抗生素(antibiotics)
题目
抗生素(antibiotics)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
正确答案:抗生素是生物,包括微生物,植物和动物在内,在其生命活动过程中所产生的(或由其它方法获得的),能在低微浓度下有选择地抑制或影响它种生物机能的化学物质”。
更多“抗生素(antibiotics) ”相关问题
-
第1题:
共用题干
第三篇
Be Alert to Antimicrobial(抗微生物的)Resistance
The ability of micro-organisms to find ways to avoid the action of the drugs used to cure the infections
they cause is increasingly recognized as a global public health issue.Some bacteria have developed mecha-
nisms which make them resistant to many of the antibiotics(抗生素)normally used for their treatment. They
are known as multi一drug resistant bacteria,posing particular difficulties,as there may be few or no alternative
options for therapy.They constitute a growing and global public health problem. WHO suggests that countries
should be prepared to implement hospital infection control measures to limit the spread of multi-drug resistant
strains(菌株)and to reinforce national policy on prudent use of antibiotics , reducing the generation of
antibiotic resistant bacteria.
An article published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases on 1 1 August 2010 identified a new gene that
enables some types of bacteria to be highly resistant to almost all antibiotics.The article has drawn attention
to the issue of antimicrobial resistance,and,in particular,has raised awareness of infections caused by multi-
drug resistant bacteria.
While multi-drug resistant bacteria are not new and will continue to appear,this development requires
monitoring and further study to understand the extent and modes of transmission,and to define the most effec-
tive measures for control.
Those called upon to be alert to the problem of antimicrobial resistance and take appropriate action in-
clude consumers , managers of hospitals , patients , as well as national governments , the pharmaceutical(制药
的)industry,and international agencies.
WHO strongly recommends that governments focus control and prevention efforts in the following areas
like surveillance for antimicrobial resistance;rational antibiotic use,including education of healthcare workers
and the public in the appropriate use of antibiotics;introducing or enforcing legislation related to stopping the
selling of antibiotics without prescription;and strict adherence to infection prevention and control measures,
including the use of hand-washing measures,particularly in healthcare facilities.
Successful control of multidrug-resistant micro-organisms has been documented in many countries,and
the existing and well-known infection prevention and control measures can effectively reduce transmission of
multi-drug resistant organisms if systematically implemented.
WHO will continue to support countries to develop relevant policies,and to coordinate international
efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.Antimicrobial resistance will be the theme of WHO's World Health
Day 2011.We learn from the passage that_________.
A:antimicrobial resistance was not noticed until 2010
B:without WHO,no country will be safe in the war against antimicrobial resistance
C:WHO will focus its prevention and control efforts in poor countries
D:further study is needed to deal with the transmission of multi-drug resistant bacteria答案:D解析:由第一段中的“there may be few or no alternative...”可知选D。
根据语境可知,此处是指“慎用抗生素”,故选B。
由第二段第一句“identified a new gene...”可知选A。
由第五段中的rational antibiotic use可知C项正确;由“education of… in the appropriate use of antibiotics”可知A项正确;由“enforcing legislation related to stopping the selling...”可知D 项正确。故选B。
由最后一段中的“will”可知,会有关于“multi-drug resistant bacteria”问题的进一步研究。 -
第2题:
共用题干
第三篇
Be Alert to Antimicrobial(抗微生物的)Resistance
The ability of micro-organisms to find ways to avoid the action of the drugs used to cure the infections
they cause is increasingly recognized as a global public health issue.Some bacteria have developed mecha-
nisms which make them resistant to many of the antibiotics(抗生素)normally used for their treatment. They
are known as multi一drug resistant bacteria,posing particular difficulties,as there may be few or no alternative
options for therapy.They constitute a growing and global public health problem. WHO suggests that countries
should be prepared to implement hospital infection control measures to limit the spread of multi-drug resistant
strains(菌株)and to reinforce national policy on prudent use of antibiotics , reducing the generation of
antibiotic resistant bacteria.
An article published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases on 1 1 August 2010 identified a new gene that
enables some types of bacteria to be highly resistant to almost all antibiotics.The article has drawn attention
to the issue of antimicrobial resistance,and,in particular,has raised awareness of infections caused by multi-
drug resistant bacteria.
While multi-drug resistant bacteria are not new and will continue to appear,this development requires
monitoring and further study to understand the extent and modes of transmission,and to define the most effec-
tive measures for control.
