C Co uses material B, which has a current market price of $0·80 per kg. In a linear program, where the objective is to maximise profit, the shadow price of material B is $2 per kg. The following statements have been made:(i) Contribution will be increased
题目
C Co uses material B, which has a current market price of $0·80 per kg. In a linear program, where the objective is to maximise profit, the shadow price of material B is $2 per kg. The following statements have been made:
(i) Contribution will be increased by $2 for each additional kg of material B purchased at the current market price
(ii) The maximum price which should be paid for an additional kg of material B is $2
(iii) Contribution will be increased by $1·20 for each additional kg of material B purchased at the current market price
(iv) The maximum price which should be paid for an additional kg of material B is $2·80
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A.(ii) only
B.(ii) and (iii)
C.(i) only
D.(i) and (iv)
相似考题
更多“C Co uses material B, which has a current market price of $0·80 per kg. In a linear program, where the objective is to maximise profit, the shadow price of material B is $2 per kg. The following statements have been made:(i) Contribution will be increased”相关问题
-
第1题:
(c) Calculate the theoretical ex rights price per share and the net funds to be raised by the rights issue, and
determine and discuss the likely effect of the proposed expansion on:
(i) the current share price of Merton plc;
(ii) the gearing of the company.
Assume that the price–earnings ratio of Merton plc remains unchanged at 12 times. (11 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Rights issue price = 2·45 x 0·8 = £1·96
Theoretical ex rights price = ((2 x 2·45) + (1 x 1·96))/3 = 6·86/3 = £2·29
New shares issued = 20m x 1/2 = 10 million
Funds raised = 1·96 x 10m = £19·6 million
After issue costs of £300,000 funds raised will be £19·3 million
Annual after-tax return generated by these funds = 19·3 x 0·09 = £1,737,000
New earnings of Merton plc = 1,737,000 + 4,500,000 = £6,237,000
New number of shares = 20m + 10m = 30 million
New earnings per share = 100 x 6,237,000/30,000,000 = 20·79 pence
New share price = 20·79 x 12 = £2·49
The weaknesses in this estimate are that the predicted return on investment of 9% may or may not be achieved: the priceearnings
ratio depends on the post investment share price, rather than the post investment share price depending on the
price-earnings ratio; the current earnings seem to be declining and this share price estimate assumes they remain constant;
in fact current earnings are likely to decline because the overdraft and annual interest are increasing but operating profit is
falling.
Expected gearing = 38/(60 + 19·3) = 47·9% compared to current gearing of 63%.
Including the overdraft, expected gearing = 46/(60 + 19·3) = 58% compared to 77%.
The gearing is predictably lower, but if the overdraft is included in the calculation the gearing of the company is still higher
than the sector average. The positive effect on financial risk could have a positive effect on the company’s share price, but
this is by no means certain. -
第2题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
正确答案:
4 (i) Proposed dividend
The dividend was proposed after the balance sheet date and the company, therefore, did not have a liability at the balance
sheet date. No provision for the dividend should be recognised. The approval by the directors and the shareholders are
enough to create a valid expectation that the payment will be made and give rise to an obligation. However, this occurred
after the current year end and, therefore, will be charged against the profits for the year ending 31 October 2006.
The existence of a good record of dividend payments and an established dividend policy does not create a valid expectation
or an obligation. However, the proposed dividend will be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements as the directors
approved it prior to the authorisation of the financial statements.
(ii) Disposal of subsidiary
It would appear that the loss on the sale of the subsidiary provides evidence that the value of the consolidated net assets of
the subsidiary was impaired at the year end as there has been no significant event since 31 October 2005 which would have
caused the reduction in the value of the subsidiary. The disposal loss provides evidence of the impairment and, therefore,
the value of the net assets and goodwill should be reduced by the loss of $9 million plus the loss ($2 million) to the date of
the disposal, i.e. $11 million. The sale provides evidence of a condition that must have existed at the balance sheet date
(IAS10). This amount will be charged to the income statement and written off goodwill of $12 million, leaving a balance of
$1 million on that account. The subsidiary’s assets are impaired because the carrying values are not recoverable. The net
assets and goodwill of Krup would form. a separate income generating unit as the subsidiary is being disposed of before the
financial statements are authorised. The recoverable amount will be the sale proceeds at the date of sale and represents the
value-in-use to the group. The impairment loss is effectively taking account of the ultimate loss on sale at an earlier point in
time. IFRS5, ‘Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations’, will not apply as the company had no intention
of selling the subsidiary at the year end. IAS10 would require disclosure of the disposal of the subsidiary as a non-adjusting
event after the balance sheet date.
(iii) Issue of ordinary shares
IAS33 ‘Earnings per share’ states that if there is a bonus issue after the year end but before the date of the approval of the
financial statements, then the earnings per share figure should be based on the new number of shares issued. Additionally
a company should disclose details of all material ordinary share transactions or potential transactions entered into after the
balance sheet date other than the bonus issue or similar events (IAS10/IAS33). The principle is that if there has been a
change in the number of shares in issue without a change in the resources of the company, then the earnings per share
calculation should be based on the new number of shares even though the number of shares used in the earnings per share
calculation will be inconsistent with the number shown in the balance sheet. The conditions relating to the share issue
(contingent) have been met by the end of the period. Although the shares were issued after the balance sheet date, the issue
of the shares was no longer contingent at 31 October 2005, and therefore the relevant shares will be included in the
computation of both basic and diluted EPS. Thus, in this case both the bonus issue and the contingent consideration issue
should be taken into account in the earnings per share calculation and disclosure made to that effect. Any subsequent change
in the estimate of the contingent consideration will be adjusted in the period when the revision is made in accordance with
IAS8.
