23 The capital structure of a company at 30 June 2005 is as follows:$mOrdinary share capital 100Share premium account 40Retained earnings 6010% Loan notes 40The company’s income statement for the year ended 30 June 2005 showed:$mOperating profit 44Loan no
题目
23 The capital structure of a company at 30 June 2005 is as follows:
$m
Ordinary share capital 100
Share premium account 40
Retained earnings 60
10% Loan notes 40
The company’s income statement for the year ended 30 June 2005 showed:
$m
Operating profit 44
Loan note interest (4)
___
Profit for year 40
____
What is the company’s return on capital employed?
A 40/240 = 162/3 per cent
B 40/100 = 40 per cent
C 44/240 = 181/3 per cent
D 44/200 = 22 per cent
相似考题
更多“23 The capital structure of a company at 30 June 2005 is as follows:$mOrdinary share capital 100Share premium account 40Retained earnings 6010% Loan notes 40The company’s income statement for the year ended 30 June 2005 showed:$mOperating profit 44Loan no”相关问题
-
第1题:
17 A company sublets part of its office accommodation. In the year ended 30 June 2005 cash received from tenants
was $83,700.
Details of rent in arrears and in advance at the beginning and end of the year were:
In arrears In advance
$ $
30 June 2004 3,800 2,400
30 June 2005 4,700 3,000
All arrears of rent were subsequently received.
What figure for rental income should be included in the company’s income statement for the year ended 30 June
2005?
A $84,000
B $83,400
C $80,600
D $85,800
正确答案:A
-
第2题:
24 Sigma’s bank statement shows an overdrawn balance of $38,600 at 30 June 2005. A check against the company’s cash book revealed the following differences:
1 Bank charges of $200 have not been entered in the cash book.
2 Lodgements recorded on 30 June 2005 but credited by the bank on 2 July $14,700.
3 Cheque payments entered in cash book but not presented for payment at 30 June 2005 $27,800.
4 A cheque payment to a supplier of $4,200 charged to the account in June 2005 recorded in the cash book as a receipt.
Based on this information, what was the cash book balance BEFORE any adjustments?
A $43,100 overdrawn
B $16,900 overdrawn
C $60,300 overdrawn
D $34,100 overdrawn
正确答案:A
-
第3题:
(c) (i) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended
30 September 2005 should be submitted, and advise the company of the penalties that will be due if
the return is not submitted until 31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(ii) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005
should be paid, and advise the company of the interest that will be due if the liability is not paid until
31 May 2007. (3 marks)
正确答案:(c) Self-assessment tax return
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be submitted by
30 September 2006.
(2) If the company does not submit its self-assessment tax return until 31 May 2007, then there will be an automatic fixed
penalty of £200 since the return is more than three months late.
(3) There will also be an additional corporation tax related penalty of £4,415 (44,150 × 10%) being 10% of the tax unpaid,
since the self-assessment tax return is more than six months late.
Corporation tax liability
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be paid by 1 July 2006.
(2) If the company does not pay its corporation tax until 31 May 2007, then interest of £3,035 (44,150 at 7·5% = 3,311
× 11/12) will be charged by HM Revenue & Customs for the period 1 July 2006 to 31 May 2007. -
第4题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
正确答案:
4 (i) Proposed dividend
The dividend was proposed after the balance sheet date and the company, therefore, did not have a liability at the balance
sheet date. No provision for the dividend should be recognised. The approval by the directors and the shareholders are
enough to create a valid expectation that the payment will be made and give rise to an obligation. However, this occurred
after the current year end and, therefore, will be charged against the profits for the year ending 31 October 2006.
The existence of a good record of dividend payments and an established dividend policy does not create a valid expectation
or an obligation. However, the proposed dividend will be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements as the directors
approved it prior to the authorisation of the financial statements.