Those called upon to be alert to the problem of antimicrobial resistance and take appropriate action in-
clude consumers , managers of hospitals , patients , as well as national governments , the pharmaceutical(制药
的)industry,and international agencies.
WHO strongly recommends that governments focus control and prevention efforts in the following areas
like surveillance for antimicrobial resistance;rational antibiotic use,including education of healthcare workers
and the public in the appropriate use of antibiotics;introducing or enforcing legislation related to stopping the
selling of antibiotics without prescription;and strict adherence to infection prevention and control measures,
including the use of hand-washing measures,particularly in healthcare facilities.
Successful control of multidrug-resistant micro-organisms has been documented in many countries,and
the existing and well-known infection prevention and control measures can effectively reduce transmission of
multi-drug resistant organisms if systematically implemented.
WHO will continue to support countries to develop relevant policies,and to coordinate international
efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.Antimicrobial resistance will be the theme of WHO's World Health
Day 2011.WHO recommends governments to focus on the following areas EXCEPT_________.
A:education on the use of antibiotics
B:keeping hospitals from storing more antibiotics than they can use
C:control of antibiotic use
D:introduction of new regulations on the sale of antibiotics答案:B解析:由第一段中的“there may be few or no alternative...”可知选D。
根据语境可知,此处是指“慎用抗生素”,故选B。
由第二段第一句“identified a new gene...”可知选A。
由第五段中的rational antibiotic use可知C项正确;由“education of… in the appropriate use of antibiotics”可知A项正确;由“enforcing legislation related to stopping the selling...”可知D 项正确。故选B。
由最后一段中的“will”可知,会有关于“multi-drug resistant bacteria”问题的进一步研究。 -
第3题:
Doctors must stop telling patients to finish an entire course of antibiotics because it is driving antimicrobial resistance,and patients should be encouraged to continue taking medication only until they feel better to avoid the overuse of drugs,experts from bodies including Pubtic Health England and the University of Oxford are now advising.Current guidance from the NHS and the World Health Organisation says it is essential to'finish a course'of antibiotics to avoid triggering more virulent forms of disease.But in a new article in the British Medical Journal(BMJ),10 leading experts said the public health message is not backed by evidence and should be dropped.They claim it actually puts the public at greater risk from antimicrobial resistance."Historically,antibiotic courses were driven by fear of undertreatment,with less concern about overuse,"said lead author Martin Llewelyn,professor of infectious diseases at Brighton and Sussex Medical School."The idea that stopping antibiotic treatment early encourages antibiotic resistance is not supported by evidence,while taking antibiotics for longer than necessary increases the risk of resistance.We encourage policy makers,educators,and doctors to stop advocating'complete the course'when communicating with the public."Fears that stopping antibiotics early could trigger more dangerous forms of disease date back to Alexander Fleming who found that bacteria quickly become~acclimatised to penicillin and patients who take insufficient doses may transmit a more dangerous strain to family members.In his Nobel Prize acceptance speech in 1945,Fleming warned:"If you use penicillin,use enough."But in the BMJ article the experts argue that when a patient takes any antibiotics it allows dangerous strains of bacteria to grow on the skin and gut which could cause problems later.The longer the course,the more the resistance builds.They also warn that current guidance ignores the fact that patients often respond differently to the same antibiotic,with some needing longer courses than others.Commenting on the research Alison Holmes,Professor of Infectious Diseases at Imperial College London said it was'astonishing'that doctors still do not know the optimum duration for taking drugs even though a long course raises the risk of bacterial resistance."The'complete the course'message directly conflicts with the societal messages regarding the changes needed in behaviour and attitudes to minimise unnecessary exposure to anribiotics,"she said.However.Professor Helen Stokes-l.ampard.Chair of the Royal College of GPs,said:"Recommended courses of antibiotics are not random-they are tailored to individual conditions,and in many cases courses are quite short,for example for urinary tract infections.three days is ofren enough to cure the infection.We are concerned about the concept of patients stopping taking their medication mid-way through a course once ihey'feel better'.because improvement in symptoms does not necessarily mean the infection has been completely eradicated.It's important that patients have clear messages and the message to always take the full course of antibioiics is well known-changing this will simply confuse people."Chief medical officer Dame Sally Davies,also said that the message to the public shoulcl remain unchanged until there was further research."National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is currently developing guidance for managing common infections,which will look at all available evidence on appropriate prescribing of antibiotics,"she said."The Departmcnt of Health will continue to review the evidence on prescribing and drug resistant infections.As we aim to continue the great progress we have made at home and abroad on this i-ssue."
