(ii) Describe the claim of each of the four identified stakeholders. (4 marks)
题目
(ii) Describe the claim of each of the four identified stakeholders. (4 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(ii) Stakeholder claims
Four external stakeholders in the case and their claims are as follows.
The client, i.e. the government of the East Asian country. This stakeholder wants the project completed to budget and
on time. It may also be concerned to minimise negative publicity in respect of the construction of the dam and the
possible negative environmental consequences.
Stop-the-dam, the vocal and well organised pressure group. This stakeholder wants the project stopped completely,
seemingly and slightly paradoxically, for environmental and social footprint reasons.
First Nation, the indigenous people group currently resident on the land behind the dam that would be flooded after its
construction. This stakeholder also wants the project stopped so they can continue to live on and farm the land.
The banks (identified as a single group). These seem happy to lend to the project and will want it to proceed so they
make a return on their loans commensurate with the risk of the loan. They do not want to be publicly identified as being
associated with the Giant Dam Project.
Shareholders. The shareholders have the right to have their investment in the company managed in such a way as to
maximise the value of their shareholding. The shareholders seek projects providing positive NPVs within the normal
constraints of sound risk management.
Tutorial note: only four stakeholders need to be identified. Marks will be given for up to four relevant stakeholders
only.
更多“(ii) Describe the claim of each of the four identified stakeholders. (4 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(d) Draft a letter for Tim Blake to send to WM’s investors to include the following:
(i) why you believe robust internal controls to be important; and
(ii) proposals on how internal systems might be improved in the light of the overestimation of mallerite at
WM.
Note: four professional marks are available within the marks allocated to requirement (d) for the structure,
content, style. and layout of the letter.
(16 marks)
正确答案:
You will be aware of the importance of accurate resource valuation to Worldwide Minerals (WM). Unfortunately, I have to
inform. you that the reserve of mallerite, one of our key minerals in a new area of exploration, was found to have been
overestimated after the purchase of a mine. It has been suggested that this information may have an effect on shareholder
value and so I thought it appropriate to write to inform. you of how the board intends to respond to the situation.
In particular, I would like to address two issues. It has been suggested that the overestimation arose because of issues with
the internal control systems at WM. I would firstly like to reassure you of the importance that your board places on sound
internal control systems and then I would like to highlight improvements to internal controls that we shall be implementing
to ensure that the problem should not recur.
(i) Importance of internal control
Internal control systems are essential in all public companies and Worldwide Minerals (WM) is no exception. If anything,
WM’s strategic position makes internal control even more important, operating as it does in many international situations
and dealing with minerals that must be guaranteed in terms of volume, grade and quality. Accordingly, your board
recognises that internal control underpins investor confidence. Investors have traditionally trusted WM’s management
because they have assumed it capable of managing its internal operations. This has, specifically, meant becoming aware
of and controlling known risks. Risks would not be known about and managed without adequate internal control
systems. Internal control, furthermore, helps to manage quality throughout the organisation and it provides
management with information on internal operations and compliance. These features are important in ensuring quality
at all stages in the WM value chain from the extraction of minerals to the delivery of product to our customers. Linked
to this is the importance of internal control in helping to expose and improve underperforming internal operations.
Finally, internal control systems are essential in providing information for internal and external reporting upon which, in
turn, investor confidence rests.
(ii) Proposals to improve internal systems at WM
As you may be aware, mineral estimation and measurement can be problematic, particularly in some regions. Indeed,
there are several factors that can lead to under or overestimation of reserves valuations as a result of geological survey
techniques and regional cultural/social factors. In the case of mallerite, however, the issues that have been brought to
the board’s attention are matters of internal control and it is to these that I would now like to turn.
In first instance, it is clear from the fact that the overestimate was made that we will need to audit geological reports at
an appropriate (and probably lower) level in the organisation in future.
Once a claim has been made about a given mineral resource level, especially one upon which investor returns might
depend, appropriate systems will be instituted to ask for and obtain evidence that such reserves have been correctly and
accurately quantified.
We will recognise that single and verbal source reports of reserve quantities may not necessarily be accurate. This was
one of the apparent causes of the overestimation of mallerite. A system of auditing actual reserves rather than relying
on verbal evidence will rectify this.