(ii) Disposal of subsidiary
It would appear that the loss on the sale of the subsidiary provides evidence that the value of the consolidated net assets of
the subsidiary was impaired at the year end as there has been no significant event since 31 October 2005 which would have
caused the reduction in the value of the subsidiary. The disposal loss provides evidence of the impairment and, therefore,
the value of the net assets and goodwill should be reduced by the loss of $9 million plus the loss ($2 million) to the date of
the disposal, i.e. $11 million. The sale provides evidence of a condition that must have existed at the balance sheet date
(IAS10). This amount will be charged to the income statement and written off goodwill of $12 million, leaving a balance of
$1 million on that account. The subsidiary’s assets are impaired because the carrying values are not recoverable. The net
assets and goodwill of Krup would form. a separate income generating unit as the subsidiary is being disposed of before the
financial statements are authorised. The recoverable amount will be the sale proceeds at the date of sale and represents the
value-in-use to the group. The impairment loss is effectively taking account of the ultimate loss on sale at an earlier point in
time. IFRS5, ‘Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations’, will not apply as the company had no intention
of selling the subsidiary at the year end. IAS10 would require disclosure of the disposal of the subsidiary as a non-adjusting
event after the balance sheet date.
(iii) Issue of ordinary shares
IAS33 ‘Earnings per share’ states that if there is a bonus issue after the year end but before the date of the approval of the
financial statements, then the earnings per share figure should be based on the new number of shares issued. Additionally
a company should disclose details of all material ordinary share transactions or potential transactions entered into after the
balance sheet date other than the bonus issue or similar events (IAS10/IAS33). The principle is that if there has been a
change in the number of shares in issue without a change in the resources of the company, then the earnings per share
calculation should be based on the new number of shares even though the number of shares used in the earnings per share
calculation will be inconsistent with the number shown in the balance sheet. The conditions relating to the share issue
(contingent) have been met by the end of the period. Although the shares were issued after the balance sheet date, the issue
of the shares was no longer contingent at 31 October 2005, and therefore the relevant shares will be included in the
computation of both basic and diluted EPS. Thus, in this case both the bonus issue and the contingent consideration issue
should be taken into account in the earnings per share calculation and disclosure made to that effect. Any subsequent change
in the estimate of the contingent consideration will be adjusted in the period when the revision is made in accordance with
IAS8.
Additionally IFRS3 ‘Business Combinations’ requires the fair value of all types of consideration to be reflected in the cost of
the acquisition. The contingent consideration should be included in the cost of the business combination at the acquisition
date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. In the case of Metalic, the contingent consideration has
been paid in the post-balance sheet period and the value of such consideration can be determined ($11 per share). Thus
an accurate calculation of the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Metalic can be made in the period to 31 October 2005.
Prior to the issue of the shares on 12 November 2005, a value of $10 per share would have been used to value the
contingent consideration. The payment of the contingent consideration was probable because the average profits of Metalic
averaged over $7 million for several years. At 31 October 2005 the value of the contingent shares would be included in a
separate category of equity until they were issued on 12 November 2005 when they would be transferred to the share capital
and share premium account. Goodwill will increase by 300,000 x ($11 – $10) i.e. $300,000.
(iv) Property
IFRS5 (paragraph 7) states that for a non-current asset to be classified as held for sale, the asset must be available for
immediate sale in its present condition subject to the usual selling terms, and its sale must be highly probable. The delay in
this case in the selling of the property would indicate that at 31 October 2005 the property was not available for sale. The
property was not to be made available for sale until the repairs were completed and thus could not have been available for
sale at the year end. If the criteria are met after the year end (in this case on 30 November 2005), then the non-current
asset should not be classified as held for sale in the previous financial statements. However, disclosure of the event should
be made if it meets the criteria before the financial statements are authorised (IFRS5 paragraph 12). Thus in this case,
disclosure should be made.
The property on the application of IFRS5 should have been carried at the lower of its carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell. However, the company has simply used fair value less costs to sell as the basis of valuation and shown the
property at $27 million in the financial statements.
The carrying amount of the property would have been $20 million less depreciation $1 million, i.e. $19 million. Because
the property is not held for sale under IFRS5, then its classification in the balance sheet will change and the property will be
valued at $19 million. Thus the gain of $7 million on the wrong application of IFRS5 will be deducted from reserves, and
the property included in property, plant and equipment. Total equity will therefore be reduced by $8 million.