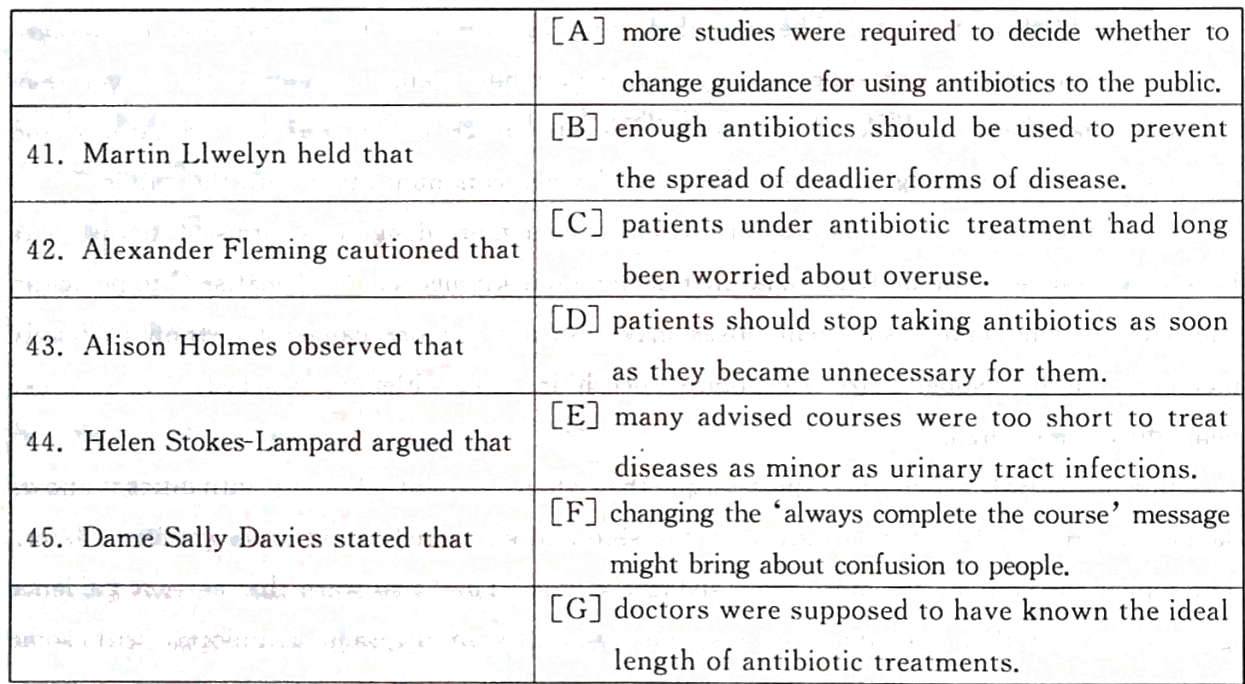
Alexander Fleming cautioned thatA.more studies were required to decide whether to change guldance for using antibiotics to the public.
B.enough antibiotics should be used to prevent the spread of deadlier forms of disease.
C.patients under antibiotic treatment had long been worried about overuse.
D.patients should stop taking antibiotics as soon as they became unnecessary for them.
E.many advised courses were too short to treat diseases as minor as urinary tract infections.
F.changing the'always complete the course'message might bring about confusion to people.