The purchase of any going concern business, such as the mallerite mine, is subject to due diligence. WM will be
examining its procedures in this area to ensure that they are fit for purpose in the way that they may not have been in
respect of the purchase of the mallerite mine. I will be taking all appropriate steps to ensure that all of these internal
control issues can be addressed in future.
Thank you for your continued support of Worldwide Minerals and I hope the foregoing goes some way to reassure you
that the company places the highest value on its investors and their loyalty.
Yours faithfully,
Tim Blake
Chairman -
第2题:
(ii) Using the previous overhead allocation basis (as per note 4), calculate the budgeted profit/(loss)
attributable to each type of service for the year ending 31 December 2006 and comment on the results
obtained using the previous and revised methods of overhead allocation. (5 marks)
正确答案: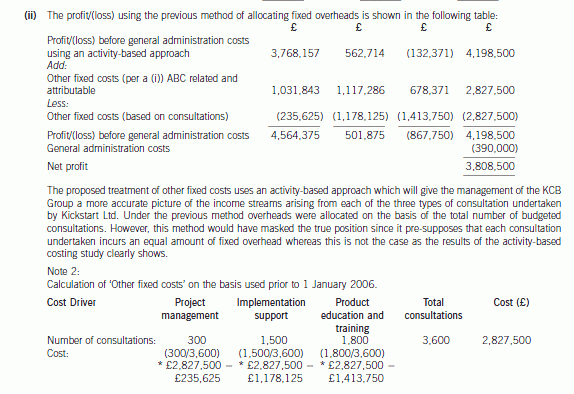
-
第3题:
(ii) Briefly discuss FOUR non-financial factors which might influence the above decision. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Four factors that could be considered are as follows:
(i) The quality of the service provided by NSC as evidenced by, for example, the comfort of the ferries, on-board
facilities, friendliness and responsiveness of staff.
(ii) The health and safety track record of NSC – passenger safety is a ‘must’ in such operations.
(iii) The reliability, timeliness and dependability of NSC as a service provider.
(iv) The potential loss of image due to redundancies within Wonderland plc. -
第4题:
(b) Using sensitivity analysis, estimate by what percentage each of the under-mentioned items, taken separately,
would need to change before the recommendation in (a) above is varied:
(i) Initial outlay;
(ii) Annual contribution. (4 marks)
正确答案: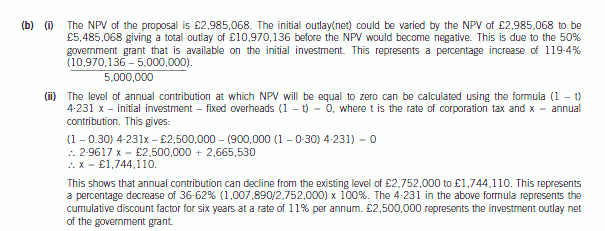
-
第5题:
(b) The management of Division C has identified the need to achieve cost savings in order to become more
competitive. They have decided that an analysis and investigation of quality costs into four sub-categories will
provide a focus for performance measurement and improvement.
Required:
Identify the FOUR sub-categories into which quality costs can be analysed and provide examples (which
must relate to Division C) of each of the four sub-categories of quality cost that can be investigated in order
that overall cost savings might be achieved and hence the performance improved. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Quality costs may be monitored by measuring costs of non-conformance and costs of conformance.
Costs of non-conformance occur when the product fails to reach the design quality standards. Such costs may be subdivided
into internal failure costs and external failure costs.
Internal failure costs occur when the failure is detected before the transfer of the product to the customer.
External failure costs occur when the failure to reach the required standards is not detected until after the product has been
transferred to the customer.
Costs of conformance are those incurred in reducing or eliminating the costs of non-conformance. Such costs may be
subdivided into appraisal costs and prevention costs.
Appraisal costs are those associated with the evaluation of items such as purchased material and services in order to ensure
that they conform. to the agreed specification.
Prevention costs are those associated with the implementation of a quality improvement programme. Such costs are planned
in advance and their implementation should lead to continuous improvement.
Examples of quality costs relevant to Division C may include:
Internal failure costs: cost of materials scrapped due to poor receipt and storage procedures or losses of CC output due to poor
processing routines.
External failure costs: cost of quality problems with batch of CC not detected until it has reached Division B. This may require
free replacement of the batch and compensation for loss of output by Division B.