(v) Share appreciation rights
IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ (paragraph 30) requires a company to re-measure the fair value of a liability to pay cash-settled
share based payment transactions at each reporting date and the settlement date, until the liability is settled. An example of
such a transaction is share appreciation rights. Thus the company should recognise a liability of ($8 x 10 million shares),
i.e. $80 million at 31 October 2005, the vesting date. The liability recognised at 31 October 2005 was in fact based on the
share price at the previous year end and would have been shown at ($6 x 1/2) x 10 million shares, i.e. $30 million. This
liability at 31 October 2005 had not been changed since the previous year end by the company. The SARs vest over a twoyear
period and thus at 31 October 2004 there would be a weighting of the eventual cost by 1 year/2 years. Therefore, an
additional liability and expense of $50 million should be accounted for in the financial statements at 31 October 2005. The
SARs would be settled on 1 December 2005 at $9 x 10 million shares, i.e. $90 million. The increase in the value of the
SARs since the year end would not be accrued in the financial statements but charged to profit or loss in the year ended31 October 2006. -
第5题:
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services. -
第6题:
22 Which of the following statements about limited liability companies’ accounting is/are correct?
1 A revaluation reserve arises when a non-current asset is sold at a profit.
2 The authorised share capital of a company is the maximum nominal value of shares and loan notes the company
may issue.
3 The notes to the financial statements must contain details of all adjusting events as defined in IAS10 Events after
the balance sheet date.
A All three statements
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D None of the statements
正确答案:D
-
第7题:
11 Which of the following statements are correct?
1 A company might make a rights issue if it wished to raise more equity capital.
2 A rights issue might increase the share premium account whereas a bonus issue is likely to reduce it.
3 A bonus issue will reduce the gearing (leverage) ratio of a company.
4 A rights issue will always increase the number of shareholders in a company whereas a bonus issue will not.
A 1 and 2
B 1 and 3
C 2 and 3
D 2 and 4
正确答案:A
-
第8题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第9题:
2 Clifford and Amanda, currently aged 54 and 45 respectively, were married on 1 February 1998. Clifford is a higher
rate taxpayer who has realised taxable capital gains in 2007/08 in excess of his capital gains tax annual exemption.
Clifford moved into Amanda’s house in London on the day they were married. Clifford’s own house in Oxford, where
he had lived since acquiring it for £129,400 on 1 August 1996, has been empty since that date although he and
Amanda have used it when visiting friends. Clifford has been offered £284,950 for the Oxford house and has decided
that it is time to sell it. The house has a large garden such that Clifford is also considering an offer for the house and
a part only of the garden. He would then sell the remainder of the garden at a later date as a building plot. His total
sales proceeds will be higher if he sells the property in this way.
Amanda received the following income from quoted investments in 2006/07:
£
Dividends in respect of quoted trading company shares 1,395
Dividends paid by a Real Estate Investment Trust out of tax exempt property income 485
On 1 May 2006, Amanda was granted a 22 year lease of a commercial investment property. She paid the landlord
a premium of £6,900 and also pays rent of £2,100 per month. On 1 June 2006 Amanda granted a nine year
sub-lease of the property. She received a premium of £14,700 and receives rent of £2,100 per month.
On 1 September 2006 Amanda gave quoted shares with a value of £2,200 to a registered charity. She paid broker’s
fees of £115 in respect of the gift.
Amanda began working for Shearer plc, a quoted company, on 1 June 2006 having had a two year break from her
career. She earns an annual salary of £38,600 and was paid a bonus of £5,750 in August 2006 for agreeing to
come and work for the company. On 1 August 2006 Amanda was provided with a fully expensed company car,
including the provision of private petrol, which had a list price when new of £23,400 and a CO2 emissions rate of
187 grams per kilometre. Amanda is required to pay Shearer plc £22 per month in respect of the private use of the
car. In June and July 2006 Amanda used her own car whilst on company business. She drove 720 business miles
during this two month period and was paid 34 pence per mile. Amanda had PAYE of £6,785 deducted from her gross
salary in the tax year 2006/07.
