(b) Determine whether the factoring company’s offer can be recommended on financial grounds. Assume aworking year of 365 days and base your analysis on financial information for 2006. (8 marks)
题目
(b) Determine whether the factoring company’s offer can be recommended on financial grounds. Assume a
working year of 365 days and base your analysis on financial information for 2006. (8 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Determine whether the factoring company’s offer can be recommended on financial grounds. Assume aworking year of 365 days and base your analysis on financial information for 2006. (8 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Discuss how management’s judgement and the financial reporting infrastructure of a country can have a
significant impact on financial statements prepared under IFRS. (6 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Management judgement may have a greater impact under IFRS than generally was the case under national GAAP. IFRS
utilises fair values extensively. Management have to use their judgement in selecting valuation methods and formulating
assumptions when dealing with such areas as onerous contracts, share-based payments, pensions, intangible assets acquired
in business combinations and impairment of assets. Differences in methods or assumptions can have a major impact on
amounts recognised in financial statements. IAS1 expects companies to disclose the sensitivity of carrying amounts to the
methods, assumptions and estimates underpinning their calculation where there is a significant risk of material adjustment
to their carrying amounts within the next financial year. Often management’s judgement is that there is no ‘significant risk’
and they often fail to disclose the degree of estimation or uncertainty and thus comparability is affected.
In addition to the IFRSs themselves, a sound financial reporting infrastructure is required. This implies effective corporate
governance practices, high quality auditing standards and practices, and an effective enforcement or oversight mechanism.
Therefore, consistency and comparability of IFRS financial statements will also depend on the robust nature of the other
elements of the financial reporting infrastructure.
Many preparers of financial statements will have been trained in national GAAP and may not have been trained in the
principles underlying IFRS and this can lead to unintended inconsistencies when implementing IFRS especially where the
accounting profession does not have a CPD requirement. Additionally where the regulatory system of a country is not well
developed, there may not be sufficient market information to utilise fair value measurements and thus this could lead to
hypothetical markets being created or the use of mathematical modelling which again can lead to inconsistencies because of
lack of experience in those countries of utilising these techniques. This problem applies to other assessments or estimates
relating to such things as actuarial valuations, investment property valuations, impairment testing, etc.
The transition to IFRS can bring significant improvement to the quality of financial performance and improve comparability
worldwide. However, there are issues still remaining which can lead to inconsistency and lack of comparability with those
financial statements. -
第2题:
(b) Using the unit cost information available and your calculations in (a), prepare a financial analysis of the
decision strategy which TOC may implement with regard to the manufacture of each product. (6 marks)
正确答案: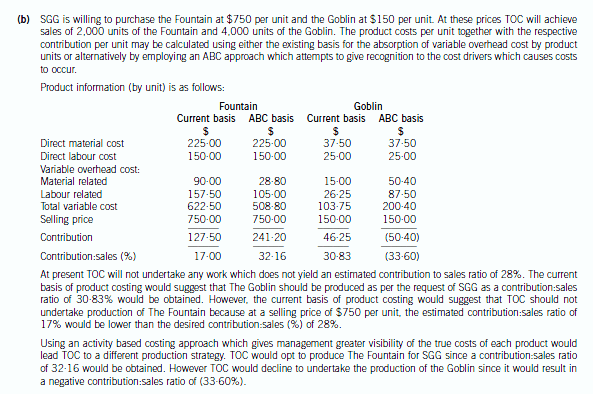
-
第3题:
(c) Prepare brief notes for the proposed meeting with Charles and Jane. Clearly identify the further information
you would need in order to advise them more fully and suggest appropriate personal financial planning
protection products, in respect of both death and serious illness. (9 marks)
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 and the corporation tax
rates for the financial year 2005 apply throughout this question.
正确答案: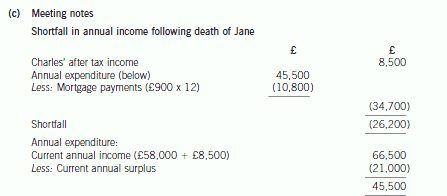
When considering the shortfall
– The family’s expenditure is likely to increase as the children get older, particularly if there is a need for school fees.
– There will be a need for some cash immediately to pay for the cost of the funeral.
– It is assumed that the whole of Jane’s estate has been left to Charles such that there will be no inheritance tax on her
death.
– The shortfall may be reduced by:
(i) State benefits and tax credits.
(ii) Expenditure on non-essential items, e.g. holidays and entertainment included in the annual expenditure of
£45,500.
(iii) The income generated by Charles if he were to return to work.
– The shortfall may be increased by additional child-care costs due to Charles being a single parent, particularly if he
returns to work full-time.
Further information required
– The level of state benefits and tax credits available to Charles.
– The current level of expenditure on non-essential items.
– The costs of child-care if Charles were to return to work.
– Details of any wills made by Charles or Jane.
– Whether Charles’ investment properties could be sold and the proceeds invested in assets with a higher annual return.
– Whether there is any value in Speak Write Ltd independent of Jane, such that the company could be sold after Jane’s
death.
Other related issues
– The couple should consider making provision for their retirement via pension contributions or some other form. of long
term investment plan.
– The couple should recognise that there would be significant financial problems if Jane were to become seriously ill. In
addition to the family’s income falling as set out above, its expenditure would probably increase.
Protection products
– Term life assurance
A qualifying life policy would pay out a tax-free lump sum on Jane’s death.
– Permanent health insurance
Would provide a regular income if Jane were unable to work due to illness.
