(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the onlyshareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after thedate of acquisition as an incentive to a
题目
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
相似考题
更多“(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the onlyshareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after thedate of acquisition as an incentive to a”相关问题
-
第1题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第2题:
8 P and Q are in partnership, sharing profits in the ratio 2:1. On 1 July 2004 they admitted P’s son R as a partner. P
guaranteed that R’s profit share would not be less than $25,000 for the six months to 31 December 2004. The profitsharing
arrangements after R’s admission were P 50%, Q 30%, R 20%. The profit for the year ended 31 December
2004 is $240,000, accruing evenly over the year.
What should P’s final profit share be for the year ended 31 December 2004?
A $140,000
B $139,000
C $114,000
D $139,375
正确答案:B
80,000 + 60,000 – 1,000 = 139,000 -
第3题:
6 Assume today’s date is 16 April 2005.
Henry, aged 48, is the managing director of Happy Home Ltd, an unquoted UK company specialising in interior
design. He is wealthy in his own right and is married to Helen, who is 45 years old. They have two children – Stephen,
who is 19, and Sally who is 17.
As part of his salary, Henry was given 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd with an option to acquire a further 10,000
shares. The options were granted on 15 July 2003, shortly after the company started trading, and were not part of
an approved share option scheme. The free shares were given to Henry on the same day.
The exercise price of the share options was set at the then market value of £1·00 per share. The options are not
capable of being exercised after 10 years from the date of grant. The company has been successful, and the current
value of the shares is now £14·00 per share. Another shareholder has offered to buy the shares at their market value,
so Henry exercised his share options on 14 April 2005 and will sell the shares next week, on 20 April 2005.
With the company growing in size, Henry wishes to recruit high quality staff, but the company lacks the funds to pay
them in cash. Henry believes that giving new employees the chance to buy shares in the company would help recruit
staff, as they could share in the growth in value of Happy Home Ltd. Henry has heard that there is a particular share
scheme that is suitable for small, fast growing companies. He would like to obtain further information on how such
a scheme would work.
Henry has accumulated substantial assets over the years. The family house is owned jointly with Helen, and is worth
£650,000. Henry has a £250,000 mortgage on the house. In addition, Henry has liquid assets worth £340,000
and Helen has shares in quoted companies currently worth £125,000. Henry has no forms of insurance, and believes
he should make sure that his wealth and family are protected. He is keen to find out what options he should be
considering.
Required:
(a) (i) State how the gift of the 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd was taxed. (1 mark)
正确答案:
(a) (i) Gift of shares
Shares, which are given free or sold at less than market value, are charged to income tax on the difference between the
market value and the amount paid (if any) for the shares. Henry was given 3,000 shares with a market value of £1 at
the time of gift, so he was assessed to income tax on £3,000, in the tax year 2003/04. -
第4题:
(b) The directors of Carver Ltd are aware that some of the company’s shareholders want to realise the value in their
shares immediately. Accordingly, instead of investing in the office building or the share portfolio they are
considering two alternative strategies whereby, following the sale of the company’s business, a payment will be
made to the company’s shareholders.
(i) Liquidate the company. The payment by the liquidator would be £126 per share.
(ii) The payment of a dividend of £125 per share following which a liquidator will be appointed. The payment
by the liquidator to the shareholders would then be £1 per share.
The company originally issued 20,000 £1 ordinary shares at par value to 19 members of the Cutler family.
Following a number of gifts and inheritances there are now 41 shareholders, all of whom are family members.
The directors have asked you to attend a meeting to set out the tax implications of these two alternative strategies
for each of the two main groups of shareholders: adults with shareholdings of more than 500 shares and children
with shareholdings of 200 shares or less.
Required:
Prepare notes explaining:
– the amount chargeable to tax; and
– the rates of tax that will apply
in respect of each of the two strategies for each of the two groups of shareholders ready for your meeting
with the directors of Carver Ltd. You should assume that none of the shareholders will have any capital
losses either in the tax year 2007/08 or brought forward as at 5 April 2007. (10 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 will continue to apply for the
foreseeable future.