After working for Shearer plc for a full year, Amanda becomes entitled to the following additional benefits:
– The opportunity to purchase a large number of shares in Shearer plc on 1 July 2007 for £3·30 per share. It is
anticipated that the share price on that day will be at least £7·50 per share. The company will make an interestfree
loan to Amanda equal to the cost of the shares to be repaid in two years.
– Exclusive free use of the company sailing boat for one week in August 2007. The sailing boat was purchased by
Shearer plc in January 2005 for use by its senior employees and costs the company £1,400 a week in respect
of its crew and other running expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clifford’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2007/08 on the assumption that the Oxford
house together with its entire garden is sold on 31 July 2007 for £284,950. Comment on the relevance
to your calculations of the size of the garden; (5 marks)
正确答案: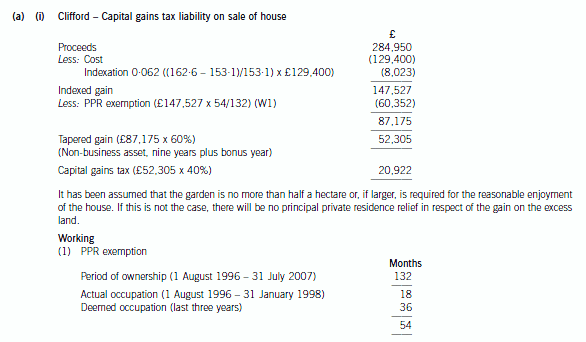
-
第10题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Volcan, a long-established limited liability company. Volcan operates
a national supermarket chain of 23 stores, five of which are in the capital city, Urvina. All the stores are managed in
the same way with purchases being made through Volcan’s central buying department and product pricing, marketing,
advertising and human resources policies being decided centrally. The draft financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2005 show revenue of $303 million (2004 – $282 million), profit before taxation of $9·5 million (2004
– $7·3 million) and total assets of $178 million (2004 – $173 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) On 1 May 2005, Volcan announced its intention to downsize one of the stores in Urvina from a supermarket to
a ‘City Metro’ in response to a significant decline in the demand for supermarket-style. shopping in the capital.
The store will be closed throughout June, re-opening on 1 July 2005. Goodwill of $5·5 million was recognised
three years ago when this store, together with two others, was bought from a national competitor. It is Volcan’s
policy to write off goodwill over five years. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 VOLCAN
(a) Store impairment
(i) Matters
■ Materiality
? The cost of goodwill represents 3·1% of total assets and is therefore material.
? However, after three years the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) represents only 1·2% of total assets –
and is therefore immaterial in the context of the balance sheet.
? The annual amortisation charge ($1·1m) represents 11·6% profit before tax (PBT) and is therefore also
material (to the income statement).
? The impact of writing off the whole of the carrying amount would be material to PBT (23%).
Tutorial note: The temporary closure of the supermarket does not constitute a discontinued operation under IFRS 5
‘Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’.
■ Under IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ Volcan should no longer be writing goodwill off over five years but
subjecting it to an annual impairment test.
■ The announcement is after the balance sheet date and is therefore a non-adjusting event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the
Balance Sheet Date’) insofar as no provision for restructuring (for example) can be made.
■ However, the event provides evidence of a possible impairment of the cash-generating unit which is this store and,
in particular, the value of goodwill assigned to it.
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) can be allocated on a reasonable and consistent basis to this and the
other two stores (purchased at the same time) Volcan’s management should have applied an impairment test to
the goodwill of the downsized store (this is likely to show impairment).
■ If more than 22% of goodwill is attributable to the City Metro store – then its write-off would be material to PBT
(22% × $2·2m ÷ $9·5m = 5%).
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill cannot be so allocated; the impairment test should be applied to the
cash-generating unit that is the three stores (this may not necessarily show impairment).
■ Management should have considered whether the other four stores in Urvina (and elsewhere) are similarly
impaired.