– Critical illness insurance
Would provide a capital sum in the event of Jane being diagnosed with an insured illness. -
第4题:
(iii) The extent to which Amy will be subject to income tax in the UK on her earnings in respect of duties
performed for Cutlass Inc and the travel costs paid for by that company. (5 marks)
Appropriateness of format and presentation of the report and the effectiveness with which its advice is
communicated. (2 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and the corporation tax
rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply throughout this questio
正确答案:
(iii) Amy’s UK income tax position
Amy will remain UK resident and ordinarily resident as she is not leaving the UK permanently or for a complete tax year
under a full time contract of employment. Accordingly, she will continue to be subject to UK tax on her worldwide income
including her earnings in respect of the duties she performs for Cutlass Inc. The earnings from these duties will also be
taxable in Sharpenia as the income arises in that country.
The double tax treaty between the UK and Sharpenia will either exempt the employment income in one of the two
countries or give double tax relief for the tax paid in Sharpenia. The double tax relief will be the lower of the UK tax and
the Sharpenian tax on the income from Cutlass Inc.
Amy will not be subject to UK income tax on the expenses borne by Cutlass Inc in respect of her flights to and from
Sharpenia provided her journeys are wholly and exclusively for the purposes of performing her duties in Sharpenia.
The amounts paid by Cutlass Inc in respect of Amy’s family travelling to Sharpenia will be subject to UK income tax as
Amy will not be absent from the UK for a continuous period of at least 60 days. -
第5题:
(c) Explanatory notes, together with relevant supporting calculations, in connection with the loan. (8 marks)
Additional marks will be awarded for the appropriateness of the format and presentation of the schedules, the
effectiveness with which the information is communicated and the extent to which the schedules are structured in
a logical manner. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and for the financial year
to 31 March 2007 apply throughout the question.
– you should ignore value added tax (VAT).
正确答案:
(c) Tax implications of there being a loan from Flores Ltd to Banda
Flores Ltd should have paid tax to HMRC equal to 25% of the loan, i.e. £5,250. The tax should have been paid on the
company’s normal due date for corporation tax in respect of the accounting period in which the loan was made, i.e. 1 April
following the end of the accounting period.
The tax is due because Flores Ltd is a close company that has made a loan to a participator and that loan is not in the ordinary
course of the company’s business.
HMRC will repay the tax when the loan is either repaid or written off.
Flores Ltd should have included the loan on Banda’s Form. P11D in order to report it to HMRC.
Banda should have paid income tax on an annual benefit equal to 5% of the amount of loan outstanding during each tax
year. Accordingly, for each full year for which the loan was outstanding, Banda should have paid income tax of £231
(£21,000 x 5% x 22%).
Interest and penalties may be charged in respect of the tax underpaid by both Flores Ltd and Banda and in respect of the
incorrect returns made to HMRC
Willingness to act for Banda
We would not wish to be associated with a client who has engaged in deliberate tax evasion as this poses a threat to the
fundamental principles of integrity and professional behaviour. Accordingly, we should refuse to act for Banda unless she is
willing to disclose the details regarding the loan to HMRC and pay the ensuing tax liabilities. Even if full disclosure is made,
we should consider whether the loan was deliberately hidden from HMRC or Banda’s previous tax adviser.
In addition, companies are prohibited from making loans to directors under the Companies Act. We should advise Banda to
seek legal advice on her own position and that of Flores Ltd. -
第6题:
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Assets
■ There is a very high risk that inventory could be materially overstated in the balance sheet (thereby overstating profit)
because:
? there is a high volume of metals (hence material);
? valuable metals are made more portable;
? subsidy gives an incentive to overstate purchases (and hence inventory);
? inventory may not exist due to lack of physical controls (e.g. aluminium can blow away);
? scrap metal in the stockyard may have zero net realisable value (e.g. iron is rusty and slow-moving);
? quantities per counts not attended by an auditor have increased by a third.
■ Inventory could be otherwise misstated (over or under) due to:
? the weighbridge being inaccurate;
? metal qualities being estimated;
? different metals being mixed up; and
? the lack of an independent expert to identify/measure/value metals.
■ Tangible non-current assets are understated as the parts of the furnaces that require replacement (the linings) are not
capitalised (and depreciated) as separate items but treated as repairs/maintenance/renewals and expensed.
■ Cash may be understated due to incomplete recording of sales.
■ Recorded cash will be overstated if it does not exist (e.g. if it has been stolen).
■ Trade receivables may be understated if cash receipts from credit customers have been misappropriated.
Liabilities
■ The provision for the replacement of the furnace linings is overstated by the amount provided in the current and previous
year (i.e. in its entirety).
Tutorial note: Last replacement was two years ago.
Income statement
■ Revenue will be understated in respect of unrecorded cash sales of salvaged metals and ‘clinker’.
■ Scrap metal purchases (for cash) are at risk of overstatement:
? to inflate the 15% subsidy;
? to conceal misappropriated cash.
■ The income subsidy will be overstated if quantities purchased are overstated and/or overvalued (on the quarterly returns)
to obtain the amount of the subsidy.
■ Cash receipts/payments that were recorded only in the cash book in November are at risk of being unrecorded (in the
absence of cash book postings for November), especially if they are of a ‘one-off’ nature.
Tutorial note: Cash purchases of scrap and sales of salvaged metal should be recorded elsewhere (i.e. in the manual
inventory records). However, a one-off expense (of a capital or revenue nature) could be omitted in the absence of
another record.
■ Expenditure is overstated in respect of the 25% provision for replacing the furnace linings. However, as depreciation
will be similarly understated (as the furnace linings have not been capitalised) there is no risk of material misstatement
to the income statement overall.
Disclosure risk
■ A going concern (‘failure’) risk may arise through the loss of:
? sales revenue (e.g. through misappropriation of salvaged metals and/or cash);
? the subsidy (e.g. if returns are prepared fraudulently);
? cash (e.g. if material amounts stolen).
Any significant doubts about going concern must be suitably disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ are not met.