正确答案:


-
第5题:
ORGANIZING A BUSINESS IN DIFFERENT WAYS Businesses are structured in different ways to meet different needs. The simplest form. of business is called an individual or sole proprietorship. The proprietor owns all of the property of the business and is responsible for everything. Another kind of business is a partnership. Two or more people go into business together. An agreement is usually needed to decide how much of the partnership each person controls. One kind of partnership is called a limited liability partnership. These have full partners and limited partners. Limited partners may not share as much in the profits, but they also have less responsibility for the business. Doctors, lawyers and accountants often form. partnerships to share their risks and profits. A husband and wife can form. a business partnership together. Partnerships exist only for as long as the owners remain alive. The same is true of individual proprietorships. But corporations are designed to have an unlimited lifetime. A corporation is the most complex kind of business organization. Corporations can sell stock as a way to raise money. Stocks represent shares of ownership in a company. Investors who buy stock can trade their shares or keep them as long as the company is in business. A corporation is recognized as an entity-its own legal being, separate from its owners. A board of directors controls corporate policies. The directors appoint top company officers. The directors might or might not hold shares in the corporation. Corporations can have a few major shareholders, or ownership can be spread among the general public. But not all corporations are traditional businesses that sell stock. Some non-profit groups are also organized as corporations.
1. This passage is mainly about ().
A. why different forms of business run
B. when different forms of business raise money
C. how different forms of business are organized
2. What is usually needed to decide the portion of the partnership each person controls?()
A. A rule.
B. An agreement.
C. A regulation.
3. Who are not included in limited liability partnerships?()
A. Full partners.
B. Limited partners.
C. Unlimited partners.
4. How can corporations raise money?()
A. By selling stock.
B. By buying stock.
C. By holding corporation shares.
5. Who controls corporate policies in a corporation?()
A. Chairman of the board.
B. A board of directors.
C. The owner of the corporation.
参考答案:1:C; 2:B;3:C; 4:A;5:B
-
第6题:
On 1 April 2009 Pandar purchased 80% of the equity shares in Salva. The acquisition was through a share exchange of three shares in Pandar for every five shares in Salva. The market prices of Pandar’s and Salva’s shares at 1 April
2009 were $6 per share and $3.20 respectively.
On the same date Pandar acquired 40% of the equity shares in Ambra paying $2 per share.
The summarised income statements for the three companies for the year ended 30 September 2009 are:
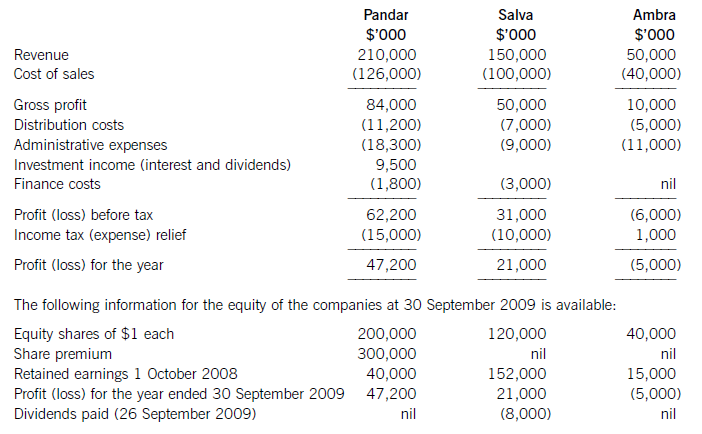
The following information is relevant:
(i) The fair values of the net assets of Salva at the date of acquisition were equal to their carrying amounts with the exception of an item of plant which had a carrying amount of $12 million and a fair value of $17 million. This plant had a remaining life of five years (straight-line depreciation) at the date of acquisition of Salva. All depreciation is charged to cost of sales.
In addition Salva owns the registration of a popular internet domain name. The registration, which had a
negligible cost, has a five year remaining life (at the date of acquisition); however, it is renewable indefinitely at a nominal cost. At the date of acquisition the domain name was valued by a specialist company at $20 million.
The fair values of the plant and the domain name have not been reflected in Salva’s financial statements.
No fair value adjustments were required on the acquisition of the investment in Ambra.