■ Going concern is unlikely to be an issue unless all the supermarkets are located in cities facing a downward trend
in demand.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for stating the rules for recognition of an impairment loss for a cash-generating
unit. However, as it is expected that the majority of candidates will not deal with this matter, the rules of IAS 36 are
not reproduced here.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Board minutes approving the store’s ‘facelift’ and documenting the need to address the fall in demand for it as a
supermarket.
■ Recomputation of the carrying amount of goodwill (2/5 × $5·5m = $2·2m).
■ A schedule identifying all the assets that relate to the store under review and the carrying amounts thereof agreed
to the underlying accounting records (e.g. non-current asset register).
■ Recalculation of value in use and/or fair value less costs to sell of the cash-generating unit (i.e. the store that is to
become the City Metro, or the three stores bought together) as at 31 March 2005.
Tutorial note: If just one of these amounts exceeds carrying amount there will be no impairment loss. Also, as
there is a plan NOT to sell the store it is most likely that value in use should be used.
■ Agreement of cash flow projections (e.g. to approved budgets/forecast revenues and costs for a maximum of five
years, unless a longer period can be justified).
■ Written management representation relating to the assumptions used in the preparation of financial budgets.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (and
the risks specific to the store) and is reasonable. For example, by comparison with Volcan’s weighted average cost
of capital.
■ Inspection of the store (if this month it should be closed for refurbishment).
■ Revenue budgets and cash flow projections for:
– the two stores purchased at the same time;
– the other stores in Urvina; and
– the stores elsewhere.
Also actual after-date sales by store compared with budget. -
第11题:
KFP Co, a company listed on a major stock market, is looking at its cost of capital as it prepares to make a bid to buy a rival unlisted company, NGN. Both companies are in the same business sector. Financial information on KFP Co and NGN is as follows:

NGN has a cost of equity of 12% per year and has maintained a dividend payout ratio of 45% for several years. The current earnings per share of the company is 80c per share and its earnings have grown at an average rate of 4·5% per year in recent years.
The ex div share price of KFP Co is $4·20 per share and it has an equity beta of 1·2. The 7% bonds of the company are trading on an ex interest basis at $94·74 per $100 bond. The price/earnings ratio of KFP Co is eight times.
The directors of KFP Co believe a cash offer for the shares of NGN would have the best chance of success. It has been suggested that a cash offer could be financed by debt.
Required:
(a) Calculate the weighted average cost of capital of KFP Co on a market value weighted basis. (10 marks)
(b) Calculate the total value of the target company, NGN, using the following valuation methods:
(i) Price/earnings ratio method, using the price/earnings ratio of KFP Co; and
(ii) Dividend growth model. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the relationship between capital structure and weighted average cost of capital, and comment on
the suggestion that debt could be used to finance a cash offer for NGN. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(b)(i)Price/earningsratiomethodEarningspershareofNGN=80cpersharePrice/earningsratioofKFPCo=8SharepriceofNGN=80x8=640cor$6·40NumberofordinarysharesofNGN=5/0·5=10millionsharesValueofNGN=6·40x10m=$64millionHowever,itcanbearguedthatareductionintheappliedprice/earningsratioisneededasNGNisunlistedandthereforeitssharesaremoredifficulttobuyandsellthanthoseofalistedcompanysuchasKFPCo.Ifwereducetheappliedprice/earningsratioby10%(othersimilarpercentagereductionswouldbeacceptable),itbecomes7·2timesandthevalueofNGNwouldbe(80/100)x7·2x10m=$57·6million(ii)DividendgrowthmodelDividendpershareofNGN=80cx0·45=36cpershareSincethepayoutratiohasbeenmaintainedforseveralyears,recentearningsgrowthisthesameasrecentdividendgrowth,i.e.4·5%.Assumingthatthisdividendgrowthcontinuesinthefuture,thefuturedividendgrowthratewillbe4·5%.Sharepricefromdividendgrowthmodel=(36x1·045)/(0·12–0·045)=502cor$5·02ValueofNGN=5·02x10m=$50·2million(c)Adiscussionofcapitalstructurecouldstartfromrecognisingthatequityismoreexpensivethandebtbecauseoftherelativeriskofthetwosourcesoffinance.Equityisriskierthandebtandsoequityismoreexpensivethandebt.Thisdoesnotdependonthetaxefficiencyofdebt,sincewecanassumethatnotaxesexist.Wecanalsoassumethatasacompanygearsup,itreplacesequitywithdebt.Thismeansthatthecompany’scapitalbaseremainsconstantanditsweightedaveragecostofcapital(WACC)isnotaffectedbyincreasinginvestment.Thetraditionalviewofcapitalstructureassumesanon-linearrelationshipbetweenthecostofequityandfinancialrisk.Asacompanygearsup,thereisinitiallyverylittleincreaseinthecostofequityandtheWACCdecreasesbecausethecostofdebtislessthanthecostofequity.Apointisreached,however,wherethecostofequityrisesataratethatexceedsthereductioneffectofcheaperdebtandtheWACCstartstoincrease.Inthetraditionalview,therefore,aminimumWACCexistsand,asaresult,amaximumvalueofthecompanyarises.ModiglianiandMillerassumedaperfectcapitalmarketandalinearrelationshipbetweenthecostofequityandfinancialrisk.Theyarguedthat,asacompanygearedup,thecostofequityincreasedataratethatexactlycancelledoutthereductioneffectofcheaperdebt.WACCwasthereforeconstantatalllevelsofgearingandnooptimalcapitalstructure,wherethevalueofthecompanywasatamaximum,couldbefound.Itwasarguedthattheno-taxassumptionmadebyModiglianiandMillerwasunrealistic,sinceintherealworldinterestpaymentswereanallowableexpenseincalculatingtaxableprofitandsotheeffectivecostofdebtwasreducedbyitstaxefficiency.Theyrevisedtheirmodeltoincludethistaxeffectandshowedthat,asaresult,theWACCdecreasedinalinearfashionasacompanygearedup.Thevalueofthecompanyincreasedbythevalueofthe‘taxshield’andanoptimalcapitalstructurewouldresultbygearingupasmuchaspossible.Itwaspointedoutthatmarketimperfectionsassociatedwithhighlevelsofgearing,suchasbankruptcyriskandagencycosts,wouldlimittheextenttowhichacompanycouldgearup.Inpractice,therefore,itappearsthatcompaniescanreducetheirWACCbyincreasinggearing,whileavoidingthefinancialdistressthatcanariseathighlevelsofgearing.Ithasfurtherbeensuggestedthatcompanieschoosethesourceoffinancewhich,foronereasonoranother,iseasiestforthemtoaccess(peckingordertheory).Thisresultsinaninitialpreferenceforretainedearnings,followedbyapreferencefordebtbeforeturningtoequity.TheviewsuggeststhatcompaniesmaynotinpracticeseektominimisetheirWACC(andconsequentlymaximisecompanyvalueandshareholderwealth).TurningtothesuggestionthatdebtcouldbeusedtofinanceacashbidforNGN,thecurrentandpostacquisitioncapitalstructuresandtheirrelativegearinglevelsshouldbeconsidered,aswellastheamountofdebtfinancethatwouldbeneeded.Earliercalculationssuggestthatatleast$58mwouldbeneeded,ignoringanypremiumpaidtopersuadetargetcompanyshareholderstoselltheirshares.Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofKFPCois60%(15m/25m).Thedebtofthecompanywouldincreaseby$58minordertofinancethebidandbyafurther$20maftertheacquisition,duetotakingontheexistingdebtofNGN,givingatotalof$93m.Ignoringotherfactors,thegearingwouldincreaseto372%(93m/25m).KFPCowouldneedtoconsiderhowitcouldservicethisdangerouslyhighlevelofgearinganddealwiththesignificantriskofbankruptcythatitmightcreate.ItwouldalsoneedtoconsiderwhetherthebenefitsarisingfromtheacquisitionofNGNwouldcompensateforthesignificantincreaseinfinancialriskandbankruptcyriskresultingfromusingdebtfinance. -
第12题:
For the year just ended, N company had an earnings of$ 2 per share and paid a dividend of $ 1. 2 on its stock. The growth rate in net income and dividend are both expected to be a constant 7 percent per year, indefinitely. N company has a Beta of 0. 8, the risk - free interest rate is 6 percent, and the market risk premium is 8 percent.