■ Disclosure risk arises if contingent liabilities in connection with the dumping of ‘clinker’ (e.g. for fines and penalties) are
not adequately disclosed in accordance with IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
Appropriate audit approach
Tutorial note: In explaining why AN audit approach is appropriate for Indigo it can be relevant to comment on the
unsuitability of other approaches.
■ A risk-based approach is suitable because:
? inherent risk is high at the entity and financial assertion levels;
? material errors are likely to arise in inventory where a high degree of subjectivity will be involved (regarding quality
of metals, quantities, net realisable value, etc);
? it directs the audit effort to inventory, purchases, income (sales and subsidy) and other risk areas (e.g. contingent
liabilities).
■ A systems-based/compliance approach is not suited to the risk areas identified because controls are lacking/ineffective
(e.g. over inventory and cash). Also, as the audit appointment was not more than three months ago and no interim
audit has been conducted (and the balance sheet date is only three weeks away) testing controls is likely to be less
efficient than a substantive approach.
■ A detailed substantive/balance sheet approach would be suitable to direct audit effort to the appropriate valuation of
assets (and liabilities) existing at balance sheet date. Principal audit work would include:
? attendance at a full physical inventory count at 31 December 2005;
? verifying cash at bank (through bank confirmation and reconciliation) and in hand (through physical count);
? confirming the accuracy of the quarterly returns to the local authority.
■ A cyclical approach/directional testing is unlikely to be suitable as cycles are incomplete. For example the purchases
cycle for metals is ‘purchase/cash’ rather than ‘purchase/payable/cash’ and there is no independent third party evidence
to compensate for that which would be available if there were trade payables (i.e. suppliers’ statements). Also the cycles
are inextricably inter-related to cash and inventory – amounts of which are subject to high inherent risk.
■ Analytical procedures may be of limited use for substantive purposes. Factors restricting the use of substantive analytical
procedures include:
? fluctuating margins (e.g. as many factors will influence the price at which scrap is purchased and subsequently
sold, when salvaged, sometime later);
? a lack of reliable/historic information on which to make comparisons. -
第7题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第8题:
(c) Describe the examination procedures you should use to verify Cusiter Co’s prospective financial information.
(9 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Examination procedures
■ The arithmetic accuracy of the PFI should be confirmed, i.e. subtotals and totals should be recast and agreed.
■ The actual information for the year to 31 December 2006 that is shown as comparative information should be agreed
to the audited financial statements for that year to ensure consistency.
■ Balances and transaction totals for the quarter to 31 March 2007 should be agreed to general ledger account balances
at that date. The net book value of property, plant and equipment should be agreed to the non-current asset register;
accounts receivable/payable to control accounts and cash at bank to a bank reconciliation statement.
■ Tenders for the new equipment should be inspected to confirm the additional cost included in property, plant and
equipment included in the forecast for the year to 31 December 2008 and that it can be purchased with the funds being
lent by the bank.
■ The reasonableness of all new assumptions should be considered. For example, the expected useful life of the new
equipment, the capacity at which it will be operating, the volume of new product that can be sold, and at what price.
■ The forecast income statement should be reviewed for completeness of costs associated with the expansion. For
example, operating expenses should include salaries of additional equipment operatives or supervisors.
■ The consistency of accounting practices reflected in the forecast with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
should be considered. For example, the intangible asset might be expected to be less than $10,000 at 31 December
2008 as it should be carried at amortised cost.
■ The cost of property, plant and equipment at 31 December 2008 is $280,000 more than as at 31 December 2007.
Consideration should be given to the adequacy of borrowing $250,000 if the actual investment is $30,000 more.
■ The terms of existing borrowings (both non-current and short-term) should be reviewed to ensure that the forecast takes
full account of existing repayment schedules. For example, to confirm that only $23,000 of term borrowings will become
current by the end of 2007.
Trends should be reviewed and fluctuations explained, for example:
■ Revenue for the first quarter of 2007 is only 22% of revenue for 2006 and so may appear to be understated. However,
revenue may not be understated if sales are seasonal and the first quarter is traditionally ‘quieter’.
■ Forecast revenue for 2007 is 18% up on 2006. However, forecast revenue for 2008 is only 19% up on 2007. As the
growth in 2007 is before the investment in new plant and equipment it does not look as though the new investment
will be contributing significantly to increased growth in the first year.
■ The gross profit % is maintained at around 29% for the three years. However, the earnings before interest and tax (EBIT)
% is forecast to fall by 2% for 2008. Earnings after interest might be worrying to the potential lender as this is forecast
to rise from 12·2% in 2006 to 13·7% in 2007 but then fall to 7·6% in 2008.
The reasonableness of relationships between income statement and balance sheet items should be considered. For example:
■ The average collection period at each of the balance sheet dates presented is 66, 69, 66 and 66 days respectively (e.g.
71/394 × 365 = 66 days). Although it may be realistic to assume that the current average collection period may be
maintained in future it is possible that it could deteriorate if, for example, new customers taken on to launch the new
product are not as credit worthy as the existing customer base.
■ The number of days sales in inventory at each balance sheet date is 66, 88, 66 and 65 days respectively (e.g. 50/278
× 365 = 66 days). The reason for the increase to 88 at the end of the first quarter must be established and
management’s assertion that 66 days will be re-established as the ‘norm’ corroborated.
■ As the $42,000 movement on retained earnings from 2007 to 2008 is the earnings before income tax for 2008 it may
be that there is no tax in 2008 or that tax effects have not been forecast. (However, some deferred tax effect might be
expected if the investment in new plant and equipment is likely to attract accelerated capital allowances.) -
第9题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it. -
第10题:
(ii) Write a letter to Donald advising him on the most tax efficient manner in which he can relieve the loss
incurred in the year to 31 March 2007. Your letter should briefly outline the types of loss relief available
and explain their relative merits in Donald’s situation. Assume that Donald will have no source of income
other than the business in the year of assessment 2006/07 and that any income he earned on a parttime
basis while at university was always less than his annual personal allowance. (9 marks)
Assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2004 and the income tax rates
and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this question.