Appraisal costs: evaluation of purchased material and services in relation to the manufacture of CC to ensure that it conforms
to the agreed specification; e.g. inspection and testing before use.
Prevention costs: the cost of implementation of staff training and the costs of equipment testing to ensure that it conforms to
the specification standards required for the production of CC.
(Alternative relevant examples would be accepted) -
第6题:
(c) State any reliefs Bob could claim regarding the fall in value of his shares in Willis Ltd, and describe how the
operation of any such reliefs could reduce Bob’s taxable income. (4 marks)
Relevant retail price index figures are:
September 1990 129·3
April 1998 162·6
December 2004 189·9
正确答案:
(c) Claims for capital losses
Where the value of shares (a chargeable asset) has become negligible (defined as <5% of the original cost), a claim can be
made to treat the asset as though it was sold and then immediately reacquired for its current market value. This is known as
a negligible value claim.
The sale and reacquisition is treated as taking place at the time that the claim is made or at a specified time (up to 2 years
before the start of the tax year in which the claim was made) if the asset was of negligible value at that time.
As the loss is on unquoted shares, a further relief (s.574 ICTA 1988) allows the loss to be relieved against the total income
of the taxpayer for the year in which the loss arose, and/or against the total income of the previous year.
Losses are first relieved against current year income, with any excess being available for offset against the prior year’s income.
Bob can therefore make a negligible value claim as at 1 December 2004. This will give rise to a loss of £14,500
(£500 – £15,000) which will be deemed to arise in the year 2004/05. By doing so, his taxable income for that year will be
reduced from £36,875 to £22,375. -
第7题:
(ii) Explain, with reasons, the relief available in respect of the fall in value of the shares in All Over plc,
identify the years in which it can be claimed and state the time limit for submitting the claim.
(3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第8题:
(ii) equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue; and (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
Tutorial note: In the context of GVF, the principal issue to be addressed is whether or not the impairment loss previously
recognised should be reversed (by considering the determination of value in use). Marks will also be awarded for
consideration of depreciation, additions etc made specific to this equipment.
■ Agree cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses at the beginning of the year to prior year working
papers (and/or last year’s published financial statements).
■ Recalculate the current year depreciation charge based on the carrying amount (as reduced by the impairment
loss).
■ Calculate the carrying amount of the equipment as at 30 September 2005 without deduction of the impairment
loss.
Tutorial note: The equipment cannot be written back up to above this amount (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ Agree management’s schedule of future cash flows estimated to be attributable to the equipment for a period of up
to five years (unless a longer period can be justified) to approved budgets and forecasts.
■ Recalculate:
– on a sample basis, the make up of the cash flows included in the forecast;
– GVF’s weighted average cost of capital.
■ Review production records and sales orders for the year, as compared with the prior period, to confirm a ‘steady
increase’.
■ Compare sales volume at 30 September 2005 with the pre-‘scare’ level to assess how much of the previously
recognised impairment loss it would be prudent to write back (if any).
■ Scrutinize sales orders in the post balance sheet event period. Sales of such produce can be very volatile and
another ‘incident’ could have sales plummeting again – in which case the impairment loss should not be reversed. -
第9题:
(c) (i) Identify and describe FOUR quality control procedures that are applicable to the individual audit
engagement; and (8 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms That Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information and Other
Assurance and Related Services Engagements provides guidance on the overall quality control systems that should be
implemented by an audit firm. ISA 220 Quality Control for Audits of Historical Financial Information specifies the quality
control procedures that should be applied by the engagement team in individual audit assignments.
Procedures include the following:
Client acceptance procedures
There should be full documentation, and conclusion on, ethical and client acceptance issues in each audit assignment.
The engagement partner should consider whether members of the audit team have complied with ethical requirements,
for example, whether all members of the team are independent of the client. Additionally, the engagement partner should
conclude whether all acceptance procedures have been followed, for example, that the audit firm has considered the
integrity of the principal owners and key management of the client. Other procedures on client acceptance should
include:
– Obtaining professional clearance from previous auditors
– Consideration of any conflict of interest
– Money laundering (client identification) procedures.
