(ii) ‘job description’. (4 marks)
题目
(ii) ‘job description’. (4 marks)
相似考题
更多“(ii) ‘job description’. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(ii) the panel interview with more than one interviewer. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Panel interviews are often used for senior appointments and consist of two or more interviewers.The advantages of such interviews are that they allow opinion and views to be shared amongst the panel. They provide a more complete and coherent approach, hence problems of bias inherent in face to face interviews can be reduced.
They may also be appropriate where an individual with specialist or technical skills has to support the interviewer in relation to assessing the technical competencies of the interviewee.The disadvantages are that panel interviews can be difficult to control, interviewers may deviate or ask irrelevant questions and they can be easily dominated by a strong personality who is able unduly to influence others. In addition,
such interviews can often result in disagreement amongst the panel members. -
第2题:
(ii) job enlargement; (5 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Job enlargement is often referred to as ‘horizontal job enlargement’ and is aimed at widening the content of jobs by increasing the number of operations in which the job holder is involved and is another method by which employees at Bailey’s might become more involved. It reduces the level of repetition and dullness by providing a horizontal extension to activity, reducing monotony and boredom inherent in the operations at Bailey’s.
-
第3题:
(ii) Analyse why moving to a ‘no frills’ low-cost strategy would be inappropriate for ONA.
Note: requirement (b) (ii) includes 3 professional marks (16 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) ‘No frills’ low-cost budget airlines are usually associated with the following characteristics. Each of these characteristics
is considered in the context of Oceania National Airlines (ONA).
– Operational economies of scale
Increased flight frequency brings operational economies and is attractive to both business and leisure travellers. In
the international sector where ONA is currently experiencing competition from established ‘no frills’ low-cost budget
airlines ONA has, on average, one flight per day to each city. It would have to greatly extend its flight network, flight
frequency and the size of its aircraft fleet if it planned to become a ‘no frills’ carrier in this sector. This fleet
expansion appears counter to the culture of an organisation that has expanded very gradually since its formation.
Table 1 shows only three aircraft added to the fleet in the period 2004–2006. It is likely that the fleet size would
have to double for ONA to become a serious ‘no frills’ operator in the international sector. In the regional sector, the
flight density, an average of three flights per day, is more characteristic of a ‘no frills’ airline. However, ONA would
have to address the relatively low utilisation of its aircraft (see Tables 1 and 2) and the cost of maintenance
associated with a relatively old fleet of aircraft.
– Reduced costs through direct sales
On-line booking is primarily aimed at eliminating commission sales (usually made through travel agents). ‘No frills’
low-cost budget airlines typically achieve over 80% of their sales on-line. The comparative figure for ONA (see
Table 2) is 40% for regional sales and 60% for international sales, compared with an average of 84% for their
competitors. Clearly a major change in selling channels would have to take place for ONA to become a ‘no frills’
low-cost budget airline. It is difficult to know whether this is possible. The low percentage of regional on-line sales
seems to suggest that the citizens of Oceania may be more comfortable buying through third parties such as travel
agents.
– Reduced customer service
‘No frills’ low-cost budget airlines usually do not offer customer services such as free meals, free drinks and the
allocation of passengers to specific seats. ONA prides itself on its in-flight customer service and this was one of the
major factors that led to its accolade as Regional Airline of the Year. To move to a ‘no frills’ strategy, ONA would
have to abandon a long held tradition of excellent customer service. This would require a major cultural change
within the organisation. It would also probably lead to disbanding the award winning (Golden Bowl) catering
department and the redundancies of catering staff could prove difficult to implement in a heavily unionised
organisation.
Johnson, Scholes and Whittington have suggested that if an organisation is to ‘achieve competitive advantage through
a low price strategy then it has two basic choices. The first is to try and identify a market segment which is unattractive
(or inaccessible) to competitors and in this way avoid competitive pressures to erode price.’ It is not possible for ONA to
pursue this policy in the international sector because of significant competition from established continental ‘no frills’
low-cost budget airlines. It may be a candidate strategy for the regional sector, but the emergence of small ‘no frills’ lowcost
budget airlines in these countries threaten this. Many of these airlines enter the market with very low overheads
and use the ‘no frills’ approach as a strategy to gain market share before progressing to alternative strategies.