(ii) Immediately after its acquisition of Salva, Pandar invested $50 million in an 8% loan note from Salva. All interest accruing to 30 September 2009 had been accounted for by both companies. Salva also has other loans in issue at 30 September 2009.
(iii) Pandar has credited the whole of the dividend it received from Salva to investment income.
(iv) After the acquisition, Pandar sold goods to Salva for $15 million on which Pandar made a gross profit of 20%. Salva had one third of these goods still in its inventory at 30 September 2009. There are no intra-group current account balances at 30 September 2009.
(v) The non-controlling interest in Salva is to be valued at its (full) fair value at the date of acquisition. For this
purpose Salva’s share price at that date can be taken to be indicative of the fair value of the shareholding of the non-controlling interest.
(vi) The goodwill of Salva has not suffered any impairment; however, due to its losses, the value of Pandar’s
investment in Ambra has been impaired by $3 million at 30 September 2009.
(vii) All items in the above income statements are deemed to accrue evenly over the year unless otherwise indicated.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Salva at 1 April 2009; (6 marks)
(ii) Calculate the carrying amount of the investment in Ambra to be included within the consolidated
statement of financial position as at 30 September 2009. (3 marks)
(b) Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pandar Group for the year ended 30 September 2009.(16 marks)
正确答案:
-
第7题:
The earliest immigrants to North America found Indians already living there.The Indians numbered about 500,000 at that time.Their society was a primitive society,but they lived peacefully and welcomed the white strangers to the land.However,these early immigrants from Europe didn't want to share the land with the natives.They killed off many of the Indians,seized their land or pushed them off to lands farther away.Today the Indians,not more than half a million,live in poverty and misery on the land on which they were once masters.
The earliest immigrants were the Spanish,who settled in the southern part of what is now the US.The next large group were the English,after the English came the French,Dutch,Irish,Germans,and other nationality groups,mostly European.
Another early group to arrive were the Negroes.But they were brought in as slaves from Africa.They didn't win freedom till generations later.
Who were the earliest people living in North America?A.The Spanis
B.The Englis
C.The Negroe
D.The Indian答案:D解析:参见本文第一句。 -
第8题:
Although the Wars of the Roses were fought intermittently for()years,ordinary people were little affected and went about their business as usual.
A20
B30
C40
D50
B
略 -
第9题:
Why did the early settlers come to America? Who were the Pilgrims? Who were the Puritans? What were the features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development?
正确答案:—— The early settlers came to America either for the opportunity to realize their dreams and better their lives or for the freedom from religious and governmental persecution. The Pilgrims were persons who suffered religious persecution in England and went to Holland and later moved to America in 1620. The Puritans were the members of a Protestant group in England who wanted to purify the Church of England. Dissatisfied and threatened in England, they saw America as a refuge and migrated to America since 1630. There were a number of features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development. They were: representative form of government, rule of law, respect of individual rights, religious tolerance and a strong spirit of individual enterprise. -
第10题:
单选题Why did Bezaq’s international branch lose 40% of its market share?ABecause the rates it offered were not competitive enough.
BBecause customers were dissatisfied with its past service.
CBecause the service offered by its competitors was far better.
DBecause it no longer received any support from the government.
正确答案: D解析:
推论题。文章说以色列服务水平提高是公司间的竞争引起的,而百扎克公司虽已提供了竞争费,但仍失去了40%的市场,其原因是第二段第四句“people wanted revenge for all the years of bad service”,故B为答案。 -
第11题:
问答题Practice 1 Twenty years ago, Motorola looked upon the Japanese with something close to fear. The Chicago company’s television-manufacturing division had been large and profitable in the 1960s. By the early 1970s, however, high costs and a rising tide of inexpensive Japanese TVs were taking a heavy toll. “The Japanese were very aggressive”, recalls Motorola spokesman Mario Salvadori. “They wanted to get market share.” With cutthroat pricing, they did—eventually running nearly every U.S. electronic company out of the TV business. Motorola sold its Quasar TV unit to a Japanese company in 1974. But while other U.S. companies were floored for foreign competition, Motorola refocused its energies, It turned to wireless communications—an industry it had pioneered (with mobile radios and walkie-talkie) in the 1920s. It was a prescient move.正确答案: 【参考译文】
20年前,摩托罗拉公司带着近乎害怕的心理看待日本企业。早在(20世纪)60年代,这个公司芝加哥的电视制造分公司规模大、利润高。但在70年代初,高成本以及日本廉价电视机日趋上升的势头使其遭受重创。“日本人非常嚣张,”摩托罗拉公司发言人马里奥·萨尔瓦多瑞追忆道,“他们想分享市场。”通过残酷无情的价格战,他们如愿以偿,并最终把几乎所有美国电子公司赶出电视机行业。1974年,摩托罗拉将其Quasar 电视生产厂卖给了一家日本公司。但是,当其他美国公司在对外竞争中败北的时候,摩托罗拉公司重新调整了产业方向,转向无线通讯。这是一个它在20年代开拓的产业(另外还有移动收音机和步话机)。此举确有先见之明。解析: 暂无解析 -
第12题:
单选题The population between the age of 25 and 44 increased by 28.1%from 1980 to 1989 because()Athis was the period of large inflow of young immigrants
Bthis was the birth age of the baby boomers.