G.doctors were supposed to have known the ideal length of antibiotic treatments.答案:B解析:根据题干Alexander Fleming定位至第四段,首句介绍他的发现:服用青霉素(一种抗生素)不足的患者会传播更致命的疾病;第二句他警告:用青霉索,就要用足量;据此可推断:Fleming警告世人服用足量抗生索是为了预防更致命疾病的传播IB.与以上两句一致。 -
第4题:
广谱抗生素治疗中发生真菌感染,除选用抗真菌药物外,宜换用()
- A、窄谱抗生素
- B、广谱抗生素
- C、抑菌性抗生素
- D、杀菌性抗生素
- E、联合应用抗生素
正确答案:A -
第5题:
根据抗生素的化学结构,抗生素分为()、()、()、()和多肽类抗生素;根据抗生素的合成途径,抗生素分为()、肽类衍生物抗生素和糖类衍生物抗生素。
正确答案:—内酰胺类;氨基糖苷类;大环内酯类;四环类;氨基酸 -
第6题:
填空题根据抗生素的抗菌范围可将其分为抗()抗生素、抗()抗生素和()抗生素。正确答案: 革兰氏阳性菌 革兰氏阴性菌 广谱解析: 暂无解析 -
第7题:
填空题根据抗生素的化学结构,抗生素分为()、()、()、()和多肽类抗生素;根据抗生素的合成途径,抗生素分为()、肽类衍生物抗生素和糖类衍生物抗生素。正确答案: —内酰胺类,氨基糖苷类,大环内酯类,四环类,氨基酸解析: 暂无解析 -
第8题:
单选题选择抗生素的原则( )。A最贵的抗生素
B最新的抗生素
C能透过血脑屏障的抗生素
D副作用最小的抗生素
E不经肾脏排泄的抗生素
正确答案: C解析: 暂无解析 -
第9题:
共用题干
第三篇
Be Alert to Antimicrobial(抗微生物的)Resistance
The ability of micro-organisms to find ways to avoid the action of the drugs used to cure the infections
they cause is increasingly recognized as a global public health issue.Some bacteria have developed mecha-
nisms which make them resistant to many of the antibiotics(抗生素)normally used for their treatment. They
are known as multi一drug resistant bacteria,posing particular difficulties,as there may be few or no alternative
options for therapy.They constitute a growing and global public health problem. WHO suggests that countries
should be prepared to implement hospital infection control measures to limit the spread of multi-drug resistant
strains(菌株)and to reinforce national policy on prudent use of antibiotics , reducing the generation of
antibiotic resistant bacteria.
An article published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases on 1 1 August 2010 identified a new gene that
enables some types of bacteria to be highly resistant to almost all antibiotics.The article has drawn attention
to the issue of antimicrobial resistance,and,in particular,has raised awareness of infections caused by multi-
drug resistant bacteria.
While multi-drug resistant bacteria are not new and will continue to appear,this development requires
monitoring and further study to understand the extent and modes of transmission,and to define the most effec-
tive measures for control.
Those called upon to be alert to the problem of antimicrobial resistance and take appropriate action in-
clude consumers , managers of hospitals , patients , as well as national governments , the pharmaceutical(制药
的)industry,and international agencies.
WHO strongly recommends that governments focus control and prevention efforts in the following areas
like surveillance for antimicrobial resistance;rational antibiotic use,including education of healthcare workers
and the public in the appropriate use of antibiotics;introducing or enforcing legislation related to stopping the
selling of antibiotics without prescription;and strict adherence to infection prevention and control measures,
including the use of hand-washing measures,particularly in healthcare facilities.
Successful control of multidrug-resistant micro-organisms has been documented in many countries,and
the existing and well-known infection prevention and control measures can effectively reduce transmission of
multi-drug resistant organisms if systematically implemented.
WHO will continue to support countries to develop relevant policies,and to coordinate international
efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.Antimicrobial resistance will be the theme of WHO's World Health
Day 2011.Antimicrobial resistance has become a global public health issue because_________.
A:new antibiotics are too expensive for poor countries
B:infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria have killed a lot of people
C:scientists know nothing about multi-drug resistant bacteria
D:there may be few or no treatment to infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria答案:D解析:由第一段中的“there may be few or no alternative...”可知选D。
根据语境可知,此处是指“慎用抗生素”,故选B。
由第二段第一句“identified a new gene...”可知选A。
由第五段中的rational antibiotic use可知C项正确;由“education of… in the appropriate use of antibiotics”可知A项正确;由“enforcing legislation related to stopping the selling...”可知D 项正确。故选B。
由最后一段中的“will”可知,会有关于“multi-drug resistant bacteria”问题的进一步研究。 -
第10题:
共用题干
第三篇
Be Alert to Antimicrobial(抗微生物的)Resistance
The ability of micro-organisms to find ways to avoid the action of the drugs used to cure the infections
they cause is increasingly recognized as a global public health issue.Some bacteria have developed mecha-
nisms which make them resistant to many of the antibiotics(抗生素)normally used for their treatment. They
are known as multi一drug resistant bacteria,posing particular difficulties,as there may be few or no alternative
options for therapy.They constitute a growing and global public health problem. WHO suggests that countries
should be prepared to implement hospital infection control measures to limit the spread of multi-drug resistant
strains(菌株)and to reinforce national policy on prudent use of antibiotics , reducing the generation of
antibiotic resistant bacteria.