Additionally IFRS3 ‘Business Combinations’ requires the fair value of all types of consideration to be reflected in the cost of
the acquisition. The contingent consideration should be included in the cost of the business combination at the acquisition
date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. In the case of Metalic, the contingent consideration has
been paid in the post-balance sheet period and the value of such consideration can be determined ($11 per share). Thus
an accurate calculation of the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Metalic can be made in the period to 31 October 2005.
Prior to the issue of the shares on 12 November 2005, a value of $10 per share would have been used to value the
contingent consideration. The payment of the contingent consideration was probable because the average profits of Metalic
averaged over $7 million for several years. At 31 October 2005 the value of the contingent shares would be included in a
separate category of equity until they were issued on 12 November 2005 when they would be transferred to the share capital
and share premium account. Goodwill will increase by 300,000 x ($11 – $10) i.e. $300,000.
(iv) Property
IFRS5 (paragraph 7) states that for a non-current asset to be classified as held for sale, the asset must be available for
immediate sale in its present condition subject to the usual selling terms, and its sale must be highly probable. The delay in
this case in the selling of the property would indicate that at 31 October 2005 the property was not available for sale. The
property was not to be made available for sale until the repairs were completed and thus could not have been available for
sale at the year end. If the criteria are met after the year end (in this case on 30 November 2005), then the non-current
asset should not be classified as held for sale in the previous financial statements. However, disclosure of the event should
be made if it meets the criteria before the financial statements are authorised (IFRS5 paragraph 12). Thus in this case,
disclosure should be made.
The property on the application of IFRS5 should have been carried at the lower of its carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell. However, the company has simply used fair value less costs to sell as the basis of valuation and shown the
property at $27 million in the financial statements.
The carrying amount of the property would have been $20 million less depreciation $1 million, i.e. $19 million. Because
the property is not held for sale under IFRS5, then its classification in the balance sheet will change and the property will be
valued at $19 million. Thus the gain of $7 million on the wrong application of IFRS5 will be deducted from reserves, and
the property included in property, plant and equipment. Total equity will therefore be reduced by $8 million.
(v) Share appreciation rights
IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ (paragraph 30) requires a company to re-measure the fair value of a liability to pay cash-settled
share based payment transactions at each reporting date and the settlement date, until the liability is settled. An example of
such a transaction is share appreciation rights. Thus the company should recognise a liability of ($8 x 10 million shares),
i.e. $80 million at 31 October 2005, the vesting date. The liability recognised at 31 October 2005 was in fact based on the
share price at the previous year end and would have been shown at ($6 x 1/2) x 10 million shares, i.e. $30 million. This
liability at 31 October 2005 had not been changed since the previous year end by the company. The SARs vest over a twoyear
period and thus at 31 October 2004 there would be a weighting of the eventual cost by 1 year/2 years. Therefore, an
additional liability and expense of $50 million should be accounted for in the financial statements at 31 October 2005. The
SARs would be settled on 1 December 2005 at $9 x 10 million shares, i.e. $90 million. The increase in the value of the
SARs since the year end would not be accrued in the financial statements but charged to profit or loss in the year ended31 October 2006. -
第3题:
2 Ice-Time Ltd (ITL) manufactures a range of sports equipment used in a variety of winter-sports in Snowland.
Development engineers within ITL have recently developed a prototype of a small engine-propelled bobsleigh named
the ‘Snowballer’, which has been designed for use by young children. The directors of ITL recently spent £200,000
on market research, the findings of which led them to believe that a market exists for the Snowballer.
The marketing director has suggested that ITL should use the ‘Olympic’ brand in order to market the Snowballer.
The finance director of ITL has gathered relevant information and prepared the following evaluation relating to the
proposed manufacture and sale of the Snowballer.
(1) Sales are expected to be 3,200 units per annum at a selling price of £2,500 per unit.
(2) Variable material, labour, and overhead costs are estimated at £1,490 per unit.
(3) In addition, a royalty of £150 per unit would be payable to Olympic plc, for the use of their brand name.
(4) Fixed overheads are estimated at £900,000 per annum. These overheads cannot be avoided until the end of the
year in which the Snowballer is withdrawn from the market.
(5) An initial investment of £5 million would be required. A government grant equal to 50% of the initial investment
would be received on the date the investment is made. However, because the Snowballer would be classified as
a luxury good, no tax allowances would be available on this initial investment. The estimated life cycle of the
Snowballer is six years.
(6) Corporation tax at the rate of 30% per annum is payable in the year in which profit occurs.
(7) All cash flows are stated in current prices and, with the exception of the initial investment and the government
grant, will occur at the end of each year.
(8) The nominal cost of capital is 15·44%. Annual inflation during the period is expected to amount to 4%.
Required:
(a) Calculate the net present value (NPV) of the Snowballer proposal and recommend whether it should be
undertaken by the directors of ITL. (4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第4题:
听力原文:M: Good news! The current price of land we bought last year has increased greatly. How about reporting it in the profit and loss account?