Cthe large number born during WW II reached this age bracket
Dthose who were born in the period of baby boom reached this age bracket
正确答案: B解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is to
be paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirus
to redeem the loan after seven years by paying the full amount of the interest to be charged over the ten year
period, plus a penalty of $200,000 and the principal of $2 million. The effective interest rate of the repayment
option is 9·1%. The directors of Sirus are currently restructuring the funding of the company and are in initial
discussions with the bank about the possibility of repaying the loan within the next financial year. Sirus is
uncertain about the accounting treatment for the current loan agreement and whether the loan can be shown as
a current liability because of the discussions with the bank. (6 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(d) Repayment of the loan
If at the beginning of the loan agreement, it was expected that the repayment option would not be exercised, then the effective
interest rate would be 8% and at 30 April 2008, the loan would be stated at $2 million in the statement of financial position
with interest of $160,000 having been paid and accounted for. If, however, at 1 May 2007, the option was expected to be
exercised, then the effective interest rate would be 9·1% and at 30 April 2008, the cash interest paid would have been
$160,000 and the interest charged to the income statement would have been (9·1% x $2 million) $182,000, giving a
statement of financial position figure of $2,022,000 for the amount of the financial liability. However, IAS39 requires the
carrying amount of the financial instrument to be adjusted to reflect actual and revised estimated cash flows. Thus, even if
the option was not expected to be exercised at the outset but at a later date exercise became likely, then the carrying amount
would be revised so that it represented the expected future cash flows using the effective interest rate. As regards the
discussions with the bank over repayment in the next financial year, if the loan was shown as current, then the requirements
of IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ would not be met. Sirus has an unconditional right to defer settlement for longer
than twelve months and the liability is not due to be legally settled in 12 months. Sirus’s discussions should not be considered
when determining the loan’s classification.
It is hoped that the above report clarifies matters. -
第14题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第15题:
5 (a) Carver Ltd was incorporated and began trading in August 2002. It is a close company with no associated
companies. It has always prepared accounts to 31 December and will continue to do so in the future.
It has been decided that Carver Ltd will sell its business as a going concern to Blade Ltd, an unconnected
company, on 31 July 2007. Its premises and goodwill will be sold for £2,135,000 and £290,000 respectively
and its machinery and equipment for £187,000. The premises, which do not constitute an industrial building,
were acquired on 1 August 2002 for £1,808,000 and the goodwill has been generated internally by the
company. The machinery and equipment cost £294,000; no one item will be sold for more than its original cost.
The tax adjusted trading profit of Carver Ltd in 2007, before taking account of both capital allowances and the
sale of the business assets, is expected to be £81,000. The balance on the plant and machinery pool for the
purposes of capital allowances as at 31 December 2006 was £231,500. Machinery costing £38,000 was
purchased on 1 March 2007. Carver Ltd is classified as a small company for the purposes of capital allowances.
On 1 August 2007, the proceeds from the sale of the business will be invested in either an office building or a
portfolio of UK quoted company shares, as follows:
Office building
The office building would be acquired for £3,100,000; the vendor is not registered for value added tax (VAT).