Secondly, a ‘no frills’ strategy depends for its success on margin. Johnson, Scholes and Whittington suggest that ‘in the
long run, a low price strategy cannot be pursued without a low-cost base’. Evidence from the scenario suggests that ONA
does not have a low cost base. It continues to maintain overheads (such as a catering department) that its competitors
have either disbanded or outsourced. More fundamentally (from Table 2), its flight crew enjoy above average wages and
the whole company is heavily unionised. The scenario acknowledges that the company pays above industry salaries and
offers excellent benefits such as a generous non-contributory pension. Aircraft utilisation and aircraft age also suggest a
relatively high cost base. The aircraft are older than their competitors and presumably incur greater maintenance costs.
ONA’s utilisation of its aircraft is also lower than its competitors. It seems highly unlikely that ONA can achieve the
changes required in culture, cost base and operations required for it to become a ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airline. Other
factors serve to reinforce this. For example:
– Many ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airlines fly into airports that offer cheaper taking off and landing fees. Many of these
airports are relatively remote from the cities they serve. This may be acceptable to leisure travellers, but not to
business travellers – ONA’s primary market in the regional sector.
– Most ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airlines have a standardised fleet leading to commonality and familiarity in
maintenance. Although ONA has a relatively small fleet it is split between three aircraft types. This is due to
historical reasons. The Boeing 737s and Airbus A320s appear to be very similar aircraft. However, the Boeings
were inherited from OceaniaAir and the Airbuses from Transport Oceania.
In conclusion, the CEO’s decision to reject a ‘no frills’ strategy for ONA appears to be justifiable. It would require major
changes in structure, cost and culture that would be difficult to justify given ONA’s current position. Revolution is the
term used by Baligan and Hope to describe a major rapid strategic change. It is associated with a sudden transformation
required to react to extreme pressures on the organisation. Such an approach is often required when the company is
facing a crisis and needs to quickly change direction. There is no evidence to support the need for a radical
transformation. This is why the CEO brands the change to a ‘no frills’ low-cost budget airline as ‘unnecessary’. The
financial situation (Table 3) is still relatively healthy and there is no evidence of corporate predators. It can be argued
that a more incremental approach to change would be beneficial, building on the strengths of the organisation and the
competencies of its employees. Moving ONA to a ‘no frills’ model would require seismic changes in cost and culture. If
ONA really wanted to move into this sector then they would be better advised to start afresh with a separate brand andairline and to concentrate on the regional sector where it has a head start over many of its competitors. -
第4题:
(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements of
Ambush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) There is objective evidence of impairment because of the financial difficulties and reorganisation of Bromwich. The
impairment loss on the loan will be calculated by discounting the estimated future cash flows. The future cash flows
will be $100,000 on 30 November 2007. This will be discounted at an effective interest rate of 8% to give a present
value of $85,733. The loan will, therefore, be impaired by ($200,000 – $85,733) i.e. $114,267.
(Note: IAS 39 requires accrual of interest on impaired loans at the original effective interest rate. In the year to
30 November 2006 interest of 8% of $85,733 i.e. $6,859 would be accrued.)
-
第5题:
(ii) Explain why the disclosure of voluntary information in annual reports can enhance the company’s
accountability to equity investors. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Accountability to equity investors
Voluntary disclosures are an effective way of redressing the information asymmetry that exists between management and
investors. In adding to mandatory content, voluntary disclosures give a fuller picture of the state of the company.
More information helps investors decide whether the company matches their risk, strategic and ethical criteria, and
expectations.
Makes the annual report more forward looking (predictive) whereas the majority of the numerical content is backward
facing on what has been.
Helps transparency in communicating more fully thereby better meeting the agency accountability to investors,
particularly shareholders.