W: Wait a minute. According to the Prudence Concept, if the market price is higher than the cost, the higher amount is ignored in the accounts.
Q: Why can't they record the gains right now?
(16)
A.Because of the prudence concept.
B.Because of the materiality concept.
C.Because of the matching principle.
D.Because of the Dual Aspects Concept.
正确答案:A
解析:女士说“根据会计的谨慎原则,当市场价高于成本时,按成本价入账。” -
第5题:
The primary purpose of a stock split include ().A.to increase the number of shares outstanding
B.reduce the market price of the stock per share
C.reduce earnings per share
D.increase the market activity of the shares
E.increase paid-in capital
正确答案:ABCD
-
第6题:
A manufacturing company, Man Co, has two divisions: Division L and Division M. Both divisions make a single standardised product. Division L makes component L, which is supplied to both Division M and external customers.
Division M makes product M using one unit of component L and other materials. It then sells the completed
product M to external customers. To date, Division M has always bought component L from Division L.
The following information is available:

Division L charges the same price for component L to both Division M and external customers. However, it does not incur the selling and distribution costs when transferring internally.
Division M has just been approached by a new supplier who has offered to supply it with component L for $37 per unit. Prior to this offer, the cheapest price which Division M could have bought component L for from outside the group was $42 per unit.
It is head office policy to let the divisions operate autonomously without interference at all.
Required:
(a) Calculate the incremental profit/(loss) per component for the group if Division M accepts the new supplier’s
offer and recommend how many components Division L should sell to Division M if group profits are to be
maximised. (3 marks)
(b) Using the quantities calculated in (a) and the current transfer price, calculate the total annual profits of each division and the group as a whole. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the problems which will arise if the transfer price remains unchanged and advise the divisions on a suitable alternative transfer price for component L. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)MaximisinggroupprofitDivisionLhasenoughcapacitytosupplybothDivisionManditsexternalcustomerswithcomponentL.Therefore,incrementalcostofDivisionMbuyingexternallyisasfollows:CostperunitofcomponentLwhenboughtfromexternalsupplier:$37CostperunitforDivisionLofmakingcomponentL:$20.ThereforeincrementalcosttogroupofeachunitofcomponentLbeingboughtinbyDivisionMratherthantransferredinternally:$17($37–20).Fromthegroup’spointofview,themostprofitablecourseofactionisthereforethatall120,000unitsofcomponentLshouldbetransferredinternally.(b)CalculatingtotalgroupprofitTotalgroupprofitswillbeasfollows:DivisionL:Contributionearnedpertransferredcomponent=$40–$20=$20Profitearnedpercomponentsoldexternally=$40–$24=$16(c)ProblemswithcurrenttransferpriceandsuggestedalternativeTheproblemisthatthecurrenttransferpriceof$40perunitisnowtoohigh.Whilstthishasnotbeenaproblembeforesinceexternalsupplierswerecharging$42perunit,itisaproblemnowthatDivisionMhasbeenofferedcomponentLfor$37perunit.IfDivisionMnowactsinitsowninterestsratherthantheinterestsofthegroupasawhole,itwillbuycomponentLfromtheexternalsupplierratherthanfromDivisionL.ThiswillmeanthattheprofitsofthegroupwillfallsubstantiallyandDivisionLwillhavesignificantunusedcapacity.Consequently,DivisionLneedstoreduceitsprice.Thecurrentpricedoesnotreflectthefactthattherearenosellinganddistributioncostsassociatedwithtransferringinternally,i.e.thecostofsellinginternallyis$4lessforDivisionLthansellingexternally.So,itcouldreducethepriceto$36andstillmakethesameprofitonthesesalesasonitsexternalsales.ThiswouldthereforebethesuggestedtransferpricesothatDivisionMisstillsaving$1perunitcomparedtotheexternalprice.Atransferpriceof$37wouldalsopresumablybeacceptabletoDivisionMsincethisisthesameastheexternalsupplierisoffering. -
第7题:
PV Co is evaluating an investment proposal to manufacture Product W33, which has performed well in test marketing trials conducted recently by the company’s research and development division. The following information relating to this investment proposal has now been prepared.
Initial investment $2 million
Selling price (current price terms) $20 per unit
Expected selling price inflation 3% per year
Variable operating costs (current price terms) $8 per unit
Fixed operating costs (current price terms) $170,000 per year
Expected operating cost inflation 4% per year
The research and development division has prepared the following demand forecast as a result of its test marketing trials. The forecast reflects expected technological change and its effect on the anticipated life-cycle of Product W33.