Carver Ltd would borrow the additional funds required from a UK bank. The building is let to a number of
commercial tenants who are not connected with Carver Ltd and will pay rent, in total, of £54,000 per calendar
quarter, in advance, commencing on 1 August 2007. The company’s expenditure for the period from 1 August
2007 to 31 December 2007 is expected to be:
£
Loan interest payable to UK bank 16,000
Building maintenance costs 7,500
Share portfolio
Shares would be purchased for the amount of the proceeds from the sale of the business with no need for further
loan finance. It is estimated that the share portfolio would generate dividends of £36,000 and capital gains, after
indexation allowance, of £10,000 in the period from 1 August 2007 to 31 December 2007.
All figures are stated exclusive of value added tax (VAT).
Required:
(i) Taking account of the proposed sale of the business on 31 July 2007, state with reasons the date(s) on
which Carver Ltd must submit its corporation tax return(s) for the year ending 31 December 2007.
(2 marks)
正确答案:
(a) (i) Due date for submission of corporation tax return
Carver Ltd intends to cease trading on 31 July 2007. This will bring to an end the accounting period that began on
1 January 2007. A new accounting period will commence on 1 August 2007 and end on the company’s accounting
reference date on 31 December 2007.
Carver Ltd is required to submit its corporation tax return by the later of:
– one year after the end of its accounting period; and
– one year after the end of the period of account in which the last day of the accounting period falls.
Accordingly, the company must submit its corporation tax returns for both accounting periods by 31 December 2008. -
第16题:
(d) Wader has decided to close one of its overseas branches. A board meeting was held on 30 April 2007 when a
detailed formal plan was presented to the board. The plan was formalised and accepted at that meeting. Letters
were sent out to customers, suppliers and workers on 15 May 2007 and meetings were held prior to the year
end to determine the issues involved in the closure. The plan is to be implemented in June 2007. The company
wish to provide $8 million for the restructuring but are unsure as to whether this is permissible. Additionally there
was an issue raised at one of the meetings. The operations of the branch are to be moved to another country
from June 2007 but the operating lease on the present buildings of the branch is non-cancellable and runs for
another two years, until 31 May 2009. The annual rent of the buildings is $150,000 payable in arrears on
31 May and the lessor has offered to take a single payment of $270,000 on 31 May 2008 to settle the
outstanding amount owing and terminate the lease on that date. Wader has additionally obtained permission to
sublet the building at a rental of $100,000 per year, payable in advance on 1 June. The company needs advice
on how to treat the above under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
正确答案:(d) A provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent assets’ can only be made in relation to the entity’s
restructuring plans where there is both a detailed formal plan in place and the plans have been announced to those affected.
The plan should identify areas of the business affected, the impact on employees and the likely cost of the restructuring and
the timescale for implementation. There should be a short timescale between communicating the plan and starting to
implement it. A provision should not be recognised until a plan is formalised.
A decision to restructure before the balance sheet date is not sufficient in itself for a provision to be recognised. A formal plan
should be announced prior to the balance sheet date. A constructive obligation should have arisen. It arises where there has
been a detailed formal plan and this has raised a valid expectation in the minds of those affected. The provision should only
include direct expenditure arising from the restructuring. Such amounts do not include costs associated with ongoing business
operations. Costs of retraining staff or relocating continuing staff or marketing or investment in new systems and distribution
networks, are excluded. It seems as though in this case a constructive obligation has arisen as there have been detailed formal
plans approved and communicated thus raising valid expectations. The provision can be allowed subject to the exclusion of
the costs outlined above.
Although executory contracts are outside IAS37, it is permissible to recognise a provision that is onerous. Onerous contracts
can result from restructuring plans or on a stand alone basis. A provision should be made for the best estimate of the excess
unavoidable costs under the onerous contract. This estimate should assess any likely level of future income from new sources.
Thus in this case, the rental income from sub-letting the building should be taken into account. The provision should be
-
第17题:
Shoe Co, a shoe manufacturer, has developed a new product called the ‘Smart Shoe’ for children, which has a built-in tracking device. The shoes are expected to have a life cycle of two years, at which point Shoe Co hopes to introduce a new type of Smart Shoe with even more advanced technology. Shoe Co plans to use life cycle costing to work out the total production cost of the Smart Shoe and the total estimated profit for the two-year period.
