on PFI for many reasons (e.g. to help secure a bank loan). Such forecasts
and projections are inherently unreliable. If the forecast or projection does not materialise, and the client or lenders (or
investors) consequently sustain financial loss, the accountant may face lawsuits claiming financial loss.
Courts in different jurisdictions use various criteria to define the group of persons to whom independent accountants may be
held liable for providing a report on an inaccurate forecast or projection. The most common of these are that an accountant
is liable to persons with whom there is proximity:
(i) only (i.e. the client who engaged the independent accountant);
(ii) or whose relationship with the accountant sufficiently approaches privity;
(iii) and to persons or members of a limited group of persons for whose benefit and guidance the accountant supplied the
information or knew that the recipient of the information intended to supply it;
(iv) and to persons who reasonably can be foreseen to rely on the information.
Measures to reduce liability
As significant assumptions will be essential to a reader’s understanding of a financial forecast, the independent accountant
should ensure that they are adequately disclosed and clearly stated to be the management’s responsibility. Hypothetical
assumptions should be clearly distinguished from best estimates.
The introduction to any forecast (and/or report thereon) should include a caveat that the prospective results may not be
attained. Specific and extensive warnings (‘the actual results … will vary’) and disclaimers (‘we do not express an opinion’)
may be effective in protecting an independent accountant sued for inaccuracies in forecasts or projections that they have
reported on.
Any report to a third party should state:
■ for whom it is prepared, who is entitled to rely on it (if anyone) and for what purpose;
■ that the engagement was undertaken in accordance with the engagement terms;
■ the work performed and the findings.
An independent accountant’s report should avoid inappropriate and open-ended wording, for example, ‘we certify …’ and ‘we
obtained all the explanations we considered necessary’.
Engagement terms to report on PFI should include an appropriate liability cap that is reasonable given the specific
circumstances of the engagement.
The independent accountant may be able to obtain indemnity from a client in respect of claims from third parties. Such ‘hold
harmless’ clauses obligate the client to indemnify the independent accountant from third party claims. -
第22题:
(c) Identify and discuss the ethical and professional matters raised at the inventory count of LA Shots Co.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) There are several ethical and professional issues raised in relation to the inventory count of LA Shots Co.
Firstly, it was inappropriate of Brenda Mangle to offer the incentive to the audit juniors. As she is a new manager, it may be
that she didn’t realise how the incentive would be perceived. Brenda should be informed that her actions could have serious
implications.
The offer could be viewed as a bribe of the audit juniors, and could be perceived as a self-interest independence threat as
there is a financial benefit offered to members of the audit team.
The value of the ten bottles of ‘Super Juice’ should be considered, as it is only appropriate for a member of the audit team to
accept any goods or hospitality from the audit client if the value is ‘clearly insignificant’. Ultimately it would be the decision
of the audit partner as to whether the value is clearly insignificant. It is likely that this does not constitute a significant threat
to independence, however the offer should still be referred to the audit partner.
Also, if the juniors took ten bottles of ‘Super Juice’, this could interfere with the physical count of goods and/or with cut off
details obtained at the count. The juniors should therefore have declined the offer and informed a senior member of the audit
team of the situation.
There may be a need to adequately train new members of staff on ethical matters if the juniors were unsure of how to react
to the offer.
The work performed by the juniors at the inventory count must be reviewed. The audit procedures were performed very
quickly compared to last year and therefore sufficient evidence may not have been gathered. In an extreme situation the whole
inventory count may have to be reperformed if it is found that the procedures performed cannot be relied upon.
In addition, the juniors should not have attended the audit client’s office party without the permission of the audit manager.
The party appears to have taken place during work time, when the juniors should have been completing the inventory count
procedures. The two juniors have not acted with due professional consideration, and could be considered to lack integrity.
The actions of the juniors should be discussed with them, possibly with a view to disciplinary action.
There may also be questions over whether the direction and supervision of the juniors was adequate. As the two juniors are
both recent recruits, this is likely to be the first inventory count that they have attended. It appears that they may not have
been adequately briefed as to the importance of the inventory count as a source of audit evidence, or that they have
disregarded any such briefing that was provided to them. In either case possibly a more senior auditor should have
accompanied them to the inventory count and supervised their actions. -
第23题:
(ii) Identify and explain the potential financial statement risks caused by the breach of planning regulations
discussed in the press cutting. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Several significant financial statement risks are indicated by the press cutting.
Overstatement of property, plant and equipment
Medix Co has constructed a research laboratory which is likely to be impaired at the year end. The local authority has
the power to shut down the facility, and it is clear from the press cutting that this is likely to happen before the year end.
Following IAS 36 Impairment of Assets, the premises should be written down to recoverable amount, and the
impairment loss recognised as an expense. The directors should carry out an impairment review before the year end. If
the premises cannot be used as intended then the recoverable amount (measured using the higher of value in use and
fair value less selling cost) is likely to be less than current carrying value. In this case, assuming the local authority is
successful in shutting down the research laboratory, the recoverable amount is likely to be nil, as the premises have no
value in use, as it will never be used commercially, and has no market value as it is likely to be demolished.
In addition, any tangible assets such as laboratory equipment located at the premises should be tested for impairment
as if the company cannot use the premises then the assets contained within it are likely to have a lower recoverable
amount than carrying value.
Contingency – fines or penalties imposed by local authority
The press cutting indicates that Medix Co has been sued before, and that the local authority may again take legal action
against the company. IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets states that a provision should be
recognised if the company has a probable obligation at the year end which can be measured reliably. If payment is
deemed only possible at the year end, then disclosure of the contingent liability should be made in a note to the financial
statements.
If the local authority commences legal proceedings against Medix Co before the year end of 30 June 2008, then
management should assess the probability of payment. The financial statement risk is not recognising a provision (and
associated expense within the income statement), or not disclosing a contingency.
Demolition costs
The local authority may require Medix Co to demolish the premises. If this demand is made before the year end, Medix
Co should recognise a provision for demolition costs as an unavoidable legal obligation would have been created. The
financial statement risk is that in this situation, Medix Co fails to recognise a provision and associated expense within
the income statement.
Going concern
The above issues could indicate that the company may not continue in operational existence. The potential lack of
disclosure of these issues represents a financial statement risk.