It is expected that all units of Product W33 produced will be sold, in line with the company’s policy of keeping no inventory of finished goods. No terminal value or machinery scrap value is expected at the end of four years, when production of Product W33 is planned to end. For investment appraisal purposes, PV Co uses a nominal (money) discount rate of 10% per year and a target return on capital employed of 30% per year. Ignore taxation.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the key stages in the capital investment decision-making process, and the role of
investment appraisal in this process. (7 marks)
(b) Calculate the following values for the investment proposal:
(i) net present value;
(ii) internal rate of return;
(iii) return on capital employed (accounting rate of return) based on average investment; and
(iv) discounted payback period. (13 marks)
(c) Discuss your findings in each section of (b) above and advise whether the investment proposal is financially acceptable. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Thekeystagesinthecapitalinvestmentdecision-makingprocessareidentifyinginvestmentopportunities,screeninginvestmentproposals,analysingandevaluatinginvestmentproposals,approvinginvestmentproposals,andimplementing,monitoringandreviewinginvestments.IdentifyinginvestmentopportunitiesInvestmentopportunitiesorproposalscouldarisefromanalysisofstrategicchoices,analysisofthebusinessenvironment,researchanddevelopment,orlegalrequirements.Thekeyrequirementisthatinvestmentproposalsshouldsupporttheachievementoforganisationalobjectives.ScreeninginvestmentproposalsIntherealworld,capitalmarketsareimperfect,soitisusualforcompaniestoberestrictedintheamountoffinanceavailableforcapitalinvestment.Companiesthereforeneedtochoosebetweencompetinginvestmentproposalsandselectthosewiththebeststrategicfitandthemostappropriateuseofeconomicresources.AnalysingandevaluatinginvestmentproposalsCandidateinvestmentproposalsneedtobeanalysedindepthandevaluatedtodeterminewhichofferthemostattractiveopportunitiestoachieveorganisationalobjectives,forexampletoincreaseshareholderwealth.Thisisthestagewhereinvestmentappraisalplaysakeyrole,indicatingforexamplewhichinvestmentproposalshavethehighestnetpresentvalue.ApprovinginvestmentproposalsThemostsuitableinvestmentproposalsarepassedtotherelevantlevelofauthorityforconsiderationandapproval.Verylargeproposalsmayrequireapprovalbytheboardofdirectors,whilesmallerproposalsmaybeapprovedatdivisionallevel,andsoon.Onceapprovalhasbeengiven,implementationcanbegin.Implementing,monitoringandreviewinginvestmentsThetimerequiredtoimplementtheinvestmentproposalorprojectwilldependonitssizeandcomplexity,andislikelytobeseveralmonths.Followingimplementation,theinvestmentprojectmustbemonitoredtoensurethattheexpectedresultsarebeingachievedandtheperformanceisasexpected.Thewholeoftheinvestmentdecision-makingprocessshouldalsobereviewedinordertofacilitateorganisationallearningandtoimprovefutureinvestmentdecisions. -
第8题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第9题:
For the year just ended, N company had an earnings of$ 2 per share and paid a dividend of $ 1. 2 on its stock. The growth rate in net income and dividend are both expected to be a constant 7 percent per year, indefinitely. N company has a Beta of 0. 8, the risk - free interest rate is 6 percent, and the market risk premium is 8 percent.
P Company is very similar to N company in growth rate, risk and dividend. payout ratio. It had 20 million shares outstanding and an earnings of $ 36 million for the year just ended. The earnings will increase to $ 38. 5 million the next year.
Requirement :
A. Calculate the expected rate of return on N company 's equity.
B. Calculate N Company 's current price-earning ratio and prospective price - earning ratio.
C. Using N company 's current price-earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
D. Using N company 's prospective price - earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
答案:解析:A. The expected rate of return on N company's equity =6% +0. 8*8% =12.4%
B. Current price -earning ratio = (1. 2/2) * (1 +7% )/ (12.4% -7% ) =11. 89
Prospective price - earning ratio = (1. 2/2) / (12. 4% - 70% ) =11. 11
C. P company's stock = 11. 89* 36/20 = 21. 4
D. P company's stock = 11. 11* 38. 5/20 = 21. 39
-
第10题:
M company is a manufactory which produces toys.The budgeted production and sales of the company are both expected to be 200 units in the coming year, the budgeted selling price is $ 370 per unit. The following information mimes to the costs of producing 200 toys:
Per unit ($) Total ($)
Direct material costs 1 50 30 000
Direct labor costs 80 1 6 000
Variable production overheads 50 10 000
Variable selling and administration overheads 30 6 000
Fixed production overheads 6 000
Fixed selling and administration overheads 3 000
Requirement:
A.Calculate the total contribution margin.
B.Calculate the amounts of profit at the budgeted level of production.
C.Calculate the break - even point in units and the margin of safety.
D.If M company desires a profit of$4 800, calculate the number of units that it must produce and sell.
答案:解析:A.Total contribution margin=370*200 - (150 +80 +50 +30) *200 =12 000
B.The amounts of profit at the budgeted level of production=12 000 -(6 000 +3 000) =3 000
C.Break - even point in units= (6 000 +3 000)/(3 70 - 310) =150
The marsin of safety= (200 - 150) *370 =18 500
D.4 800= (370 - 310) *Q-9 000
The number of units = (4 800 +9 000)/ (370 -310) =230
-
第11题:
填空题The price of oil in the world market has (great) ____ increased in recent months.正确答案: greatly解析:
本题考查词性转换。句意:最近几个月,世界油价大幅度上涨。great修饰的是动词increased,要用副词形式。故填入greatly。 -
第12题:
单选题Which of the following statements is closest in meaning to what was said in the recording?ACounterfeiting has led to the drop of the price of desktop-publishing systems.
BCounterfeiting has gone mainstream since the price of desktop-publishing systems has dropped.
CSkilled crooks have led to the drop of the price of desktop-publishing systems.
D14% of the counterfeits seized this year were digitally produced, compared with 1% a decade ago.