Shoe Co has spent $5·6m developing the Smart Shoe. The time spent on this development meant that the company missed out on the opportunity of earning an estimated $800,000 contribution from the sale of another product.
The company has applied for and been granted a ten-year patent for the technology, although it must be renewed each year at a cost of $200,000. The costs of the patent application were $500,000, which included $20,000 for the salary costs of Shoe Co’s lawyer, who is a permanent employee of the company and was responsible for preparing the application.
The following information is also available for the next two years:
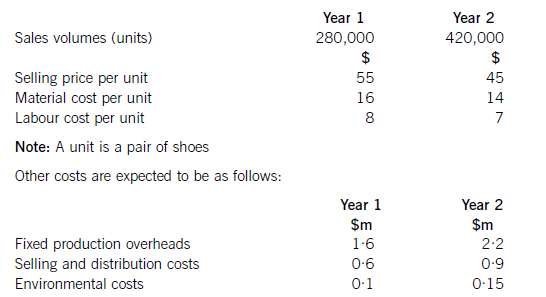
Shoe Co is still negotiating with marketing companies with regard to its advertising campaign, so is uncertain as to what the total marketing costs will be each year. However, the following information is available as regards the probabilities of the range of costs which are likely to be incurred:

Required:
Applying the principles of life cycle costing, calculate the total expected profit for Shoe Co for the two-year period.
(10 marks)
正确答案:
Totalsalesrevenue=(280,000x$55)+(420,000x$45)=$15·4m+18·9m=$34·3m.NoteTheexpectedprofithasbeencalculatedusinglifecyclecostingnotrelevantcosting.Hence,the$20,000salarycostincludedinpatentcostsshouldbeincludedinthelifecyclecost.Similarly,theopportunitycostof$800,000isnotincludedusinglifecyclecostingwhereasifrelevantcostingwasbeingusedtodecideonaparticularcourseofaction,theopportunitycostwouldbeincluded.Working1Expectedmarketingcostinyear1:(0·2x$2·2m)+(0·5x$2·6m)+(0·3x$2·9m)=$2·61mExpectedmarketingcostyear2:(0·3x$1·8m)+(0·4x$2·1m)+(0·3x$2·3m)=$2·07mTotalexpectedmarketingcost=$4·68m -
第18题:
(a) Kayte operates in the shipping industry and owns vessels for transportation. In June 2014, Kayte acquired Ceemone whose assets were entirely investments in small companies. The small companies each owned and operated one or two shipping vessels. There were no employees in Ceemone or the small companies. At the acquisition date, there were only limited activities related to managing the small companies as most activities were outsourced. All the personnel in Ceemone were employed by a separate management company. The companies owning the vessels had an agreement with the management company concerning assistance with chartering, purchase and sale of vessels and any technical management. The management company used a shipbroker to assist with some of these tasks.
Kayte accounted for the investment in Ceemone as an asset acquisition. The consideration paid and related transaction costs were recognised as the acquisition price of the vessels. Kayte argued that the vessels were only passive investments and that Ceemone did not own a business consisting of processes, since all activities regarding commercial and technical management were outsourced to the management company. As a result, the acquisition was accounted for as if the vessels were acquired on a stand-alone basis.
Additionally, Kayte had borrowed heavily to purchase some vessels and was struggling to meet its debt obligations. Kayte had sold some of these vessels but in some cases, the bank did not wish Kayte to sell the vessel. In these cases, the vessel was transferred to a new entity, in which the bank retained a variable interest based upon the level of the indebtedness. Kayte’s directors felt that the entity was a subsidiary of the bank and are uncertain as to whether they have complied with the requirements of IFRS 3 Business Combinations and IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements as regards the above transactions. (12 marks)
(b) Kayte’s vessels constitute a material part of its total assets. The economic life of the vessels is estimated to be 30 years, but the useful life of some of the vessels is only 10 years because Kayte’s policy is to sell these vessels when they are 10 years old. Kayte estimated the residual value of these vessels at sale to be half of acquisition cost and this value was assumed to be constant during their useful life. Kayte argued that the estimates of residual value used were conservative in view of an immature market with a high degree of uncertainty and presented documentation which indicated some vessels were being sold for a price considerably above carrying value. Broker valuations of the residual value were considerably higher than those used by Kayte. Kayte argued against broker valuations on the grounds that it would result in greater volatility in reporting.