There is a considerable amount of qualitative information that cannot be conveyed using statutory numbers (such as
strategy, ethical content, social reporting, etc).
Voluntary disclosure gives a more rounded and more complete view of the company, its activities, strategies, purposes
and values.
Voluntary disclosure enables the company to address specific shareholder concerns as they arise (such as responding
to negative publicity).
[Tutorial note: other valid points will attract marks] -
第6题:
(ii) Explain the ethical tensions between these roles that Anne is now experiencing. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Tensions in roles
On one hand, Anne needs to cultivate and manage her relationship with her manager (Zachary) who seems convinced
that Van Buren, and Frank in particular, are incapable of bad practice. He shows evidence of poor judgment and
compromised independence. Anne must decide how to deal with Zachary’s poor judgment.
On the other hand, Anne has a duty to both the public interest and the shareholders of Van Buren to ensure that the
accounts do contain a ‘true and fair view’. Under a materiality test, she may ultimately decide that the payment in
question need not hold up the audit signoff but the poor client explanation (from Frank) is also a matter of concern to
Anne as a professional accountant. -
第7题:
(ii) Service quality; and (7 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Quality of service is the totality of features and characteristics of the service package that bear upon its ability to satisfy
client needs. To some extent the number of complaints and the need to provide non-chargeable consultations associated
with the remedying of those complaints is indicative of a service quality problem that must be addressed. Hence this
problem needs to be investigated at the earliest opportunity. Assuming consultants could have otherwise undertaken
chargeable work, the revenue foregone as a consequence of the remedial consultations relating to commercial work
amounted to (180 x £1500) = £27,000. Client complaints received by HLP during the year amounted to 1·24% of
consultations undertaken by commercial advisors whereas none were budgeted. In contrast, competitor MAS received
135 complaints which coincided with the number of non-chargeable consultations undertaken by them. This may
indicate that MAS operate a policy of a remedial consultation in respect of all complaints received from clients.
With regard to the number of on-time consultations, HLP only achieved an on-time consultation percentage of 94·4%
which is far inferior to that of 99% achieved by competitor MAS. Also, HLP re-scheduled the appointment times of
1,620 (3%) of its total consultations whereas competitor MAS only re-scheduled 0·5% of its consultation times. The
percentage number of successful consultations provided by HLP and MAS was 85% and 95% respectively which
indicates that competitor MAS possesses a superior skills-base to that of HLP.
The most alarming statistic lies in the fact that HLP was subject to three successful legal actions for negligence. This
may not only account for the 150% increase in the cost of professional indemnity insurance premiums but may also
result in a loss of client confidence and precipitate a considerable fall in future levels of business should the claims
become much publicised. -
第8题:
(ii) equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue; and (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
Tutorial note: In the context of GVF, the principal issue to be addressed is whether or not the impairment loss previously
recognised should be reversed (by considering the determination of value in use). Marks will also be awarded for
consideration of depreciation, additions etc made specific to this equipment.
■ Agree cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses at the beginning of the year to prior year working
papers (and/or last year’s published financial statements).
■ Recalculate the current year depreciation charge based on the carrying amount (as reduced by the impairment
loss).
■ Calculate the carrying amount of the equipment as at 30 September 2005 without deduction of the impairment
loss.
Tutorial note: The equipment cannot be written back up to above this amount (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ Agree management’s schedule of future cash flows estimated to be attributable to the equipment for a period of up
to five years (unless a longer period can be justified) to approved budgets and forecasts.
■ Recalculate:
– on a sample basis, the make up of the cash flows included in the forecast;
– GVF’s weighted average cost of capital.
■ Review production records and sales orders for the year, as compared with the prior period, to confirm a ‘steady
increase’.
■ Compare sales volume at 30 September 2005 with the pre-‘scare’ level to assess how much of the previously
recognised impairment loss it would be prudent to write back (if any).