Engagement team
Procedures should be followed to ensure that the engagement team collectively has the skills, competence and time to
perform. the audit engagement. The engagement partner should assess that the audit team, for example:
– Has the appropriate level of technical knowledge
– Has experience of audit engagements of a similar nature and complexity
– Has the ability to apply professional judgement
– Understands professional standards, and regulatory and legal requirements.
Direction
The engagement team should be directed by the engagement partner. Procedures such as an engagement planning
meeting should be undertaken to ensure that the team understands:
– Their responsibilities
– The objectives of the work they are to perform
– The nature of the client’s business
– Risk related issues
– How to deal with any problems that may arise; and
– The detailed approach to the performance of the audit.
The planning meeting should be led by the partner and should include all people involved with the audit. There should
be a discussion of the key issues identified at the planning stage.
Supervision
Supervision should be continuous during the engagement. Any problems that arise during the audit should be rectified
as soon as possible. Attention should be focused on ensuring that members of the audit team are carrying out their work
in accordance with the planned approach to the engagement. Significant matters should be brought to the attention of
senior members of the audit team. Documentation should be made of key decisions made during the audit engagement.
Review
The review process is one of the key quality control procedures. All work performed must be reviewed by a more senior
member of the audit team. Reviewers should consider for example whether:
– Work has been performed in accordance with professional standards
– The objectives of the procedures performed have been achieved
– Work supports conclusions drawn and is appropriately documented.
The review process itself must be evidenced.
Consultation
Finally the engagement partner should arrange consultation on difficult or contentious matters. This is a procedure
whereby the matter is discussed with a professional outside the engagement team, and sometimes outside the audit
firm. Consultations must be documented to show:
– The issue on which the consultation was sought; and
– The results of the consultation. -
第10题:
(ii) Describe the procedures to verify the number of serious accidents in the year ended 30 November 2007.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Procedures to verify the number of serious accidents during 2007 could include the following:
Tutorial note: procedures should focus on the completeness of the disclosure as it is in the interest of Sci-Tech Co to
understate the number of serious accidents.
– Review the accident log book and count the total number of accidents during the year
– Discuss the definition of ‘serious accident’ with the directors and clarify exactly what criteria need to be met to
satisfy the definition
– For serious accidents identified:
? review HR records to determine the amount of time taken off work
? review payroll records to determine the financial amount of sick pay awarded to the employee
? review correspondence with the employee regarding the accident.
Tutorial note: the above will help to clarify that the accident was indeed serious.
– Review board minutes where the increase in the number of serious accidents has been discussed
– Review correspondence with Sci-Tech Co’s legal advisors to ascertain any legal claims made against the company
due to accidents at work
– Enquire as to whether any health and safety visits have been conducted during the year by regulatory bodies, and
review any documentation or correspondence issued to Sci-Tech Co after such visits.
Tutorial note: it is highly likely that in a regulated industry such as pharmaceutical research, any serious accident
would trigger a health and safety inspection from the appropriate regulatory body.
– Discuss the level of accidents with representatives of Sci-Tech Co’s employees to reach an understanding as to
whether accidents sometimes go unreported in the accident log book. -
第11题:
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several benefits for Hugh Co in choosing a voluntary financial statement audit.
An annual audit will ensure that any material mistakes made by the part-qualified accountant in preparing the year end
financial statements will be detected. This is important as the directors will be using the year end accounts to review their
progress in the first year of trading and will need reliable figures to assess performance. An audit will give the directors comfort
that the financial statements are a sound basis for making business decisions.
Accurate first year figures will also enable more effective budgeting and forecasting, which will be crucial if rapid growth is to
be achieved.
The auditors are likely to use the quarterly management accounts as part of normal audit procedures. The auditors will be
able to advise Monty Parkes of any improvements that could be made to the management accounts, for example, increased
level of detail, more frequent reporting. Better quality management accounts will help the day-to-day running of the business
and enable a speedier response to any problems arising during the year.
As a by-product of the audit, a management letter (report to those charged with governance) will be produced, identifying
weaknesses and making recommendations on areas such as systems and controls which will improve the smooth running of
the business.
It is likely that Hugh Co will require more bank funding in order to expand, and it is likely that the bank would like to see
audited figures for review, before deciding on further finance. It will be easier and potentially cheaper to raise finance from
other providers with an audited set of financial statements.