正确答案: B解析:
录音开头提到“没有任何文件是安全的了,伪造曾经是熟练使用昂贵雕刻和印刷设备的骗子的领域,自从desktop-publishing systems下降后,伪造已成为了主流现象”,因此选项B符合录音内容。
【录音原文】
No document is safe any more. Counterfeiting, once the domain of skilled crooks who used expensive engraving and printing equipment, has gone mainstream since the price of desktop-publishing systems has dropped. Virtually any kind of paper can be forged, including cheques, banknotes, stock and bond certificates, passports and security cards. For currency alone, millions of dollars in counterfeit banknotes make their way into circulation each year, and 40% of the counterfeits seized this year were digitally produced, compared with 1% a decade ago. -
第13题:
18 Which of the following statements about accounting ratios and their interpretation are correct?
1 A low-geared company is more able to survive a downturn in profit than a highly-geared company.
2 If a company has a high price earnings ratio, this will often indicate that the market expects its profits to rise.
3 All companies should try to achieve a current ratio (current assets/current liabilities) of 2:1.
A 2 and 3 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 and 2 only
D All three statements are correct
正确答案:C
-
第14题:
5 An enterprise has made a material change to an accounting policy in preparing its current financial statements.
Which of the following disclosures are required by IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates
and errors in these financial statements?
1 The reasons for the change.
2 The amount of the consequent adjustment in the current period and in comparative information for prior periods.
3 An estimate of the effect of the change on future periods, where possible.
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three items
正确答案:A
-
第15题:
(ii) Division C is considering a decision to lower its selling price to customers external to the group to $95
per kilogram. If implemented, this decision is expected to increase sales to external customers to
70,000 kilograms.
Required:
For BOTH the current selling price of CC of $105 per kilogram and the proposed selling price of $95
per kilogram, prepare a detailed analysis of revenue, costs and net profits of BAG.
Note: in addition, comment on other considerations that should be taken into account before this selling
price change is implemented. (6 marks)
正确答案: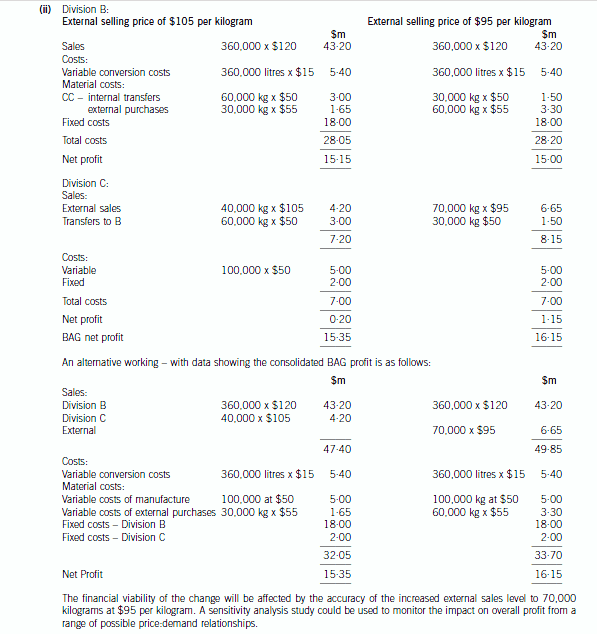
-
第16题:
The _______ price in our market is $8 per case.A.prevalence
B.prevailing
C.prevailed
D.prevail
正确答案:B
-
第17题:
The primary purpose of a stock split is to ( )
A. increase paid-in capital
B. reduce the market price of the stock per share
C. increase the market price of the stock per share
D. increase retained earnings
正确答案:B
-
第18题:
KFP Co, a company listed on a major stock market, is looking at its cost of capital as it prepares to make a bid to buy a rival unlisted company, NGN. Both companies are in the same business sector. Financial information on KFP Co and NGN is as follows:

NGN has a cost of equity of 12% per year and has maintained a dividend payout ratio of 45% for several years. The current earnings per share of the company is 80c per share and its earnings have grown at an average rate of 4·5% per year in recent years.
The ex div share price of KFP Co is $4·20 per share and it has an equity beta of 1·2. The 7% bonds of the company are trading on an ex interest basis at $94·74 per $100 bond. The price/earnings ratio of KFP Co is eight times.
The directors of KFP Co believe a cash offer for the shares of NGN would have the best chance of success. It has been suggested that a cash offer could be financed by debt.