■ Scrutinize sales orders in the post balance sheet event period. Sales of such produce can be very volatile and
another ‘incident’ could have sales plummeting again – in which case the impairment loss should not be reversed. -
第9题:
(ii) Describe the procedures to verify the number of serious accidents in the year ended 30 November 2007.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Procedures to verify the number of serious accidents during 2007 could include the following:
Tutorial note: procedures should focus on the completeness of the disclosure as it is in the interest of Sci-Tech Co to
understate the number of serious accidents.
– Review the accident log book and count the total number of accidents during the year
– Discuss the definition of ‘serious accident’ with the directors and clarify exactly what criteria need to be met to
satisfy the definition
– For serious accidents identified:
? review HR records to determine the amount of time taken off work
? review payroll records to determine the financial amount of sick pay awarded to the employee
? review correspondence with the employee regarding the accident.
Tutorial note: the above will help to clarify that the accident was indeed serious.
– Review board minutes where the increase in the number of serious accidents has been discussed
– Review correspondence with Sci-Tech Co’s legal advisors to ascertain any legal claims made against the company
due to accidents at work
– Enquire as to whether any health and safety visits have been conducted during the year by regulatory bodies, and
review any documentation or correspondence issued to Sci-Tech Co after such visits.
Tutorial note: it is highly likely that in a regulated industry such as pharmaceutical research, any serious accident
would trigger a health and safety inspection from the appropriate regulatory body.
– Discuss the level of accidents with representatives of Sci-Tech Co’s employees to reach an understanding as to
whether accidents sometimes go unreported in the accident log book. -
第10题:
(ii) State the principal audit procedures to be performed on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Audit procedures on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group:
– Agree correct extraction of individual company figures by reference to individual company audited financial
statements.
– Cast and cross cast all consolidation schedules.
– Recalculate all consolidation adjustments, including goodwill, elimination of pre acquisition reserves, cancellation
of intercompany balances, fair value adjustments and accounting policy adjustments.
– By reference to prior year audited consolidated accounts, agree accounting policies have been consistently applied.
– Agree brought down figures to prior year audited consolidated accounts and audit working papers (e.g. goodwill
figures for Timber Co and Ben Co, consolidated reserves).
– Agree that any post acquisition profits consolidated for Dylan Co arose since the date of acquisition by reference to
date of control passing per the purchase agreement.
– Reconcile opening and closing group reserves and agree reconciling items to group financial statements. -
第11题:
A well () job description can answer a lot of questions from job seekers.A.written
B.write
C.wrote
正确答案:A
-
第12题:
单选题To be successful in our training program, we must understand the difference between _____.Aa job description and a job specification
Bwhat is taught and how it is taught
Clearning about skills and training in using them
Dthe savings in time and the savings in cost
正确答案: B解析:
由第三段第二句“Successful training programs depend on an understanding of the difference between learning about skills and training in using them”可知,C项符合题意要求。 -
第13题:
(d) Job rotation. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Job rotation is an important training method and is often also seen as a means of motivation. It involves moving the trainee from one job to another and is therefore more suitable for lower level employees. The trainee is required to do different jobs in logical succession, thus broadening experience and gaining a picture of the organisation’s wider activities.
-
第14题:
(ii) Theory Y. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Theory Y is at the opposite end of the continuum and reflects a contemporary approach to motivation, reflecting growth in professional and service employment. It is based on the idea that the goals of the individual and the organsiation can– indeed should – be integrated and that personal fulfilment can be achieved through the workplace. It assumes that for most people, work is as natural as rest or play and employees will exercise self-discipline and self-direction in helping to achieve the organisation’s objectives. Physical and mental effort at work is perfectly natural and is actively sought as a source of personal satisfaction.
In addition, the average employee seeks and accepts responsibilty and creativity. Innovative thinking is widely distributed amongst the whole population and should therefore be encouraged in the work situation.
The intellectual ability of the average person is only partly used and should be encouraged and thus individuals are motivated by seeking self-achievement. Since control and punishment are not required, management therefore has to encourage and develop the individual. However, the operation of a Theory Y approach can be difficult and frustrating,time consuming and sometimes regarded with suspicion.