As the business deals in cash sales, and retails small, luxury items there is a high risk of theft of assets. The external audit
can act as both a deterrent and a detective control, thus reducing the risk of fraud and resultant detrimental impact on the
financial statements.
Accurate financial statements will be the best basis for tax assessment and tax planning. An audit opinion will enhance the
credibility of the figures.
If the business grows rapidly, then it is likely that at some point in the future, the audit exemption limit will be exceeded and
thus an audit will become mandatory.
Choosing to have an audit from the first year of incorporation will reduce potential errors carried down to subsequent periods
and thus avoid qualifications of opening balances. -
第12题:
(a) List and explain FOUR methods of selecting a sample of items to test from a population in accordance with ISA 530 (Redrafted) Audit Sampling and Other Means of Testing. (4 marks)
(b) List and explain FOUR assertions from ISA 500 Audit Evidence that relate to the recording of classes of
transactions. (4 marks)
(c) In terms of audit reports, explain the term ‘modified’. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(a)SamplingmethodsMethodsofsamplinginaccordancewithISA530AuditSamplingandOtherMeansofTesting:Randomselection.Ensureseachiteminapopulationhasanequalchanceofselection,forexamplebyusingrandomnumbertables.Systematicselection.Inwhichanumberofsamplingunitsinthepopulationisdividedbythesamplesizetogiveasamplinginterval.Haphazardselection.Theauditorselectsthesamplewithoutfollowingastructuredtechnique–theauditorwouldavoidanyconsciousbiasorpredictability.Sequenceorblock.Involvesselectingablock(s)ofcontinguousitemsfromwithinapopulation.Tutorialnote:Othermethodsofsamplingareasfollows:MonetaryUnitSampling.Thisselectionmethodensuresthateachindividual$1inthepopulationhasanequalchanceofbeingselected.Judgementalsampling.Selectingitemsbasedontheskillandjudgementoftheauditor.(b)Assertions–classesoftransactionsOccurrence.Thetransactionsandeventsthathavebeenrecordedhaveactuallyoccurredandpertaintotheentity.Completeness.Alltransactionsandeventsthatshouldhavebeenrecordedhavebeenrecorded.Accuracy.Theamountsandotherdatarelatingtorecordedtransactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedappropriately.Cut-off.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedinthecorrectaccountingperiod.Classification.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedintheproperaccounts.(c)AuditreporttermModified.Anauditormodifiesanauditreportinanysituationwhereitisinappropriatetoprovideanunmodifiedreport.Forexample,theauditormayprovideadditionalinformationinanemphasisofmatter(whichdoesnotaffecttheauditor’sopinion)orqualifytheauditreportforlimitationofscopeordisagreement. -
第13题:
(b) Using the TARA framework, construct four possible strategies for managing the risk presented by Product 2.
Your answer should describe each strategy and explain how each might be applied in the case.
(10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Risk management strategies and Chen Products
Risk transference strategy
This would involve the company accepting a portion of the risk and seeking to transfer a part to a third party. Although an
unlikely possibility given the state of existing claims, insurance against future claims would serve to limit Chen’s potential
losses and place a limit on its losses. Outsourcing manufacture may be a way of transferring risk if the ourtsourcee can be
persuaded to accept some of the product liability.
Risk avoidance strategy
An avoidance strategy involves discontinuing the activity that is exposing the company to risk. In the case of Chen this would
involve ceasing production of Product 2. This would be pursued if the impact (hazard) and probability of incurring an
acceptable level of liability were both considered to be unacceptably high and there were no options for transference or
reduction.
Risk reduction strategy
A risk reduction strategy involves seeking to retain a component of the risk (in order to enjoy the return assumed to be
associated with that risk) but to reduce it and thereby limit its ability to create liability. Chen produces four products and it
could reconfigure its production capacity to produce proportionately more of Products 1, 3 and 4 and proportionately less of
Product 2. This would reduce Product 2 in the overall portfolio and therefore Chen’s exposure to its risks. This would need
to be associated with instructions to other departments (e.g. sales and marketing) to similarly reconfigure activities to sell
more of the other products and less of Product 2.