P Company is very similar to N company in growth rate, risk and dividend. payout ratio. It had 20 million shares outstanding and an earnings of $ 36 million for the year just ended. The earnings will increase to $ 38. 5 million the next year.
Requirement :
A. Calculate the expected rate of return on N company 's equity.
B. Calculate N Company 's current price-earning ratio and prospective price - earning ratio.
C. Using N company 's current price-earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
D. Using N company 's prospective price - earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
答案:解析:A. The expected rate of return on N company's equity =6% +0. 8*8% =12.4%
B. Current price -earning ratio = (1. 2/2) * (1 +7% )/ (12.4% -7% ) =11. 89
Prospective price - earning ratio = (1. 2/2) / (12. 4% - 70% ) =11. 11
C. P company's stock = 11. 89* 36/20 = 21. 4
D. P company's stock = 11. 11* 38. 5/20 = 21. 39
-
第13题:
19 At 30 June 2004 a company’s allowance for receivables was $39,000. At 30 June 2005 trade receivables totalled $517,000. It was decided to write off debts totalling $37,000 and to adjust the allowance for receivables to the equivalent of 5 per cent of the trade receivables based on past events.
What figure should appear in the income statement for these items?
A $61,000
B $22,000
C $24,000
D $23,850
正确答案:B
-
第14题:
(b) Assuming that Thai Curry Ltd claims relief for its trading loss against total profits under s.393A ICTA 1988,calculate the company’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
-
第15题:
(b) Assuming that the cost of equity and cost of debt do not alter, estimate the effect of the share repurchase on the company’s cost of capital and value. (5 marks)
正确答案:(b) Estimated new cost of capital:
If equity is repurchased such that the gearing becomes 50% equity, 50% debt, the new estimated weighted average cost of capital is:
-
第16题:
(ii) Explain the accounting treatment under IAS39 of the loan to Bromwich in the financial statements of
Ambush for the year ended 30 November 2005. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) There is objective evidence of impairment because of the financial difficulties and reorganisation of Bromwich. The
impairment loss on the loan will be calculated by discounting the estimated future cash flows. The future cash flows
will be $100,000 on 30 November 2007. This will be discounted at an effective interest rate of 8% to give a present
value of $85,733. The loan will, therefore, be impaired by ($200,000 – $85,733) i.e. $114,267.
(Note: IAS 39 requires accrual of interest on impaired loans at the original effective interest rate. In the year to
30 November 2006 interest of 8% of $85,733 i.e. $6,859 would be accrued.)
-
第17题:
17 A business income statement for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed a net profit of $83,600. It was later
found that $18,000 paid for the purchase of a motor van had been debited to motor expenses account. It is the
company’s policy to depreciate motor vans at 25 per cent per year, with a full year’s charge in the year of acquisition.
What would the net profit be after adjusting for this error?
A $106,100
B $70,100
C $97,100
D $101,600
正确答案:C
83,600 + 18,000 – 4,500 = 97,100 -
第18题:
The following information is relevant for questions 9 and 10
A company’s draft financial statements for 2005 showed a profit of $630,000. However, the trial balance did not agree,
and a suspense account appeared in the company’s draft balance sheet.
Subsequent checking revealed the following errors:
(1) The cost of an item of plant $48,000 had been entered in the cash book and in the plant account as $4,800.
Depreciation at the rate of 10% per year ($480) had been charged.
(2) Bank charges of $440 appeared in the bank statement in December 2005 but had not been entered in the
company’s records.
(3) One of the directors of the company paid $800 due to a supplier in the company’s payables ledger by a personal
cheque. The bookkeeper recorded a debit in the supplier’s ledger account but did not complete the double entry
for the transaction. (The company does not maintain a payables ledger control account).