-
第15题:
(ii) Describe the basis for the calculation of the provision for deferred taxation on first time adoption of IFRS
including the provision in the opening IFRS balance sheet. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) A company has to apply IAS12 to the temporary differences between the carrying amount of the assets and liabilities in
its opening IFRS balance sheet (1 November 2003) and their tax bases (IFRS1 ‘First time adoption of IFRS’). The
deferred tax provision will be calculated using tax rates that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance
sheet date. The carrying values of the assets and liabilities at the opening balance sheet date will be determined by
reference to IFRS1 and will use the applicable IFRS in the first IFRS financial statements. Any adjustments required to
the deferred tax balance will be recognised directly in retained earnings.
Subsequent balance sheets (at 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005) will be drawn up using the IFRS used in the
financial statements to 31 October 2005. The deferred tax provision will be adjusted as at 31 October 2004 and thenas at 31 October 2005 to reflect the temporary differences arising at those dates. -
第16题:
(ii) the strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies. (3 marks)
(Marks will be awarded in part (b) for the identification and discussion of relevant points and for the style. of the
report.)
正确答案:
(ii) Strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies
Treasury policies are reviewed regularly by the Board. It is group policy to account for all financial instruments as cash
flow hedges. As a result, changes in the fair values of financial instruments are deferred in reserves to the extent the
hedge is effective and released to profit or loss in the time periods in which the hedged item impacts profit or loss.
The Group contracts fixed rate currency swaps and issues floating to fixed rate interest rate swaps to meet the objective
of protecting borrowing costs. The cash flow effects of the interest rate swaps match the cash flows on the underlying
instruments so that there is no net cash flow effect from movements in market interest rates. If the interest rate swaps
had not been transacted there could have been an increase in the annual net interest payable to the Group. The strategy
of the group is to minimise the exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
-
第17题:
(ii) Describe the claim of each of the four identified stakeholders. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Stakeholder claims
Four external stakeholders in the case and their claims are as follows.
The client, i.e. the government of the East Asian country. This stakeholder wants the project completed to budget and
on time. It may also be concerned to minimise negative publicity in respect of the construction of the dam and the
possible negative environmental consequences.
Stop-the-dam, the vocal and well organised pressure group. This stakeholder wants the project stopped completely,
seemingly and slightly paradoxically, for environmental and social footprint reasons.
First Nation, the indigenous people group currently resident on the land behind the dam that would be flooded after its
construction. This stakeholder also wants the project stopped so they can continue to live on and farm the land.
The banks (identified as a single group). These seem happy to lend to the project and will want it to proceed so they
make a return on their loans commensurate with the risk of the loan. They do not want to be publicly identified as being
associated with the Giant Dam Project.
Shareholders. The shareholders have the right to have their investment in the company managed in such a way as to
maximise the value of their shareholding. The shareholders seek projects providing positive NPVs within the normal
constraints of sound risk management.
Tutorial note: only four stakeholders need to be identified. Marks will be given for up to four relevant stakeholders
only. -
第18题:
(ii) Briefly discuss FOUR non-financial factors which might influence the above decision. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Four factors that could be considered are as follows:
(i) The quality of the service provided by NSC as evidenced by, for example, the comfort of the ferries, on-board
facilities, friendliness and responsiveness of staff.
(ii) The health and safety track record of NSC – passenger safety is a ‘must’ in such operations.
(iii) The reliability, timeliness and dependability of NSC as a service provider.
(iv) The potential loss of image due to redundancies within Wonderland plc. -
第19题:
(ii) Calculate the chargeable gain arising as a consequence of Jan accepting Jumper’s offer. (4 marks)
正确答案: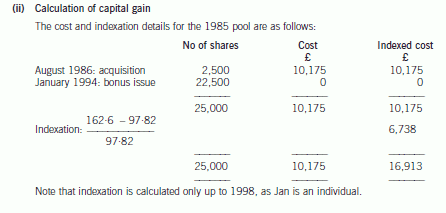

-
第20题:
(ii) Discuss TWO problems that may be faced in implementing quality control procedures in a small firm of
Chartered Certified Accountants, and recommend how these problems may be overcome. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Consultation – it may not be possible to hold extensive consultations on specialist issues within a small firm, due to a
lack of specialist professionals. There may be a lack of suitably experienced peers to discuss issues arising on client
engagements. Arrangements with other practices for consultation may be necessary.