Required:
(a) Calculate the weighted average cost of capital of KFP Co on a market value weighted basis. (10 marks)
(b) Calculate the total value of the target company, NGN, using the following valuation methods:
(i) Price/earnings ratio method, using the price/earnings ratio of KFP Co; and
(ii) Dividend growth model. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the relationship between capital structure and weighted average cost of capital, and comment on
the suggestion that debt could be used to finance a cash offer for NGN. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(b)(i)Price/earningsratiomethodEarningspershareofNGN=80cpersharePrice/earningsratioofKFPCo=8SharepriceofNGN=80x8=640cor$6·40NumberofordinarysharesofNGN=5/0·5=10millionsharesValueofNGN=6·40x10m=$64millionHowever,itcanbearguedthatareductionintheappliedprice/earningsratioisneededasNGNisunlistedandthereforeitssharesaremoredifficulttobuyandsellthanthoseofalistedcompanysuchasKFPCo.Ifwereducetheappliedprice/earningsratioby10%(othersimilarpercentagereductionswouldbeacceptable),itbecomes7·2timesandthevalueofNGNwouldbe(80/100)x7·2x10m=$57·6million(ii)DividendgrowthmodelDividendpershareofNGN=80cx0·45=36cpershareSincethepayoutratiohasbeenmaintainedforseveralyears,recentearningsgrowthisthesameasrecentdividendgrowth,i.e.4·5%.Assumingthatthisdividendgrowthcontinuesinthefuture,thefuturedividendgrowthratewillbe4·5%.Sharepricefromdividendgrowthmodel=(36x1·045)/(0·12–0·045)=502cor$5·02ValueofNGN=5·02x10m=$50·2million(c)Adiscussionofcapitalstructurecouldstartfromrecognisingthatequityismoreexpensivethandebtbecauseoftherelativeriskofthetwosourcesoffinance.Equityisriskierthandebtandsoequityismoreexpensivethandebt.Thisdoesnotdependonthetaxefficiencyofdebt,sincewecanassumethatnotaxesexist.Wecanalsoassumethatasacompanygearsup,itreplacesequitywithdebt.Thismeansthatthecompany’scapitalbaseremainsconstantanditsweightedaveragecostofcapital(WACC)isnotaffectedbyincreasinginvestment.Thetraditionalviewofcapitalstructureassumesanon-linearrelationshipbetweenthecostofequityandfinancialrisk.Asacompanygearsup,thereisinitiallyverylittleincreaseinthecostofequityandtheWACCdecreasesbecausethecostofdebtislessthanthecostofequity.Apointisreached,however,wherethecostofequityrisesataratethatexceedsthereductioneffectofcheaperdebtandtheWACCstartstoincrease.Inthetraditionalview,therefore,aminimumWACCexistsand,asaresult,amaximumvalueofthecompanyarises.ModiglianiandMillerassumedaperfectcapitalmarketandalinearrelationshipbetweenthecostofequityandfinancialrisk.Theyarguedthat,asacompanygearedup,thecostofequityincreasedataratethatexactlycancelledoutthereductioneffectofcheaperdebt.WACCwasthereforeconstantatalllevelsofgearingandnooptimalcapitalstructure,wherethevalueofthecompanywasatamaximum,couldbefound.Itwasarguedthattheno-taxassumptionmadebyModiglianiandMillerwasunrealistic,sinceintherealworldinterestpaymentswereanallowableexpenseincalculatingtaxableprofitandsotheeffectivecostofdebtwasreducedbyitstaxefficiency.Theyrevisedtheirmodeltoincludethistaxeffectandshowedthat,asaresult,theWACCdecreasedinalinearfashionasacompanygearedup.Thevalueofthecompanyincreasedbythevalueofthe‘taxshield’andanoptimalcapitalstructurewouldresultbygearingupasmuchaspossible.Itwaspointedoutthatmarketimperfectionsassociatedwithhighlevelsofgearing,suchasbankruptcyriskandagencycosts,wouldlimittheextenttowhichacompanycouldgearup.Inpractice,therefore,itappearsthatcompaniescanreducetheirWACCbyincreasinggearing,whileavoidingthefinancialdistressthatcanariseathighlevelsofgearing.Ithasfurtherbeensuggestedthatcompanieschoosethesourceoffinancewhich,foronereasonoranother,iseasiestforthemtoaccess(peckingordertheory).Thisresultsinaninitialpreferenceforretainedearnings,followedbyapreferencefordebtbeforeturningtoequity.TheviewsuggeststhatcompaniesmaynotinpracticeseektominimisetheirWACC(andconsequentlymaximisecompanyvalueandshareholderwealth).TurningtothesuggestionthatdebtcouldbeusedtofinanceacashbidforNGN,thecurrentandpostacquisitioncapitalstructuresandtheirrelativegearinglevelsshouldbeconsidered,aswellastheamountofdebtfinancethatwouldbeneeded.Earliercalculationssuggestthatatleast$58mwouldbeneeded,ignoringanypremiumpaidtopersuadetargetcompanyshareholderstoselltheirshares.Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofKFPCois60%(15m/25m).Thedebtofthecompanywouldincreaseby$58minordertofinancethebidandbyafurther$20maftertheacquisition,duetotakingontheexistingdebtofNGN,givingatotalof$93m.Ignoringotherfactors,thegearingwouldincreaseto372%(93m/25m).KFPCowouldneedtoconsiderhowitcouldservicethisdangerouslyhighlevelofgearinganddealwiththesignificantriskofbankruptcythatitmightcreate.ItwouldalsoneedtoconsiderwhetherthebenefitsarisingfromtheacquisitionofNGNwouldcompensateforthesignificantincreaseinfinancialriskandbankruptcyriskresultingfromusingdebtfinance. -
第19题:
JJG Co is planning to raise $15 million of new finance for a major expansion of existing business and is considering a rights issue, a placing or an issue of bonds. The corporate objectives of JJG Co, as stated in its Annual Report, are to maximise the wealth of its shareholders and to achieve continuous growth in earnings per share. Recent financial information on JJG Co is as follows:
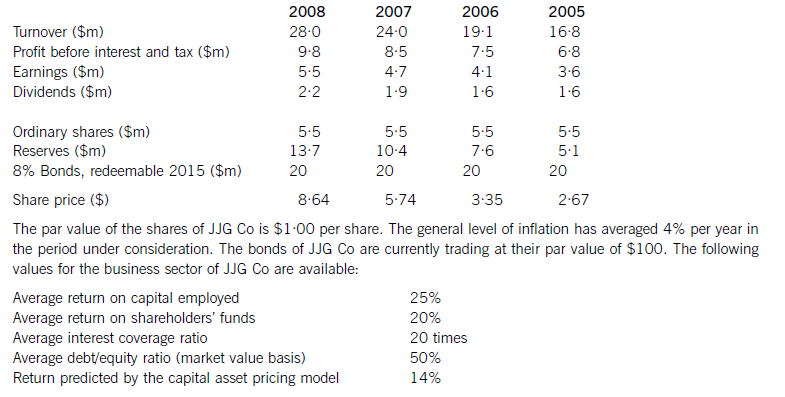
Required:
(a) Evaluate the financial performance of JJG Co, and analyse and discuss the extent to which the company has achieved its stated corporate objectives of:
(i) maximising the wealth of its shareholders;
(ii) achieving continuous growth in earnings per share.