Relevant retail price index figures are:
January 1998 159·5
April 1998 162·6
正确答案:(ii) [Donald’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Donald [Date]
I understand that you have incurred a tax loss in your first year of trading. The following options are available in respect
of this loss.
1. The first option is to use the trading loss against other forms of income in the same year. If such a claim is made,
losses are offset against income before personal allowances.
Any excess loss can still be offset against capital gains of the year. However, any offset against capital gains is
before both taper relief and annual exemptions.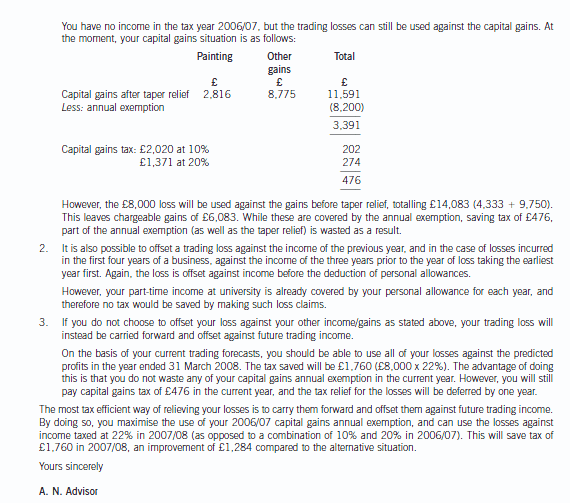
-
第11题:
听力原文:M: There are several reasons why careful analysis of financial statements is necessary. What are they?
W: First, financial statements are general-purpose statements. Secondly, the relationships between amounts on successive financial statements are not obvious without analysis. And thirdly, users of financial statements may be interested in seeing how well a company is performing.
Q: What are they talking about?
(17)
A.The methods of financial statements.
B.The necessity of careful analysis of financial statements
C.The relationship among financial statements.
D.The purpose of financial statements.
正确答案:B
解析:男士问的是仔细分析财务报表的必要性的理由,故B选项符合。D项说的是财务报表的目的,并非分析财务报表的目的。 -
第12题:
The following financial information relates to HGR Co:
Statement of financial position at the current date (extracts)
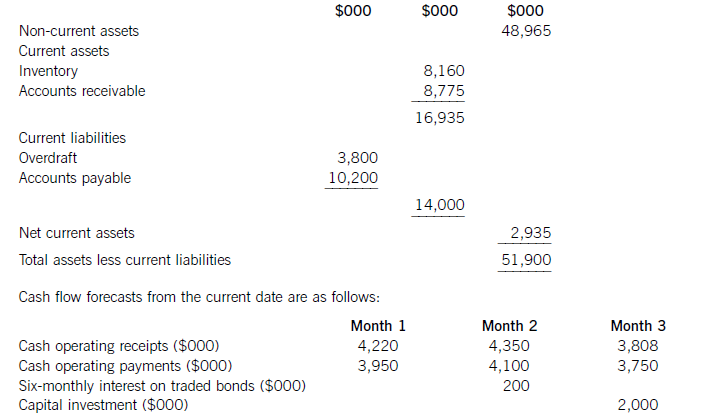
The finance director has completed a review of accounts receivable management and has proposed staff training and operating procedure improvements, which he believes will reduce accounts receivable days to the average sector value of 53 days. This reduction would take six months to achieve from the current date, with an equal reduction in each month. He has also proposed changes to inventory management methods, which he hopes will reduce inventory days by two days per month each month over a three-month period from the current date. He does not expect any change in the current level of accounts payable.
HGR Co has an overdraft limit of $4,000,000. Overdraft interest is payable at an annual rate of 6·17% per year, with payments being made each month based on the opening balance at the start of that month. Credit sales for the year to the current date were $49,275,000 and cost of sales was $37,230,000. These levels of credit sales and cost of sales are expected to be maintained in the coming year. Assume that there are 365 working days in each year.
Required:
(a) Discuss the working capital financing strategy of HGR Co. (7 marks)
(b) For HGR Co, calculate:
(i) the bank balance in three months’ time if no action is taken; and
(ii) the bank balance in three months’ time if the finance director’s proposals are implemented.
Comment on the forecast cash flow position of HGR Co and recommend a suitable course of action.
(10 marks)
(c) Discuss how risks arising from granting credit to foreign customers can be managed and reduced.