Risk acceptance strategy
A risk acceptance strategy involves taking limited or no action to reduce the exposure to risk and would be taken if the returns
expected from bearing the risk were expected to be greater than the potential liabilities. The case mentions that Product 2 is
highly profitable and it may be that the returns attainable by maintaining and even increasing Product 2’s sales are worth the
liabilities incurred by compensation claims. This is a risk acceptance strategy. -
第14题:
(b) Discuss FOUR factors that distinguish service from manufacturing organisations and explain how each of
these factors relates to the services provided by the Dental Health Partnership. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The major characteristics of services which distinguish services from manufacturing are as follows:
– Intangibility.
When a dentist provides a service to a client there are many intangible factors involved such as for example the
appearance of the surgery, the personality of the dentist, the manner and efficiency of the dental assistant. The output
of the service is ‘performance’ by the dentist as opposed to tangible goods.
– Simultaneity.
The service provided by the dentist to the patient is created by the dentist at the same time as the patient consumed it
thus preventing any advance verification of quality.
– Heterogeneity.
Many service organisations face the problem of achieving consistency in the quality of its output. Whilst each of the
dentists within the Dental Health Partnership will have similar professional qualifications there will be differences in the
manner they provide services to clients.
– Perishability.
Many services are perishable. The services of a dentist are purchased only for the duration of an appointment. -
第15题:
(e) Briefly discuss FOUR initiatives that management might consider in order to further enhance profitability.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(e) In order to enhance profitability management might take the following actions:
(i) Increase the maximum capacity of the circus.
(ii) Undertake a detailed review of operating costs which are budgeted at £239,200,000. Such a review might identify nonvalue
added costs which may be eliminated thereby increasing profitability.
(iii) Enter into a strategic arrangement with large hotels and travel agencies to offer travel and accommodation inclusive
arrangements for visitors to Cinola Island. This might help to increase the number of visitors to the zoo thereby increasing
profits.
(iv) Change the price structure and entitlement of tickets so that purchasers might visit Cinola Island on two separate days
in order to attend the zoo and circus. Additional revenues would arise as a consequence of the increased number of
visitors to the zoo, thereby increasing profitability.
(v) Hold prize draws for free tickets to the zoo for families on an ‘all-inclusive basis’, including restaurants, photographs,
souvenirs etc.
N.B. Only four initiatives were required to be discussed. -
第16题:
(ii) evaluates the relative performance of the four depots as indicated by the analysis in the summary table
prepared in (i); (5 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The summary analysis in (a)(i) shows that using overall points gained, Michaelangelotown has achieved the best
performance with 12 points. Donatellotown and Leonardotown have achieved a reasonable level of performance with
eight points each. Raphaeltown has under performed, however, gaining only four out of the available 12 points.
Michaelangelotown is the only depot to have achieved both an increase in revenue over budget and an increased
profit:revenue percentage.
In the customer care and service delivery statistics, Michaelangelotown has achieved all six of the target standards,
Donatellotown four; Leonardotown three. The Raphaeltown statistic of achieving only one out of six targets indicates the
need for investigation.
With regard to the credit control and administrative efficiency statistics, Leonardotown and Michaelangelotown achieved
all four standards and Donatellotown achieved three of the four standards. Once again, Raphaeltown is the ‘poor
performer’ achieving only two of the four standards. -
第17题:
(ii) Comment on the figures in the statement prepared in (a)(i) above. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The statement of product profitability shows that CTC is forecast to achieve a profit of $2·185 million in 2008 giving a
profit:sales ratio of 11·9%. However, the forecast profit in 2009 is only $22,000 which would give a profit:sales ratio
of just 0·19%! Total sales volume in 2008 is 390,000 units which represent 97·5% utilisation of total annual capacity.
In stark contrast, the total sales volume in 2009 is forecast to be 240,000 units which represents 60% utilisation of
total annual capacity and shows the expected rapid decline in sales volumes of Bruno and Kong products. The rapid
decline in the sales of these two products is only offset to a relatively small extent by increased sales volume from the
Leo product. It is vital that a new product or products with healthy contribution to sales ratios are introduced.
Management should also undertake cost/benefit analyses in order to assess the potential of extending the life of Bruno
and Kong products. -
第18题:
(ii) Briefly outline the tax consequences for Henry if the types of protection identified in (i) were to be
provided for him by Happy Home Ltd compared to providing them for himself. You are not required to
discuss the corporation tax (CT) consequences for Happy Home Ltd. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Provision of protection: company or individual
If any of the policies are taken out and paid for by Henry personally, then there will be no tax relief on the premiums,
but neither will there normally be any tax payable on the proceeds or benefits received.
