若有如下程序:public class Test {public static void main (String[] args) {int x=20;if (x>10) System.out.print(x-=5);if (x>5) System.out.print(x--);}}则程序运行后的输出结果是【 】。
题目
若有如下程序:
public class Test {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int x=20;
if (x>10) System.out.print(x-=5);
if (x>5) System.out.print(x--);
}
}则程序运行后的输出结果是【 】。
相似考题
更多“若有如下程序:public class Test {public static void main (String[] args) {int x=20;if (x>10 ”相关问题
-
第1题:
若有以下程序:includeusing namespace std;class Base{public:Base (){x=0;}int x;} 若有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: Base () { x=0; } int x; }; class Derived1 : virtual public Base { public: Derived1 () { x=10; } }; class Derived2 : virtual public Base { public: Derived2 () { x=20; } }; class Derived : public Derived1,protected Derived2{ }; int main() { Derived obi; cout<<obj.x<<endl; return 0; } 该程序运行后的输出结果是
A.20
B.30
C.10
D.0
正确答案:A
解析:本题考核虚基类的应用。本题中,虽然Derived1和Derived2都是由共同的基类x派生而来的,但由于引入了虚基类,使得它们分别对应基类的不同副本。这时数据成员x只存在一份拷贝,不论在类Derived1中修改,还是在类Derived2中修改,都是直接对这惟一拷贝进行操作。本题程序执行语句“Derived obj;”时,就会先调用虚基类Base的构造函数,使得x=0,然后执行类Derived1的构造函数使得x=10,再执行类Derived2的构造函数,使得x=20。最后输出x的值为20。 -
第2题:
若有以下程序:includeusing namespace Std;Class Base{public:Base(){x=0;}int x;};c 若有以下程序: #include<iostream> using namespace Std; Class Base {public: Base() {x=0;} int x;}; class Derivedl:virtua1 public Base {public: Derived1() {x=10;}}; class Derived2:virtual1 public Base {public: Derived2()
A.20
B.30
C.10
D.0
正确答案:A
解析: 本题考查虚基类的应用。虽然Derived1和Derived2都是由共同的基类x派生而来的,但由于引入了虚基类,使得它们分别对应基类的不同副本,这时数据成员x只存在一份拷贝,不论在类Derivedl中修改,还是在De- rived2中修改,都是直接对这惟一拷贝进行操作。本题程序执行语句“Derivedob“”时,就会先调用虚基类Base的构造函数,使得x=0,然后执行类Derived1的构造函数使得x=10,再执行类Derived2的构造函数,使得x=20。最后输出x的值为20。 -
第3题:
阅读下列说明和C++代码,填写程序中的空(1)~(6),将解答写入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
以下C++代码实现一个简单绘图工具,绘制不同形状以及不同颜色的图形。部分类及其关系如图6-1所示。
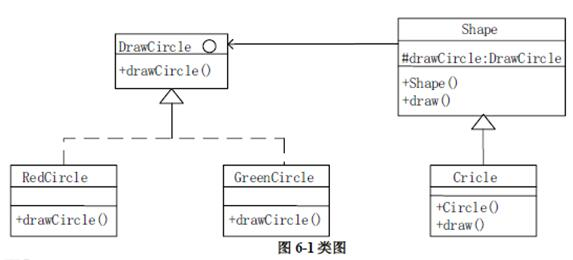
【C++代码】
#include?#include?using?namespace?std;class?DrawCircle?{??????//绘制圆形,抽象类? ? ? public: (1);//定义参数为?int?radius,?int?x,?inty? ?virtual~DrawCircle()?{?}};class?RedCircle:public?DrawCircle?{????//绘制红色圆形? ? ? ? public: void?drawCircle(intradius,?int?x,?int?y)?{cout?<?drawCircle?=?drawCircle;? }? ?virtual~shape()?{?}? public:? ?virtual?void?draw()?=?0;};class?Circle:public?Shape?{????//圆形? ? private:? ? ?int?x,y,radius;? ? public:? Circle(int?x,inty,int?radius,DrawCircle?*drawCircle)? (3)? {? this->x?=?x;? ?this->y?=?y;? ? this->radius?=?radius; }? ? ? public:? void?draw(){? drawCircle?-> (4); }};int?main(){Shape?*redCirclenew?Circle(100,100,10,????(5)????);//绘制红色圆形? Shape?*greenCircle=new?Circle(100,100,10, (6)??);//绘制绿色圆形redCircle >draw();? ?greenCircle?->draw();? ?return?0;}答案:解析:(6)(1)void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y)
(2)DrawCircle*drawCircle
(3)drawcircle
(4)drawCircle(radius,x,y)