Kayte keeps some of the vessels for the whole 30 years and these vessels are required to undergo an engine overhaul in dry dock every 10 years to restore their service potential, hence the reason why some of the vessels are sold. The residual value of the vessels kept for 30 years is based upon the steel value of the vessel at the end of its economic life. At the time of purchase, the service potential which will be required to be restored by the engine overhaul is measured based on the cost as if it had been performed at the time of the purchase of the vessel. In the current period, one of the vessels had to have its engine totally replaced after only eight years. Normally, engines last for the 30-year economic life if overhauled every 10 years. Additionally, one type of vessel was having its funnels replaced after 15 years but the funnels had not been depreciated separately. (11 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in the financial statements of Kayte.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the elements above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 3 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) The accounting for the transaction as an asset acquisition does not comply with the requirements of IFRS 3 Business Combinations and should have been accounted as a business combination. This would mean that transaction costs would be expensed, the vessels recognised at fair value, any deferred tax recognised at nominal value and the difference between these amounts and the consideration paid to be recognised as goodwill.
In accordance with IFRS 3, an entity should determine whether a transaction is a business combination by applying the definition of a business in IFRS 3. A business is an integrated set of activities and assets which is capable of being conducted and managed for the purpose of providing a return in the form. of dividends, lower costs or other economic benefits directly to investors or other owners, members or participants. A business consists of inputs and processes applied to those inputs which have the ability to create outputs. Although businesses usually have outputs, outputs are not required to qualify as a business.
When analysing the transaction, the following elements are relevant:
(i) Inputs: Shares in vessel owning companies, charter arrangements, outsourcing arrangements with a management company, and relationships with a shipping broker.
(ii) Processes: Activities regarding chartering and operating the vessels, financing the business, purchase and sales of vessels.
(iii) Outputs: Ceemone would generate revenue from charter agreements and has the ability to gain economic benefit from the vessels.
IFRS 3 states that whether a seller operated a set of assets and activities as a business or intends to operate it as a business is not relevant in evaluating whether it is a business. It is not relevant therefore that some activities were outsourced as Ceemone could chose to conduct and manage the integrated set of assets and activities as a business. As a result, the acquisition included all the elements which constitute a business, in accordance with IFRS 3.
IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements sets out the situation where an investor controls an investee. This is the case, if and only if, the investor has all of the following elements:
(i) power over the investee, that is, the investor has existing rights which give it the ability to direct the relevant activities (the activities which significantly affect the investee’s returns);
(ii) exposure, or rights, to variable returns from its involvement with the investee;
(iii) the ability to use its power over the investee to affect the amount of the investor’s returns.
Where a party has all three elements, then it is a parent; where at least one element is missing, then it is not. In every case, IFRS 10 looks to the substance of the arrangement and not just to its legal form. Each situation needs to be assessed individually. The question arises in this case as to whether the entities created are subsidiaries of the bank. The bank is likely to have power over the investee, may be exposed to variable returns and certainly may have the power to affect the amount of the returns. Thus the bank is likely to have a measure of control but the extent will depend on the constitution of the entity.
(b) Kayte’s calculation of the residual value of the vessels with a 10-year useful life is unacceptable under IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment because estimating residual value based on acquisition cost does not comply with the requirements of IAS 16. Kayte should prepare a new model to determine residual value which would take account of broker valuations at the end of each reporting period and which would produce zero depreciation charge when estimated residual value was higher than the carrying amount.
IAS 16 paragraph 6 defines residual value as the estimated amount which an entity would currently obtain from disposal of the asset, after deducting the estimated costs of disposal, if the asset were already at the age and in the condition expected at the end of its useful life.
IAS 16 requires the residual value to be reviewed at least at the end of each financial year end with the depreciable amount of an asset allocated on a systematic basis over its useful life. IAS 16 specifies that the depreciable amount of an asset is determined after deducting its residual value.