If Happy Home Ltd were to pay the premiums on a policy taken out by Henry, and of which he was the direct beneficiary,
then this will constitute a benefit, on the grounds that the company will have satisfied a personal liability of Henry’s.
Accordingly, income tax and Class 1A national insurance contributions will be payable on the benefit.
If, however, Happy Home Ltd were to decide to offer protection benefits to their employees on a group basis (and not
just to Henry), then it would be possible to avoid a charge under the benefits rules and/or obtain a lower rate of premium
under a collective policy. For example:
– A death in service benefit of up to four times remuneration can be provided as part of an approved pension scheme.
No benefit charge arises on Henry and any lump sum will be paid tax free. This could be considered a substitute
for a term assurance policy.
– If a group permanent health insurance policy were taken out, no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but any
benefits payable under the policy would be paid to Happy Home Ltd in the first instance. When subsequently paid
on to Henry, such payments would be treated as arising from his employment and subject to PAYE and national
insurance as for normal salary payments.
– If a group critical illness policy were taken out, again no benefit charge would arise on Henry, but in this case also,
any benefits received by Henry directly from Happy Home Ltd as a result of the payments under the policy would
be considered as derived from his employment and subject to income tax and national insurance. Such a charge
to tax and national insurance would however be avoided if these payments were made in terms of a trust. -
第19题:
(ii) Audit work on after-date bank transactions identified a transfer of cash from Batik Co. The audit senior has
documented that the finance director explained that Batik commenced trading on 7 October 2005, after
being set up as a wholly-owned foreign subsidiary of Jinack. No other evidence has been obtained.
(4 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
(ii) Wholly-owned foreign subsidiary
■ The cash transfer is a non-adjusting post balance sheet event. It indicates that Batik was trading after the balance
sheet date. However, that does not preclude Batik having commenced trading before the year end.
■ The finance director’s oral representation is wholly insufficient evidence with regard to the existence (or otherwise)
of Batik at 30 September 2005. If it existed at the balance sheet date its financial statements should have been
consolidated (unless immaterial).
■ The lack of evidence that might reasonably be expected to be available (e.g. legal papers, registration payments,
etc) suggests a limitation on the scope of the audit.
■ If such evidence has been sought but not obtained then the limitation is imposed by the entity (rather than by
circumstances).
■ Whilst the transaction itself may not be material, the information concerning the existence of Batik may be material
to users and should therefore be disclosed (as a non-adjusting event). The absence of such disclosure, if the
auditor considered necessary, would result in a qualified ‘except for’, opinion.
Tutorial note: Any matter that is considered sufficiently material to be worthy of disclosure as a non-adjusting
event must result in such a qualified opinion if the disclosure is not made.
■ If Batik existed at the balance sheet date and had material assets and liabilities then its non-consolidation would
have a pervasive effect. This would warrant an adverse opinion.
■ Also, the nature of the limitation (being imposed by the entity) could have a pervasive effect if the auditor is
suspicious that other audit evidence has been withheld. In this case the auditor should disclaim an opinion. -
第20题:
4 (a) ISA 701 Modifications to The Independent Auditor’s Report includes ‘suggested wording of modifying phrases
for use when issuing modified reports’.
Required:
Explain and distinguish between each of the following terms:
(i) ‘qualified opinion’;
(ii) ‘disclaimer of opinion’;
(iii) ‘emphasis of matter paragraph’. (6 marks)
正确答案:
4 PETRIE CO
(a) Independent auditor’s report terms
(i) Qualified opinion – A qualified opinion is expressed when the auditor concludes that an unqualified opinion cannot be
expressed but that the effect of any disagreement with management, or limitation on scope is not so material and
pervasive as to require an adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion.
(ii) Disclaimer of opinion – A disclaimer of opinion is expressed when the possible effect of a limitation on scope is so
material and pervasive that the auditor has not been able to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence and accordingly
is unable to express an opinion on the financial statements.