(4) The payments side of the cash book had been understated by $10,000.
9 Which of the above items would require an entry to the suspense account in correcting them?
A All four items
B 3 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 4 only
正确答案:B
-
第19题:
13 At 1 January 2005 a company had an allowance for receivables of $18,000
At 31 December 2005 the company’s trade receivables were $458,000.
It was decided:
(a) To write off debts totalling $28,000 as irrecoverable;
(b) To adjust the allowance for receivables to the equivalent of 5% of the remaining receivables based on past
experience.
What figure should appear in the company’s income statement for the total of debts written off as irrecoverable
and the movement in the allowance for receivables for the year ended 31 December 2005?
A $49,500
B $31,500
C $32,900
D $50,900
正确答案:B
430,000 x 5% = 21,500 – 18,000 + 28,000 -
第20题:
(ii) Illustrate the benefit of revising the corporate structure by calculating the corporation tax (CT) payable
for the year ended 31 March 2006, on the assumptions that:
(1) no action is taken; and
(2) an amended structure as recommended in (i) above is implemented from 1 June 2005. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第21题:
5 You are an audit manager in Dedza, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Recently, you have been assigned
specific responsibility for undertaking annual reviews of existing clients. The following situations have arisen in
connection with three client companies:
(a) Dedza was appointed auditor and tax advisor to Kora Co, a limited liability company, last year and has recently
issued an unmodified opinion on the financial statements for the year ended 30 June 2005. To your surprise,
the tax authority has just launched an investigation into the affairs of Kora on suspicion of underdeclaring income.
(7 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of these matters and state what
action, if any, Dedza should now take.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three situations.
正确答案:
5 DEDZA CO
(a) Tax investigation
■ Kora is a relatively new client. Before accepting the assignment(s) Dedza should have carried out customer due
diligence (CDD). Dedza should therefore have a sufficient knowledge and understanding of Kora to be aware of any
suspicions that the tax authority might have.
■ As the investigation has come as a surprise it is possible that, for example:
– the tax authority’s suspicions are unfounded;
– Dedza has failed to recognise suspicious circumstances.
Tutorial note: In either case, Dedza should seek clarification on the period of suspicion and review relevant procedures.
■ Dedza should review any communication from the predecessor auditor obtained in response to its ‘professional inquiry’
(for any professional reasons why the appointment should not have been accepted).
■ A quality control for new audits is that the audit opinion should be subject to a second partner review before it is issued.
It should be considered now whether or not such a review took place. If it did, then it should be sufficiently well
documented to evidence that the review was thorough and not a mere formality.
■ Criminal property includes the proceeds of tax evasion. If Kora is found to be guilty of under-declaring income that is a
money laundering offence.
■ Dedza’s reputational risk will be increased if implicated because it knew (or ought to have known) about Kora’s activities.
(Dedza may also be liable if found to have been negligent in failing to detect any material misstatement arising in the
2004/05 financial statements as a result.)
■ Kora’s audit working paper files and tax returns should be reviewed for any suspicion of fraud being committed by Kora
or error overlooked by Dedza. Tax advisory work should have been undertaken and/or reviewed by a manager/partner
not involved in the audit work.
■ As tax advisor, Dedza could soon be making disclosures of misstatements to the tax authority on behalf of Kora. Dedza
should encourage Kora to make necessary disclosure voluntarily.
■ Dedza will not be in breach of its duty of confidentiality to Kora if Kora gives Dedza permission to disclose information
to the tax authority (or Dedza is legally required to do so).
■ If Dedza finds reasonable grounds to know or suspect that potential disclosures to the tax authority relate to criminal
conduct, then a suspicious transaction report (STR) should be made to the financial intelligence unit (FIU) also.
Tutorial note: Though not the main issue credit will be awarded for other ethical issues such as the potential selfinterest/
self-review threat arising from the provision of other services. -
第22题:
For a limited company, this will include the money ______ issuing shares, and is known as the share capital.A raise for ;
B raised by ;
C raising at
参考答案:B
-
第23题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS.