(8 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whenconsideringthefinancingofworkingcapital,itisusefultodividecurrentassetsintofluctuatingcurrentassetsandpermanentcurrentassets.Fluctuatingcurrentassetsrepresentchangesinthelevelofcurrentassetsduetotheunpredictabilityofbusinessactivity.Permanentcurrentassetsrepresentthecorelevelofinvestmentincurrentassetsneededtosupportagivenlevelofturnoverorbusinessactivity.Asturnoverorlevelofbusinessactivityincreases,thelevelofpermanentcurrentassetswillalsoincrease.Thisrelationshipcanbemeasuredbytheratioofturnovertonetcurrentassets.Thefinancingchoiceasfarasworkingcapitalisconcernedisbetweenshort-termandlong-termfinance.Short-termfinanceismoreflexiblethanlong-termfinance:anoverdraft,forexample,isusedbyabusinessorganisationastheneedarisesandvariableinterestischargedontheoutstandingbalance.Short-termfinanceisalsomoreriskythanlong-termfinance:anoverdraftfacilitymaybewithdrawn,orashort-termloanmayberenewedonlessfavourableterms.Intermsofcost,thetermstructureofinterestratessuggeststhatshort-termdebtfinancehasalowercostthanlong-termdebtfinance.Thematchingprinciplesuggeststhatlong-termfinanceshouldbeusedforlong-terminvestment.Applyingthisprincipletoworkingcapitalfinancing,long-termfinanceshouldbematchedwithpermanentcurrentassetsandnon-currentassets.Afinancingpolicywiththisobjectiveiscalleda‘matchingpolicy’.HGRCoisnotusingthisfinancingpolicy,sinceofthe$16,935,000ofcurrentassets,$14,000,000or83%isfinancedfromshort-termsources(overdraftandtradepayables)andonly$2,935,000or17%isfinancedfromalong-termsource,inthiscaseequityfinance(shareholders’funds)ortradedbonds.ThefinancingpolicyorapproachtakenbyHGRCotowardsthefinancingofworkingcapital,whereshort-termfinanceispreferred,iscalledanaggressivepolicy.Relianceonshort-termfinancemakesthisriskierthanamatchingapproach,butalsomoreprofitableduetothelowercostofshort-termfinance.Followinganaggressiveapproachtofinancingcanleadtoovertrading(undercapitalisation)andthepossibilityofliquidityproblems.(b)Bankbalanceinthreemonths’timeifnoactionistaken:Workings:ReductioninaccountsreceivabledaysCurrentaccountsreceivabledays=(8,775/49,275)x365=65daysReductionindaysoversixmonths=65–53=12daysMonthlyreduction=12/6=2daysEachreceivablesdayisequivalentto8,775,000/65=$135,000(Alternatively,eachreceivablesdayisequivalentto49,275,000/365=$135,000)Monthlyreductioninaccountsreceivable=2x135,000=$270,000ReductionininventorydaysCurrentinventorydays=(8,160/37,230)x365=80daysEachinventorydayisequivalentto8,160,000/80=$102,000(Alternatively,eachinventoryday=37,230,000/365=$102,000)Monthlyreductionininventory=102,000x2=$204,000OverdraftinterestcalculationsMonthlyoverdraftinterestrate=1·06171/12=1·005or0·5%Ifnoactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0·005=$19,000Period2interest=3,549,000x0·005=$17,745or$18,000Period3interest=3,517,000x0·005=$17,585or$18,000Ifactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0.005=$19,000Period2interest=3,075,000x0.005=$15,375or$15,000Period3interest=2,566,000x0.005=$12,830or$13,000DiscussionIfnoactionistaken,thecashflowforecastshowsthatHGRCowillexceeditsoverdraftlimitof$4millionby$1·48millioninthreemonths’time.Ifthefinancedirector’sproposalsareimplemented,thereisapositiveeffectonthebankbalance,buttheoverdraftlimitisstillexceededinthreemonths’time,althoughonlyby$47,000ratherthanby$1·47million.Ineachofthethreemonthsfollowingthat,thecontinuingreductioninaccountsreceivabledayswillimprovethebankbalanceby$270,000permonth.Withoutfurtherinformationonoperatingreceiptsandpayments,itcannotbeforecastwhetherthebankbalancewillreturntolessthanthelimit,orevencontinuetoimprove.Themainreasonfortheproblemwiththebankbalanceisthe$2millioncapitalexpenditure.Purchaseofnon-currentassetsshouldnotbefinancedbyanoverdraft,butalong-termsourceoffinancesuchasequityorbonds.Ifthecapitalexpenditurewereremovedfromtheareaofworkingcapitalmanagement,theoverdraftbalanceattheendofthreemonthswouldbe$3·48millionifnoactionweretakenand$2·05millionifthefinancedirector’sproposalswereimplemented.GiventhatHGRCohasalmost$50millionofnon-currentassetsthatcouldpossiblybeusedassecurity,raisinglong-termdebtthrougheitherabankloanorabondissueappearstobesensible.Assumingabondinterestrateof10%peryear,currentlong-termdebtintheform.oftradedbondsisapproximately($200mx2)/0·1=$4m,whichismuchlessthantheamountofnoncurrentassets.AsuitablecourseofactionforHGRCotofollowwouldthereforebe,firstly,toimplementthefinancedirector’sproposalsand,secondly,tofinancethecapitalexpenditurefromalong-termsource.Considerationcouldalsobegiventousingsomelong-termdebtfinancetoreducetheoverdraftandtoreducethelevelofaccountspayable,currentlystandingat100days.(c)Whencreditisgrantedtoforeigncustomers,twoproblemsmaybecomeespeciallysignificant.First,thelongerdistancesoverwhichtradetakesplaceandthemorecomplexnatureoftradetransactionsandtheirelementsmeansforeignaccountsreceivableneedmoreinvestmentthantheirdomesticcounterparts.Longertransactiontimesincreaseaccountsreceivablebalancesandhencetheleveloffinancingandfinancingcosts.Second,theriskofbaddebtsishigherwithforeignaccountsreceivablethanwiththeirdomesticcounterparts.Inordertomanageandreducecreditrisks,therefore,exportersseektoreducetheriskofbaddebtandtoreducethelevelofinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivable.Manyforeigntransactionsareon‘openaccount’,whichisanagreementtosettletheamountoutstandingonapredetermineddate.Openaccountreflectsagoodbusinessrelationshipbetweenimporterandexporter.Italsocarriesthehighestriskofnon-payment.Onewaytoreduceinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableistoagreeearlypaymentwithanimporter,forexamplebypaymentinadvance,paymentonshipment,orcashondelivery.Thesetermsoftradeareunlikelytobecompetitive,however,anditismorelikelythatanexporterwillseektoreceivecashinadvanceofpaymentbeingmadebythecustomer.Onewaytoacceleratecashreceiptsistousebillfinance.Billsofexchangewithasignedagreementtopaytheexporteronanagreedfuturedate,supportedbyadocumentaryletterofcredit,canbediscountedbyabanktogiveimmediatefunds.Thisdiscountingiswithoutrecourseifbillsofexchangehavebeencountersignedbytheimporter’sbank.Documentarylettersofcreditareapaymentguaranteebackedbyoneormorebanks.Theycarryalmostnorisk,providedtheexportercomplieswiththetermsandconditionscontainedintheletterofcredit.Theexportermustpresentthedocumentsstatedintheletter,suchasbillsoflading,shippingdocuments,billsofexchange,andsoon,whenseekingpayment.Aseachsupportingdocumentrelatestoakeyaspectoftheoveralltransaction,lettersofcreditgivesecuritytotheimporteraswellastheexporter.Companiescanalsomanageandreduceriskbygatheringappropriateinformationwithwhichtoassessthecreditworthinessofnewcustomers,suchasbankreferencesandcreditreports.Insurancecanalsobeusedtocoversomeoftherisksassociatedwithgivingcredittoforeigncustomers.Thiswouldavoidthecostofseekingtorecovercashduefromforeignaccountsreceivablethroughaforeignlegalsystem,wheretheexportercouldbeatadisadvantageduetoalackoflocalorspecialistknowledge.Exportfactoringcanalsobeconsidered,wheretheexporterpaysforthespecialistexpertiseofthefactorasawayofreducinginvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableandreducingtheincidenceofbaddebts. -
第13题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第14题:
Assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2004 apply throughout.