Note: up to 7 marks are available for financial analysis.(12 marks)
(b) If the new finance is raised via a rights issue at $7·50 per share and the major expansion of business has
not yet begun, calculate and comment on the effect of the rights issue on:
(i) the share price of JJG Co;
(ii) the earnings per share of the company; and
(iii) the debt/equity ratio. (6 marks)
(c) Analyse and discuss the relative merits of a rights issue, a placing and an issue of bonds as ways of raising the finance for the expansion. (7 marks)
正确答案:
AchievementofcorporateobjectivesJJGCohasshareholderwealthmaximisationasanobjective.Thewealthofshareholdersisincreasedbydividendsreceivedandcapitalgainsonsharesowned.Totalshareholderreturncomparesthesumofthedividendreceivedandthecapitalgainwiththeopeningshareprice.TheshareholdersofJJGCohadareturnof58%in2008,comparedwithareturnpredictedbythecapitalassetpricingmodelof14%.Thelowestreturnshareholdershavereceivedwas21%andthehighestreturnwas82%.Onthisbasis,theshareholdersofthecompanyhaveexperiencedasignificantincreaseinwealth.Itisdebatablewhetherthishasbeenasaresultoftheactionsofthecompany,however.Sharepricesmayincreaseirrespectiveoftheactionsanddecisionsofmanagers,orevendespitethem.Infact,lookingatthedividendpersharehistoryofthecompany,therewasoneyear(2006)wheredividendswereconstant,eventhoughearningspershareincreased.Itisalsodifficulttoknowwhenwealthhasbeenmaximised.Anotherobjectiveofthecompanywastoachieveacontinuousincreaseinearningspershare.Analysisshowsthatearningspershareincreasedeveryyear,withanaverageincreaseof14·9%.Thisobjectiveappearstohavebeenachieved.CommentonfinancialperformanceReturnoncapitalemployed(ROCE)hasbeengrowingtowardsthesectoraverageof25%onayear-by-yearbasisfrom22%in2005.Thissteadygrowthintheprimaryaccountingratiocanbecontrastedwithirregulargrowthinturnover,thereasonsforwhichareunknown.Returnonshareholders’fundshasbeenconsistentlyhigherthantheaverageforthesector.ThismaybeduemoretothecapitalstructureofJJGCothantogoodperformancebythecompany,however,inthesensethatshareholders’fundsaresmalleronabookvaluebasisthanthelong-termdebtcapital.Ineverypreviousyearbut2008thegearingofthecompanywashigherthanthesectoraverage.(b)CalculationoftheoreticalexrightspershareCurrentshareprice=$8·64pershareCurrentnumberofshares=5·5millionsharesFinancetoberaised=$15mRightsissueprice=$7·50pershareNumberofsharesissued=15m/7·50=2millionsharesTheoreticalexrightspricepershare=((5·5mx8·64)+(2mx7·50))/7·5m=$8·34pershareThesharepricewouldfallfrom$8·64to$8·34pershareHowever,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonearningspershareCurrentEPS=100centspershareRevisedEPS=100x5·5m/7·5m=73centspershareTheEPSwouldfallfrom100centspershareto73centspershareHowever,asmentionedearlier,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonthedebt/equityratioCurrentdebt/equityratio=100x20/47·5=42%Revisedmarketvalueofequity=7·5mx8·34=$62·55millionReviseddebt/equityratio=100x20/62·55=32%Thedebt/equityratiowouldfallfrom42%to32%,whichiswellbelowthesectoraveragevalueandwouldsignalareductioninfinancialrisk(c)Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofJJGCois42%(20/47·5).Althoughthisislessthanthesectoraveragevalueof50%,itismoreusefulfromafinancialriskperspectivetolookattheextenttowhichinterestpaymentsarecoveredbyprofits.Theinterestonthebondissueis$1·6million(8%of$20m),givinganinterestcoverageratioof6·1times.IfJJGCohasoverdraftfinance,theinterestcoverageratiowillbelowerthanthis,butthereisinsufficientinformationtodetermineifanoverdraftexists.Theinterestcoverageratioisnotonlybelowthesectoraverage,itisalsolowenoughtobeacauseforconcern.Whiletheratioshowsanupwardtrendovertheperiodunderconsideration,itstillindicatesthatanissueoffurtherdebtwouldbeunwise.Aplacing,oranyissueofnewsharessuchasarightsissueorapublicoffer,woulddecreasegearing.Iftheexpansionofbusinessresultsinanincreaseinprofitbeforeinterestandtax,theinterestcoverageratiowillincreaseandfinancialriskwillfall.GiventhecurrentfinancialpositionofJJGCo,adecreaseinfinancialriskiscertainlypreferabletoanincrease.Aplacingwilldiluteownershipandcontrol,providingthenewequityissueistakenupbynewinstitutionalshareholders,whilearightsissuewillnotdiluteownershipandcontrol,providingexistingshareholderstakeuptheirrights.Abondissuedoesnothaveownershipandcontrolimplications,althoughrestrictiveornegativecovenantsinbondissuedocumentscanlimittheactionsofacompanyanditsmanagers.Allthreefinancingchoicesarelong-termsourcesoffinanceandsoareappropriateforalong-terminvestmentsuchastheproposedexpansionofexistingbusiness.Equityissuessuchasaplacingandarightsissuedonotrequiresecurity.Noinformationisprovidedonthenon-currentassetsofJJGCo,butitislikelythattheexistingbondissueissecured.Ifanewbondissuewasbeingconsidered,JJGCowouldneedtoconsiderwhetherithadsufficientnon-currentassetstoofferassecurity,althoughitislikelythatnewnon-currentassetswouldbeboughtaspartofthebusinessexpansion. -