(iii) Emphasis of matter paragraph – An auditor’s report may be modified by adding an emphasis of matter paragraph to
highlight a matter affecting the financial statements that is included in a note to the financial statements that more
extensively discusses the matter. Such an emphasis of matter paragraph does not affect the auditor’s opinion. An
emphasis of matter paragraph may also be used to report matters other than those affecting the financial statements
(e.g. if there is a misstatement of fact in other information included in documents containing audited financial
statements).
(iii) is clearly distinguishable from (i) and (ii) because (i) and (ii) affect the opinion paragraph, whereas (iii) does not.
(i) and (ii) are distinguishable by the degree of their impact on the financial statements. In (i) the effects of any disagreement
or limitation on scope can be identified with an ‘except for …’ opinion. In (ii) the matter is pervasive, that is, affecting the
financial statements as a whole.
(ii) can only arise in respect of a limitation in scope (i.e. insufficient evidence) that has a pervasive effect. (i) is not pervasive
and may also arise from disagreement (i.e. where there is sufficient evidence). -
第21题:
(ii) Describe the evidence you would seek to support the assertion that development costs are technically
feasible. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Evidence supporting the assertion that development costs are technically feasible would include the following:
– Review the results of scientific tests performed on the products, for example, the results of animal or human testing
of the products.
– Discuss any detrimental results of these tests, e.g. harmful side effects, with the scientists working on the project
to determine what corrective action is being taken.
– Enquire whether any licences necessary for continued development and/or commercial production have been
granted by the appropriate regulatory body.
– Compare expected to actual development costs incurred per product being developed. Where actual costs are in
excess of expected costs investigate whether the extra costs have been incurred in order to make good any problems
identified in the development process.
– Review board minutes for relevant discussion of the product development taking place during the year. -
第22题:
(ii) Deema Co. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Deema Co
The claim is an event after the balance sheet date. If the accident occurred prior to the year end of 30 September 2007,
the claim gives additional evidence of a year end condition, and thus meets the definition of an adjusting post balance
sheet event. In this case the matter appears to have been properly disclosed in the notes to the financial statements per
IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date and IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets. A
provision would only be necessary if the claim was probable to succeed and there is sufficient appropriate evidence that
this is not the case. There is therefore no disagreement, and no limitation on scope.
Therefore the senior is correct to propose an unqualified opinion.
However, it is not necessary for the audit report to contain an emphasis of matter paragraph.
ISA 701 Modifications to the Independent Auditor’s Report states that an emphasis of matter paragraph should be used
to highlight a matter where there is significant uncertainty.
Uncertainties are normally only regarded as significant if they involve a level of concern about the going concern status
of the company or would have an unusually great effect on the financial statements. This is not the case here as there
is enough cash to pay the damages in the unlikely event that the claim goes against Deema Co. This appears to be a
one-off situation with a low risk of the estimate being subject to change and thus there is no significant uncertainty. -
第23题:
(ii) Recommend further audit procedures that should be carried out. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Further audit procedures:
Request from Peter Sheffield a written representation detailing:
– the exact nature of his control over Jarvis Co, i.e. if he is a shareholder then state his percentage shareholding, if
he is a member of senior management then state his exact position within the entity,
– a comment on whether in his opinion the balance is recoverable,
– a specific date by which the amount should be expected to be repaid, and
– a confirmation that there are no further balances outstanding from Jarvis Co, or any further transactions between
Jarvis Co and Pulp Co.
Tutorial note: Reference to the Exposure Draft ISA 550 Related Parties (Revised and Redrafted) requirement for both
general and specific management representations will be awarded credit.
Review the terms of any written confirmation of the amount, such as a signed agreement or invoice, checking whether
any interest is due to Pulp Co. The terms should be reviewed for details of any security offered, and the nature of the
consideration to be provided in settlement.
From discussion with Peter Sheffield, develop an understanding of the business purpose of the transaction, particularly
to understand whether the balance is a trade receivable or an investment.
Review the board minutes for evidence of any discussion of the transaction and the recoverability of the balance
outstanding.
Obtain the most recent audited financial statements of Jarvis Co and:
– ascertain whether Peter Sheffield is disclosed as the ultimate controlling party or disclosed as a member of key
management personnel,
– scrutinise the disclosure notes to find any disclosure of the transaction, where it should be described as a related
party liability, and
– perform. a liquidity analysis to establish whether the amount can be repaid from liquid assets.