(b) Explain the corporation tax (CT) and value added tax (VAT) issues that Irroy should be aware of, if she
proceeds with her proposal for the Irish subsidiary, Green Limited. Your answer should clearly identify those
factors which will determine whether or not Green Limited is considered UK resident or Irish resident and
the tax implications of each alternative situation.
You need not repeat points that are common to each situation. (16 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several matters that Irroy will need to be aware of in relation to value added tax and corporation tax. These are set
out below.
Residence of subsidiary
Irroy will want to ensure that the subsidiary is treated as being resident in the Republic of Ireland. It will then pay corporation
tax on its profits at lower rates than in the UK. The country of incorporation usually claims taxing rights, but this is not by
itself sufficient. Irroy needs to be aware that a company can be treated as UK resident by virtue of the location of its central
management and control. This is usually defined as being where the board of directors meets to make strategic decisions. As
a result, Irroy needs to ensure that board meetings are conducted outside the UK.
If Green Limited is treated as being UK resident, it will be taxed in the UK on its worldwide income, including that arising in
the Republic of Ireland. However, as it will be conducting trading activities in the Republic of Ireland, Green Limited will also
be treated as being Irish resident as its activities in that country are likely to constitute a permanent establishment. Thus it
may also suffer tax in the Republic of Ireland as a consequence, although double tax relief will be available (see later).
A permanent establishment is broadly defined as a fixed place of business through which a business is wholly or partly carried
on. Examples of a permanent establishment include an office, factory or workshop, although certain activities (such as storage
or ancillary activities) can be excluded from the definition.
If Green Limited is treated as being an Irish resident company, any dividends paid to Aqua Limited will be taxed under
Schedule D Case V in the UK. Despite being non resident, Green Limited will still count as an associate of the existing UK
companies, and may affect the rates of tax paid by Aqua Limited and Aria Limited in the UK. However, as a non UK resident
company, Green Limited will not be able to claim losses from the UK companies by way of group relief.
Double tax relief
If Green Limited is treated as UK resident, corporation tax at UK rates will be payable on all profits earned. However, income
arising in the Republic of Ireland is likely to have been taxed in that country also by virtue of having a permanent
establishment located there. As the same profits have been taxed twice, double tax relief is available, either by reference to
the tax treaty between the UK and the Republic of Ireland, or on a unilateral basis, where the UK will give relief for the foreign
tax suffered.
If Green Limited is treated as an Irish resident company, it will pay tax in the Republic of Ireland, based on its worldwide
taxable profits. However, any repatriation of profits to the UK by dividend will be taxed on a receipts basis in the UK. Again,
double tax relief will be available as set out above.
Double tax relief is available against two types of tax. For payments made by Green Limited to Aqua Limited on which
withholding tax has been levied, credit will be given for the tax withheld. In addition, relief is available for the underlying tax
where a dividend is received from a foreign company in which Aqua Limited owns at least 10% of the voting power. The
underlying tax is the tax attributable to the relevant profits from which the dividend was paid.
Double tax relief is given at the lower rate of the UK tax and the foreign tax (withholding and underlying taxes) suffered.
Transfer pricing
Where groups have subsidiaries in other countries, they may be tempted to divert profits to subsidiaries which pay tax at lower
rates. This can be achieved by artificially changing the prices charged (known as the transfer price) between the group
companies. While they can do this commercially through common control, anti avoidance legislation seeks to correct this by
ensuring that for taxation purposes, profits on such intra-group transactions are calculated as if the transactions were carried
out on an arms length basis. Since 1 April 2004, this legislation can also be applied to transactions between UK group
companies.
If Green Limited is treated as a UK resident company, the group’s status as a small or medium sized enterprise means that
transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Limited and the other UK group companies.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Ltd and the
UK resident companies because of the group’s status as a small or medium-sized enterprise and the existence of a double
tax treaty, based on the OECD model, between the UK and the Republic of Ireland.
Controlled foreign companies
Tax legislation exists to stop a UK company accumulating profits in a foreign subsidiary which is subject to a low tax rate.
Such a subsidiary is referred to as a controlled foreign company (CFC), and exists where:
(1) the company is resident outside the UK, and
(2) is controlled by a UK resident entity or persons, and
(3) pays a ‘lower level of tax’ in its country of residence.
A lower level of tax is taken to be less than 75% of the tax that would have been payable had the company been UK resident.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, it will be paying corporation tax at 12·5% so would appear to be caught by
the above rules and is therefore likely to be treated as a CFC.