Training/Continuing Professional Development (CPD) – resources may not be available, and it is expensive to establish
an in-house training function. External training consortia can be used to provide training/CPD for qualified staff, and
training on non-exam related issues for non-qualified staff.
Review procedures – it may not be possible to hold an independent review of an engagement within the firm due to the
small number of senior and experienced auditors. In this case an external review service may be purchased.
Lack of specialist experience – where special skills are needed within an engagement; the skills may be bought in, for
example, by seconding staff from another practice. Alternatively if work is too specialised for the firm, the work could be
sub-contracted to another practice.
Working papers – the firm may lack resources to establish an in-house set of audit manuals or standard working papers.
In this case documentation can be provided by external firms or professional bodies. -
第21题:
(ii) Deema Co. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Deema Co
The claim is an event after the balance sheet date. If the accident occurred prior to the year end of 30 September 2007,
the claim gives additional evidence of a year end condition, and thus meets the definition of an adjusting post balance
sheet event. In this case the matter appears to have been properly disclosed in the notes to the financial statements per
IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date and IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets. A
provision would only be necessary if the claim was probable to succeed and there is sufficient appropriate evidence that
this is not the case. There is therefore no disagreement, and no limitation on scope.
Therefore the senior is correct to propose an unqualified opinion.
However, it is not necessary for the audit report to contain an emphasis of matter paragraph.
ISA 701 Modifications to the Independent Auditor’s Report states that an emphasis of matter paragraph should be used
to highlight a matter where there is significant uncertainty.
Uncertainties are normally only regarded as significant if they involve a level of concern about the going concern status
of the company or would have an unusually great effect on the financial statements. This is not the case here as there
is enough cash to pay the damages in the unlikely event that the claim goes against Deema Co. This appears to be a
one-off situation with a low risk of the estimate being subject to change and thus there is no significant uncertainty. -
第22题:
(ii) Recommend further audit procedures that should be carried out. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Further audit procedures:
Request from Peter Sheffield a written representation detailing:
– the exact nature of his control over Jarvis Co, i.e. if he is a shareholder then state his percentage shareholding, if
he is a member of senior management then state his exact position within the entity,
– a comment on whether in his opinion the balance is recoverable,
– a specific date by which the amount should be expected to be repaid, and
– a confirmation that there are no further balances outstanding from Jarvis Co, or any further transactions between
Jarvis Co and Pulp Co.
Tutorial note: Reference to the Exposure Draft ISA 550 Related Parties (Revised and Redrafted) requirement for both
general and specific management representations will be awarded credit.
Review the terms of any written confirmation of the amount, such as a signed agreement or invoice, checking whether
any interest is due to Pulp Co. The terms should be reviewed for details of any security offered, and the nature of the
consideration to be provided in settlement.
From discussion with Peter Sheffield, develop an understanding of the business purpose of the transaction, particularly
to understand whether the balance is a trade receivable or an investment.
Review the board minutes for evidence of any discussion of the transaction and the recoverability of the balance
outstanding.
Obtain the most recent audited financial statements of Jarvis Co and:
– ascertain whether Peter Sheffield is disclosed as the ultimate controlling party or disclosed as a member of key
management personnel,
– scrutinise the disclosure notes to find any disclosure of the transaction, where it should be described as a related
party liability, and
– perform. a liquidity analysis to establish whether the amount can be repaid from liquid assets. -
第23题:
单选题Marks and Nos.,Number and kind of packages,description of goods should be declared in ().ASHIP'S STORE LIST
BPERSONAL EFFECTS LIST
CCARGO DECLARATION
DGENERAL DECLARATION
正确答案: C解析: 暂无解析