An article published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases on 1 1 August 2010 identified a new gene that
enables some types of bacteria to be highly resistant to almost all antibiotics.The article has drawn attention
to the issue of antimicrobial resistance,and,in particular,has raised awareness of infections caused by multi-
drug resistant bacteria.
While multi-drug resistant bacteria are not new and will continue to appear,this development requires
monitoring and further study to understand the extent and modes of transmission,and to define the most effec-
tive measures for control.
Those called upon to be alert to the problem of antimicrobial resistance and take appropriate action in-
clude consumers , managers of hospitals , patients , as well as national governments , the pharmaceutical(制药
的)industry,and international agencies.
WHO strongly recommends that governments focus control and prevention efforts in the following areas
like surveillance for antimicrobial resistance;rational antibiotic use,including education of healthcare workers
and the public in the appropriate use of antibiotics;introducing or enforcing legislation related to stopping the
selling of antibiotics without prescription;and strict adherence to infection prevention and control measures,
including the use of hand-washing measures,particularly in healthcare facilities.
Successful control of multidrug-resistant micro-organisms has been documented in many countries,and
the existing and well-known infection prevention and control measures can effectively reduce transmission of
multi-drug resistant organisms if systematically implemented.
WHO will continue to support countries to develop relevant policies,and to coordinate international
efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance.Antimicrobial resistance will be the theme of WHO's World Health
Day 2011.The word"prudent"in Paragraph 1 is closest in meaning to_________.
A:unwise
B:careful
C:wasteful
D:widespread答案:B解析:由第一段中的“there may be few or no alternative...”可知选D。
根据语境可知,此处是指“慎用抗生素”,故选B。
由第二段第一句“identified a new gene...”可知选A。
由第五段中的rational antibiotic use可知C项正确;由“education of… in the appropriate use of antibiotics”可知A项正确;由“enforcing legislation related to stopping the selling...”可知D 项正确。故选B。
由最后一段中的“will”可知,会有关于“multi-drug resistant bacteria”问题的进一步研究。 -
第11题:
全身情况不良病人选用()
- A、窄谱抗生素
- B、广谱抗生素
- C、抑菌性抗生素
- D、杀菌性抗生素
- E、联合应用抗生素
正确答案:B -
第12题:
混合感染时选用()
- A、窄谱抗生素
- B、广谱抗生素
- C、抑菌性抗生素
- D、杀菌性抗生素
- E、联合应用抗生素
正确答案:E -
第13题:
半合成抗生素(semi-synthetic antibiotics)
正确答案:在天然抗生素的基础上发展起来,针对天然抗生素的化学稳定性、毒副作用、抗菌谱等方面存在的问题,通过对天然抗生素进行结构改造,旨在增加稳定性、降低毒副作用、扩大抗菌谱、减少耐药性、改善生物利用度、提高治疗效力及改变用药途径。半合成抗生素已取得较大的发展,如半合成青霉素和半合成头孢菌素。 -
第14题:
单选题Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the eye that normally effects only small children, and it usually can be treated with antibiotics.Aeffects only small children
Beffects small children ordinarily
Caffected small children
Daffects small children
Eaffects only small children
正确答案: D解析:
“effect”做动词意为“造成; 招致; 产生”与句意不符,C项时态错误,D项与句意不符,故本题选E项。 -
第15题:
名词解释题半合成抗生素(semi-synthetic antibiotics)正确答案: 在天然抗生素的基础上发展起来,针对天然抗生素的化学稳定性、毒副作用、抗菌谱等方面存在的问题,通过对天然抗生素进行结构改造,旨在增加稳定性、降低毒副作用、扩大抗菌谱、减少耐药性、改善生物利用度、提高治疗效力及改变用药途径。半合成抗生素已取得较大的发展,如半合成青霉素和半合成头孢菌素。解析: 暂无解析 -
第16题:
名词解释题抗生素(antibiotics)正确答案: 是微生物的代谢产物或合成的类似物,在体外能抑制微生物的生长和存活,而对宿主不会产生严重的毒副作用。多数抗生素用于治疗细菌感染性疾病,某些抗生素还具有抗肿瘤、免疫抑制和刺激植物生长作用。解析: 暂无解析