Where a company is treated as a CFC, its profits are apportioned to UK resident companies entitled to at least 25% of its
profits. For Aqua Limited, which would own 100% of the shares in Green Limited, any profits made by Green Limited would
be apportioned to Aqua Limited as a deemed distribution. Aqua Limited would be required to self-assess this apportionment
on its tax return and pay UK tax on the deemed distribution (with credit being given for the Irish tax suffered).
There are some exemptions which if applicable the CFC legislation does not apply and no apportionments of profits will be
made. These include where chargeable profits of the CFC do not exceed £50,000 in an accounting period, or where the CFC
follows an acceptable distribution policy (distributing at least 90% of its chargeable profits within 18 months of the relevant
period).
Value added tax (VAT)
Green Limited will be making taxable supplies in the Republic of Ireland and thus (subject to exceeding the Irish registration
limit) liable to register for VAT there. If Green Limited is registered for VAT in the Republic of Ireland, then supplies of goods
made from the UK will be zero rated. VAT on the goods will be levied in the Republic of Ireland at a rate of 21%. Aqua Limited
will need to have proof of supply in order to apply the zero rate, and will have to issue an invoice showing Green Limited’s
Irish VAT registration number as well as its own. In the absence of such evidence/registration, Aqua Limited will have to treat
its transactions with Green Limited as domestic sales and levy VAT at the UK standard rate of 17·5%.
In addition to making its normal VAT returns, Aqua Limited will also be required to complete an EU Sales List (ESL) statement
each quarter. This provides details of the sales made to customers in the return period – in this case, Green Limited. Penalties
can be applied for inaccuracies or non-compliance. -
第15题:
(iii) State the value added tax (VAT) and stamp duty (SD) issues arising as a result of inserting Bold plc as
a holding company and identify any planning actions that can be taken to defer or minimise these tax
costs. (4 marks)
You should assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates
and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(iii) Bold plc will be making a taxable supply of services, likely to exceed the VAT threshold. It should therefore consider
registering for VAT – either immediately on a voluntary basis, or when its cumulative taxable supplies in the previous
twelve months exceed £60,000.
As an alternative, the new group can apply for a group VAT registration. This will simplify its VAT administration as intragroup
transactions are broadly disregarded for VAT purposes, and only one VAT return is required for the group as a
whole.
Stamp duty normally applies at 0·5% on the consideration payable in respect of transactions in shares. However, an
exemption is available in the case of a takeover, reconstruction or amalgamation where there is no real change in
ownership, i.e. the new shareholdings mirror the old shareholdings, and the transaction is for commercial purposes. The
insertion of a new holding company over an existing company, as proposed here, would qualify for this exemption.
There is no VAT on transactions in shares. -
第16题:
(iii) The effect of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover directly and non-directly attributable input
tax. (6 marks)
You are required to prepare calculations in respect of part (ii) only of this part of this question.
Note: – You should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply
throughout this question.
正确答案:(iii) The effect of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover its input tax
Prior to the restructuring
Rapier Ltd and Switch Ltd make wholly standard rated supplies and are in a position to recover all of their input tax
other than that which is specifically blocked. Dirk Ltd and Flick Ltd are unable to register for VAT as they do not make
taxable supplies. Accordingly, they cannot recover any of their input tax.
Following the restructuring
Rapier Ltd will be carrying on four separate trades, two of which involve the making of exempt supplies such that it will
be a partially exempt trader. Its recoverable input tax will be calculated as follows.
– Input tax in respect of inputs wholly attributable to taxable supplies is recoverable.
– Input tax in respect of inputs wholly attributable to exempt supplies cannot be recovered (subject to the de minimis
limits below).
– A proportion of the company’s residual input tax, i.e. input tax in respect of inputs which cannot be directly
attributed to particular supplies, is recoverable. The proportion is taxable supplies (VAT exclusive) divided by total
supplies (VAT exclusive). This proportion is rounded up to the nearest whole percentage where total residual input
tax is no more than £400,000 per quarter.
The balance of the residual input tax cannot be recovered (subject to the de minimis limits below).
– If the de minimis limits are satisfied, Rapier Ltd will be able to recover all of its input tax (other than that which is
specifically blocked) including that which relates to exempt supplies. The de minimis limits are satisfied where the
irrecoverable input tax:
– is less than or equal to £625 per month on average; and
– is less than or equal to 50% of total input tax.
The impact of the restructuring on the group’s ability to recover its input tax will depend on the level of supplies made
by the different businesses and the amounts of input tax involved. The restructuring could result in the group being able
to recover all of its input tax (if the de minimis limits are satisfied). Alternatively the amount of irrecoverable input tax
may be more or less than the amounts which cannot be recovered by Dirk Ltd and Flick Ltd under the existing group
structure.
-
第17题:
(b) Explain why making sales of Sabals in North America will have no effect on Nikau Ltd’s ability to recover its
input tax. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year to 31 March 2007
will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
– you should ignore indexation allowance.
正确答案:
(b) Recoverability of input tax
Sales by Nikau Ltd of its existing products are subject to UK VAT at 17·5% because it is selling to domestic customers who
will not be registered for VAT. Accordingly, at present, Nikau Ltd can recover all of its input tax.
Sales to customers in North America will be zero rated because the goods are being exported from the EU. Zero rated supplies
are classified as taxable for the purposes of VAT and therefore Nikau Ltd will continue to be able to recover all of its input tax. -
第18题:
(c) Comment on the matters to be considered in seeking to determine the extent of Indigo Co’s financial loss
resulting from the alleged fraud. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Extent of alleged fraud – Matters to be considered
■ Details reported to police: The managing director may have made some estimate of the possible extent of the fraud in
reporting the chief accountant’s disappearance to the police.