Kayte’s original model implied that the residual value was constant for the vessel’s entire useful life. The residual value has to be adjusted especially when an expected sale approaches, and the residual value has to come closer to disposal proceeds minus disposal costs at the end of the useful life. IAS 16 says that in cases when the residual value is greater than the asset’s carrying amount, the depreciation charge is zero unless and until its residual value subsequently decreases to an amount below the asset’s carrying amount. The residual value should be the value at the reporting date as if the vessel were already of the age and in the condition expected at the end of its useful life. An increase in the expected residual value of an asset because of past events will affect the depreciable amount, while expectation of future changes in residual value other than the effects of expected wear and tear will not. There is no guidance in IAS 16 on how to estimate residual value when the useful life is considered to be shorter than the economic life. Undesirable volatility is not a convincing argument to support the accounting treatment, and broker valuations could be a useful starting point to estimate residual value.
As regards the vessels which are kept for the whole of their economic life, a residual value based upon the scrap value of steel is acceptable. Therefore the vessels should be depreciated based upon the cost less the scrap value of steel over the 30-year period. The engine need not be componentised as it will have the same 30-year life if maintained every 10 years. It is likely that the cost of major planned maintenance will increase over the life of a vessel due to inflation and the age of the vessel. This additional cost will be capitalised when incurred and therefore the depreciation charge on these components may be greater in the later stages of a vessel’s life.
When major planned maintenance work is to be undertaken, the cost should be capitalised. The engine overhaul will be capitalised as a new asset which will then be depreciated over the 10-year period to the next overhaul. The depreciation of the original capitalised amount will typically be calculated such that it had a net book value of nil when the overhaul is undertaken.
This is not the case with one vessel, because work was required earlier than expected. In this case, any remaining net book value of the old engine and overhaul cost should be expensed immediately.
The initial carve out of components should include all major maintenance events which are likely to occur over the economic life of the vessel. Sometimes, it may subsequently be found that the initial allocation was insufficiently detailed, in that not all components were identified. This is the case with the funnels. In this situation it is necessary to determine what the net book value of the component would currently be had it been initially identified. This will sometimes require the initial cost to be determined by reference to the replacement cost and the associated accumulated depreciation charge determined using the rate used for the vessel. This is likely to leave a significant net book value in the component being replaced, which will need to be written off at the time the replacement is capitalised.
-
第19题:
The population between the age of 25 and 44 increased by 28.1%from 1980 to 1989 because()
Athis was the period of large inflow of young immigrants
Bthis was the birth age of the baby boomers.
Cthe large number born during WW II reached this age bracket
Dthose who were born in the period of baby boom reached this age bracket
D
略 -
第20题:
The population between the age of 25 and 44 increased by 28.1%from 1980 to 1989 because()
- A、this was the period of large inflow of young immigrants
- B、this was the birth age of the baby boomers.
- C、the large number born during WW II reached this age bracket
- D、those who were born in the period of baby boom reached this age bracket
正确答案:D -
第21题:
单选题Although the Wars of the Roses were fought intermittently for()years,ordinary people were little affected and went about their business as usual.A20
B30
C40
D50
正确答案: D解析: 暂无解析 -
第22题:
单选题The author of the book believes that .Adrinking coffee was unpatriotic
B2000 insurance companies were set up hundreds of years ago
CEuropeans were responsible for the existence of slavery
Dcoffee actually influenced the rise of business
正确答案: B解析: -
第23题:
问答题Why did the early settlers come to America? Who were the Pilgrims? Who were the Puritans? What were the features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development?正确答案: —— The early settlers came to America either for the opportunity to realize their dreams and better their lives or for the freedom from religious and governmental persecution. The Pilgrims were persons who suffered religious persecution in England and went to Holland and later moved to America in 1620. The Puritans were the members of a Protestant group in England who wanted to purify the Church of England. Dissatisfied and threatened in England, they saw America as a refuge and migrated to America since 1630. There were a number of features in the colonial period which had influence on later American development. They were: representative form of government, rule of law, respect of individual rights, religious tolerance and a strong spirit of individual enterprise.解析: 暂无解析