第20题:
N Company manufactures a kind of product used throughout the machinery industry. The standard price of the materials for the products is $6 per kilogram; the standard quantity of materials allowed per unit is 1.5 kilograms. During July, 2,000 units of the products were finished, for which 3,200 kilograms of materials were used at a total direct material cost of $18560. A. Calculate the direct material price variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) and who is generally responsible for this variance. B. Calculate the direct material quantity variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) and who is generally responsible for this variance. C. Calculate the total direct material cost variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
正确答案:a. Direct material price variance
=Actual quantity ×(actual price – standard price)
=3200× [(18560/3200)-6]
=3200×(5.8-6)
=-640(0.5分) (F) (0.5分)
Purchasing department (1分)
b. Direct material quantity variance
=Standard price×(actual quantity –standard quantity)
=6×[3200-(2000×1.5)]
=6×(3200-3000)
=$1200(0.5分) (U) (0.5分)
Manufacturing department (1分)
c. Total direct material cost variance
=Direct material price variance +Direct material quantity variance
=1200-640=$560(0.5分) (U) (0.5分)
or =Actual cost-Standard cost
=18560-(1.5×6×2000)
=$560(u)
依据:《财务成本管理》教材第十四章第430页。
-
第21题:
N Company manufactures a kind of product used throughout the machinery industry.The standard price of the materials for the products is $ 6 per kilogram; the standard quantity of materials allowed per unit is 1.5 kilograms. During July, 2 000 units of the products were finished, for which 3 200 kilograms of materials were used at a total direct material cost of $ 18 560.
Requirment :
A. Calculate the direct material price variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) and who is generally responsible for this variance.
B. Calculate the direct material quantity variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) and who is generally responsible for this variance.
C. Calculate the total direct material cost variance for July. Indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
答案:解析:Answer:
A. Direct material price variance
= Actual quantity*( actual price - standard price)
=3 200 * (18 560/3 200 -6)
=3 200* (5. 8 -6)
= -640 (F)
Purchasing department
B. Direct material quantity variance= Standard price * ( actual quantity - standard quantity)=6 *(3 200 -2 000 *1.5)= $1 200 (U)
Manufacturing department
C. Total direct material cost variance
= Direct material price variance + Direct material quantity variance
=1 200 - 640 = $ 560 (U)
or = Actual cost - Standard cost
=18 560 - (1. 5*6*2 000)
=$560(U)
-
第22题:
Given the following table definition: STOCK: item VARCHAR(30) status CHAR(1) quantity INT price DEC(7,2) If items are indicated to be out of stock by setting STATUS to NULL and QUANTITY and PRICE to zero, which of the following statements would be used to update the STOCK table to indicate that all the items whose description begins with the letter "S" are out of stock?()
- A、UPDATE stock SET (status = NULL; quantity, price = 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
- B、UPDATE stock SET (status, quantity, price) = (NULL, 0, 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
- C、UPDATE stock SET status = NULL, SET quantity = 0, SET price = 0 WHERE item LIKE 'S%'
- D、UPDATE stock SET (status = NULL), (quantity = 0), (price = 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
正确答案:B -
第23题:
单选题Given the following table definition: STOCK: item VARCHAR(30) status CHAR(1) quantity INT price DEC(7,2) If items are indicated to be out of stock by setting STATUS to NULL and QUANTITY and PRICE to zero, which of the following statements would be used to update the STOCK table to indicate that all the items whose description begins with the letter "S" are out of stock?()AUPDATE stock SET (status = NULL; quantity, price = 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
BUPDATE stock SET (status, quantity, price) = (NULL, 0, 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
CUPDATE stock SET status = NULL, SET quantity = 0, SET price = 0 WHERE item LIKE 'S%'
DUPDATE stock SET (status = NULL), (quantity = 0), (price = 0) WHERE item LIKE S%
正确答案: A解析: 暂无解析