■ The minimum loss (assuming no insurance) would be sales for the three days before he left. If not known (e.g. because
the only record of them was in the cash book) a simple estimate might be 3/20 × total recorded revenue for a typical
month.
■ The pattern of cash bankings extracted from bank statements: A falling trend starting during the year might mark the
time from which the chief accountant began to misappropriate cash.
■ Whether other managers have voiced their suspicions, if any, on the chief accountant’s behaviour. For example, if there
was any marked change in his lifestyle. (what he appeared to spend his money on, the hours he worked, etc).
■ The prior year auditor’s report was unmodified. If this was appropriate the chief accountant’s alleged fraudulent activities
may have only started in the current year.
■ The amount of fidelity insurance cover (i.e. against employees handling cash) that Indigo has taken out to meet any
claim for fraud.
■ The likelihood, if any, of recovering misappropriated amounts. For example, if the chief accountant has assets (e.g. a
house) that can be used to settle Indigo’s claims against him in the event that he is caught/successfully prosecuted. -
第19题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第20题:
(d) Discuss the professional accountant’s liability for reporting on prospective financial information and the
measures that the professional accountant might take to reduce that liability. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Professional accountant’s liability
Liability for reporting on PFI
Independent accountants may be required to report on PFI for many reasons (e.g. to help secure a bank loan). Such forecasts
and projections are inherently unreliable. If the forecast or projection does not materialise, and the client or lenders (or
investors) consequently sustain financial loss, the accountant may face lawsuits claiming financial loss.
Courts in different jurisdictions use various criteria to define the group of persons to whom independent accountants may be
held liable for providing a report on an inaccurate forecast or projection. The most common of these are that an accountant
is liable to persons with whom there is proximity:
(i) only (i.e. the client who engaged the independent accountant);
(ii) or whose relationship with the accountant sufficiently approaches privity;
(iii) and to persons or members of a limited group of persons for whose benefit and guidance the accountant supplied the
information or knew that the recipient of the information intended to supply it;
(iv) and to persons who reasonably can be foreseen to rely on the information.
Measures to reduce liability
As significant assumptions will be essential to a reader’s understanding of a financial forecast, the independent accountant
should ensure that they are adequately disclosed and clearly stated to be the management’s responsibility. Hypothetical
assumptions should be clearly distinguished from best estimates.
The introduction to any forecast (and/or report thereon) should include a caveat that the prospective results may not be
attained. Specific and extensive warnings (‘the actual results … will vary’) and disclaimers (‘we do not express an opinion’)
may be effective in protecting an independent accountant sued for inaccuracies in forecasts or projections that they have
reported on.
Any report to a third party should state:
■ for whom it is prepared, who is entitled to rely on it (if anyone) and for what purpose;
■ that the engagement was undertaken in accordance with the engagement terms;
■ the work performed and the findings.
An independent accountant’s report should avoid inappropriate and open-ended wording, for example, ‘we certify …’ and ‘we
obtained all the explanations we considered necessary’.
Engagement terms to report on PFI should include an appropriate liability cap that is reasonable given the specific
circumstances of the engagement.
The independent accountant may be able to obtain indemnity from a client in respect of claims from third parties. Such ‘hold
harmless’ clauses obligate the client to indemnify the independent accountant from third party claims. -
第21题:
The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the form
to be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that the
previous auditors did not use a liability disclaimer in their audit report, and would like more information about the use
of liability disclaimer paragraphs.
Required:
(b) Discuss the ethical issues raised by the request for your firm to type the financial statements of Blod Co.
(3 marks)
正确答案:
(b) It is not uncommon for audit firms to word process and typeset the financial statements of their clients, especially where the
client is a relatively small entity, which may lack the resources and skills to perform. this task. It is not prohibited by ethical
standards.
However, there could be a perceived threat to independence, with risk magnified in the case of Blod Co, which is a listed
company. The auditors could be perceived to be involved with the preparation of the financial statements of a listed client
company, which is prohibited by ethical standards. IFAC’s Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants states that for a listed
client, the audit firm should not be involved with the preparation of financial statements, which would create a self-review
threat so severe that safeguards could not reduce the threat to an acceptable level. Although the typing of financial statements
itself is not prohibited by ethical guidance, the risk is that providing such a service could be perceived to be an element of
the preparation of the financial statements.
It is possible that during the process of typing the financial statements, decisions and judgments would be made. This could
be perceived as making management decisions in relation to the financial statements, a clear breach of independence.
Therefore to eliminate any risk exposure, the prudent decision would be not to type the financial statements, ensuring that
Blod Co appreciates the ethical problems that this would cause.
Tutorial note: This is an area not specifically covered by ethical guides, where different audit firms may have different views
on whether it is acceptable to provide a typing service for the financial statements of their clients. Credit will be awarded for
sensible discussion of the issues raised bearing in mind other options for the audit firm, for example, it could be argued that
it is acceptable to offer the typing service provided that it is performed by people independent of the audit team, and that
the matter has been discussed with the audit committee/those charged with governance -
第22题:
听力原文:The primary objective of financial reporting is to provide information useful for making investment and lending decisions.
(6)
A.The financial reporting is to provide information for the investors and lenders only.
B.The main aim of financial reporting is to offer information useful for decision-making.
C.Investment and lending decisions can be made from the financial reporting.
D.Investment and lending decisions can not be made from the financial reporting.
正确答案:B
解析:录音单句意思为“财务报告的主要目标是为投资者和贷款者做决定提供有用信息”。 -
第23题:
听力原文:The financial reporting is used to provide information useful for making investment and lending decision.
(2)
A.The objective of financial reporting is to provide information useful for making investment and lending decisions.
B.The financial reporting is useless.
C.The financial reporting can't help people to decide whether they invest on something or not.
D.The financial reporting has no objectives.
正确答案:A
解析:单句的意思为“财务报告被用来为投资及借贷决策提供有用信息。”