(5)new RedCircle()
(6)new GreenCircle()【解析】
第一空是填接口里面的方法,在接口的实现里面找,可以发现应该填void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y)。
第二空可以根据后面this drawCircle=drawCircle判断,这里应该有一个drawCircle属性,因此应该填)DrawCircle drawCircle。
第三空这里填drawcircle,用-> drawcircle来引用父类的成员。
第四空调用drawCircle(radius,x,y)方法。
第五、六空分别创建一个红色圆形对象和一个绿色圆形对象作为Circle里面的实参。 -
第4题:
若有以下程序:includeusingnamespacestd;classBase{public: Base() {x=0; } intx;}; 若有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: Base() { x=0; } int x; }; class Derivedl : virtual public Base { public: Derivedl() { x=10; } }; class Derived2 : virtual public Base { public: Derived2() { x=20; } }; class Derived : public Derivedl,protected Derived2 { }; int main () { Derived obj; cout<<obj.x<<end1; return 0; } 该程序运行后的输出结果是( )。
A.10
B.20
C.30
D.0
正确答案:B
解析:本题中,虽然Derived1和Derived2都是由共同的基类x派生而来的,但由于引入了虚基类,使得它们分别对应基类的不同副本。这时数据成员x只存在一份拷贝,不论在类Derived1修改,还是在类Derived2中修改,都是直接对这惟一拷贝进行操作。本题程序执行语句“Derivedobj”时,就会先调用虚基类Base的构造函数,使得x=O,然后执行类Derived1的构造函数使得x=10,再执行类Derived2的构造函数,使得x=20。最后输出x的值为20。 -
第5题:
阅读以下说明和Java程序,填写程序中的空(1)~(6),将解答写入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
以下Java代码实现一个简单绘图工具,绘制不同形状以及不同颜色的图形。部分接口、类及其关系如图5-1所示。


【Java代码】
interface?DrawCircle?{? //绘制圆形 public(1) ;}class?RedCircle?implements?DrawCircle?{? ?//绘制红色圆形???????public?void?drawCircle(int?radius,intx,?int?y)??{????????????System.out.println("Drawing?Circle[red,radius:"?+?radius?+",x:"?+?x?+?",y:"?+y+?"]");???????}}class?GreenCircle?implements?DrawCircle?{????//绘制绿色圆形??????public?void?drawCircle(int?radius,?int?x,int?y)?{???????????System.out.println("Drawing?Circle[green,radius:"?+radius+",x:?"?+x+?",y:?"?+y+?"]");??????}}abstract?class?Shape?{????//形状? protected? ? (2)???;? ? public?Shape(DrawCircle?drawCircle)?{? ?this.drawCircle=?drawCircle;? ? ? public?abstract?void?draw();}class?Circle?extends?Shape?{? //圆形? ?private?int?x,y,radius;? public?Circle(int?x,int?y,intradius,DrawCircle?drawCircle)?{? ?(3)???;? this.x?=?x;? ? ? this.y?=?y;? ?this.radius?=radius;? }? ? ?public?void?draw()?{? ? drawCircle.? ?(4)? ?;? ? ? }}public?class?DrawCircleMain?{? public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{? Shape?redCircle=new?Circle(?100,100,10,? (5) );//绘制红色圆形? Shape?greenCircle=new?Circle(200,200,10,(6) );//绘制绿色圆形? ?redCircle.draw(); greenCircle.draw();? ?}}答案:解析:(1)void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y)
(2)DrawCircle drawCircle
(3)super.drawcircle=drawcircle
(4)drawCircle(radius,x,y)
(5)new RedCircle()
(6)new GreenCircle()【解析】
第一空是填接口里面的方法,在接口的实现里面找,可以发现应该填void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y)。
第二空可以根据后面this drawCircle=drawCircle判断,这里应该有一个drawCircle属性,因此应该填)DrawCircle drawCircle。
第三空这里用super,用super. drawcircle来引用父类的成员。
第四空调用drawCircle(radius,x,y)方法。
第五、六空分别创建一个红色圆形对象和一个绿色圆形对象作为Circle里面的实参。
